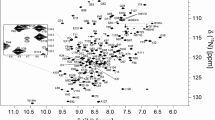
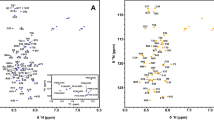
Abstract
Human TIG3 protein is a member of H-REV107 protein family which belongs to the type II tumor suppressor family. TIG3 can induce apoptosis in cancer cells, and it also possesses Ca2+-independent phospholipase A1/2 activity. The NMR assignments of the N-terminal domain of TIG3 are essential for its solution structure determination.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anantharaman V, Aravind L (2003) Evolutionary history, structural features and biochemical diversity of the nlpc/p60 superfamily of enzymes. Genome Biol 4(2):R11
Casanova B, de la Fuente MT, Garcia-Gila M, Sanz L, Silva A, Garcia-Marco JA, Garcia-Pardo A (2001) The class ii tumor-suppressor gene rarres3 is expressed in b cell lymphocytic leukemias and down-regulated with disease progression. Leukemia 15(10):1521–1526
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) Nmrpipe: A multidimensional spectral processing system based on unix pipes. J Biomol NMR 6(3):277–293
Deucher A, Nagpal S, Chandraratna RAS, Di Sepio D, Robinson NA, Dashti SR, Eckert RL (2000) The carboxy-terminal hydrophobic domain of tig3, a class ii tumor suppressor protein, is required for appropriate cellular localization and optimal biological activity. Int J Oncol 17(6):1195–1203
DiSepio D, Ghosn C, Eckert RL, Deucher A, Robinson N, Duvic M, Chandraratna RA, Nagpal S (1998) Identification and characterization of a retinoid-induced class ii tumor suppressor/growth regulatory gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(25):14811–14815
Duvic M, Helekar B, Schulz C, Cho M, DiSepio D, Hager C, DiMao D, Hazarika P, Jackson B, Breuer-McHam J, Young J, Clayman G, Lippman SM, Chandraratna RAS, Robinson NA, Deucher A, Eckert RL, Nagpal S (2000) Expression of a retinoid-inducible tumor suppressor, tazarotene-inducible gene-3, is decreased in psoriasis and skin cancer. Clin Cancer Res 6(8):3249–3259
Han BG, Cho JW, Cho YD, Kim SY, Yoon HJ, Song HK, Cheong HK, Jeon YH, Lee DK, Lee S, Lee BI (2010) Expression, purification and biochemical characterization of the n-terminal regions of human tig3 and hrasls3 proteins. Protein Expr Purif 71(1):103–107
Higuchi E, Chandraratna RAS, Hong WK, Lotan R (2003) Induction of tig3, a putative class ii tumor suppressor gene, by retinoic acid in head and neck and lung carcinoma cells and its association with suppression of the transformed phenotype. Oncogene 22(30):4627–4635
Huang SL, Shyu RY, Yeh MY, Jiang SY (2000) Cloning and characterization of a novel retinoid-inducible gene 1(rig1) deriving from human gastric cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 159(1–2):15–24
Huang SL, Shyu RY, Yeh MY, Jiang SY (2002) The retinoid-inducible gene i: Effect on apoptosis and mitogen-activated kinase signal pathways. Anticancer Res 22(2A):799–804
Johnson BA, Blevins RA (1994) Nmr view: A computer program for the visualization and analysis of nmr data. J Biomol NMR 4:603–614
Markley JL, Bax A, Arata Y, Hilbers CW, Kaptein R, Sykes BD, Wright PE, Wuthrich K (1998) Recommendations for the presentation of nmr structures of proteins and nucleic acids. Iupac-iubmb-iupab inter-union task group on the standardization of data bases of protein and nucleic acid structures determined by nmr spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 12(1):1–23
Ren X, Lin J, Jin C, Xia B (2010) Solution structure of the n-terminal catalytic domain of human h-rev107–a novel circular permutated nlpc/p60 domain. FEBS Lett 584(19):4222–4226
Shyu RY, Jiang SY, Chou JM, Shih YL, Lee MS, Yu JC, Chao PC, Hsu YJ, Jao SW (2003) Rarres3 expression positively correlated to tumour differentiation in tissues of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer 89(1):146–151
Sturniolo MT, Dashti SR, Deucher A, Rorke EA, Broome AM, Chandraratna RA, Keepers T, Eckert RL (2003) A novel tumor suppressor protein promotes keratinocyte terminal differentiation via activation of type i transglutaminase. J Biol Chem 278(48):48066–48073
Tsai FM, Shyu RY, Jiang SY (2007) Rig1 suppresses ras activation and induces cellular apoptosis at the golgi apparatus. Cell Signal 19(5):989–999
Tsai FM, Shyu RY, Lin SC, Wu CC, Jiang SY (2009) Induction of apoptosis by the retinoid inducible growth regulator rig1 depends on the nc motif in htta cervical cancer cells. BMC Cell Biol 10:15
Uyama T, Jin XH, Tsuboi K, Tonai T, Ueda N (2009) Characterization of the human tumor suppressors tig3 and hrasls2 as phospholipid-metabolizing enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1791(12):1114–1124
Acknowledgments
All NMR experiments were carried out at Beijing NMR center. This research was supported by Grant 2009CB521703 (to BX) from the 973 Program of China, Grants 31070648 (to BX) and 30800172 (to JL) from the National Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Yu, W., Ren, X. et al. 1H, 13C, and 15N resonance assignments of the N-terminal domain of human TIG3. Biomol NMR Assign 6, 201–203 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-012-9357-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-012-9357-2