Abstract
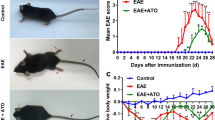
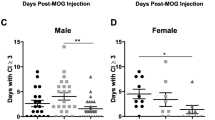
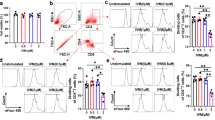
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (CNS) involving demyelinating and neurodegenerative processes. Several of the major pathological CNS alterations and behavioral deficits of MS are recapitulated in the experimental autoimmune encephalitis (EAE) mouse model in which the disease process is induced by administration of myelin peptides. Development of EAE requires infiltration of inflammatory cytokine-generating monocytes and macrophages, and auto-reactive T cells, into the CNS. Very late antigen-4 (VLA-4, α4β1) is an integrin molecule that plays a role in inflammatory responses by facilitating the migration of leukocytes across the blood–brain barrier during inflammatory disease, and antibodies against VLA-4 exhibit therapeutic efficacy in mouse and monkey MS models. Here, we report that the tellurium compound AS101 (ammonium trichloro (dioxoethylene-o,o′) tellurate) ameliorates EAE by inhibiting monocyte and T cell infiltration into the CNS. CD49d is an alpha subunit of the VLA-4 (α4β1) integrin. During the peak stage of EAE, AS101 treatment effectively ameliorated the disease process by reducing the number of CD49d+ inflammatory monocyte/macrophage cells in the spinal cord. AS101 treatment markedly reduced the pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, while increasing anti-inflammatory cytokine levels. In contrast, AS101 treatment did not affect the peripheral populations of CD11b+ monocytes and macrophages. AS101 treatment reduced the infiltration of CD4+ and CD49+/VLA4 T cells. In addition, treatment of T cells from MS patients with AS101 resulted in apoptosis, while such treatment did not affect T cells from healthy donors. These results suggest that AS101 reduces accumulation of leukocytes in the CNS by inhibiting the activity of the VLA-4 integrin and provide a rationale for the potential use of Tellurium IV compounds for the treatment of MS.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, Z., Doward, A. I., Pryce, G., Taylor, D. L., Pocock, J. M., Leonard, J. P., et al. (2002). A role for caspase-1 and -3 in the pathology of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: Inflammation versus degeneration. American Journal of Pathology, 161, 1577–1586.
Bar-Or, A., Rieckmann, P., Traboulsee, A., & Yong, V. W. (2011). Targeting progressive neuroaxonal injury: Lessons from multiple sclerosis. CNS Drugs, 25, 783–799.
Bloomgren, G., Richman, S., Hotermans, C., Subramanyam, M., Goelz, S., Natarajan, A., et al. (2012). Risk of natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. The New England Journal of Medicine, 366, 1870–1880.
Brodsky, M., Halpert, G., Albeck, M., & Sredni, B. (2010). The anti-inflammatory effects of the tellurium redox modulating compound, AS101, are associated with regulation of NFkappaB signaling pathway and nitric oxide induction in macrophages. Journal of Inflammation (London), 7, 3.
Brodsky, M., Yosef, S., Galit, R., Albeck, M., Longo, D. L., Albeck, A., et al. (2007). The synthetic tellurium compound, AS101, is a novel inhibitor of IL-1beta converting enzyme. Journal of Interferon and Cytokine Research, 27, 453–462.
Dalton, C. M., Miszkiel, K. A., Barker, G. J., MacManus, D. G., Pepple, T. I., Panzara, M., et al. (2004). Effect of natalizumab on conversion of gadolinium enhancing lesions to T1 hypointense lesions in relapsing multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology, 251, 407–413.
Dhib-Jalbut, S. (2007). Pathogenesis of myelin/oligodendrocyte damage in multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 68, S13–S21.
Floris, S., Ruuls, S. R., Wierinckx, A., van der Pol, S. M., Döpp, E., van der Meide, P. H., et al. (2002). Interferon-beta directly influences monocyte infiltration into the central nervous system. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 127, 69–79.
Friedman, M., Bayer, I., Letko, I., Duvdevani, R., Zavaro-Levy, O., Ron, B., et al. (2009). Topical treatment for human papillomavirus-associated genital warts in humans with the novel tellurium immunomodulator AS101: Assessment of its safety and efficacy. British Journal of Dermatology, 160, 403–408.
Frohman, E. M., Racke, M. K., & Raine, C. S. (2006). Multiple sclerosis—The plaque and its pathogenesis. New England Journal of Medicine, 354, 942–955.
Geissmann, F., Manz, M. G., Jung, S., Sieweke, M. H., Merad, M., & Ley, K. (2010). Development of monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Science, 327, 656–661.
Geurts, J. J., & Barkhof, F. (2008). Grey matter pathology in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurology, 7, 841–851.
Gonsette, R. E. (2008). Oxidative stress and excitotoxicity: A therapeutic issue in multiple sclerosis? Multiple Sclerosis, 14, 22–34.
Greter, M., Heppner, F. L., Lemos, M. P., Odermatt, B. M., Goebels, N., Laufer, T., et al. (2005). Dendritic cells permit immune invasion of the CNS in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Nature Medicine, 11, 328–334.
Haider, L., Fischer, M. T., Frischer, J. M., Bauer, J., Höftberger, R., Botond, G., et al. (2011). Oxidative damage in multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain, 134, 1914–1924.
Hendriks, J. J. A., Teunissen, C. E., Vries, H. E. D., & Dijkstra, C. D. (2005). Macrophages and neurodegeneration. Brain Research Reviews, 48, 185–195.
Holman, D. W., Klein, R. S., & Ransohoff, R. M. (2011). The blood-brain barrier, chemokines and multiple sclerosis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1812, 220–230.
Huitinga, I., Nv, Rooijen., Groot, C. J. A. D., Uitdehaag, B. M. J., & Dijkstra, C. D. (1990). Suppression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats after elimination of macrophages. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 172, 1025–1033.
Huo, Y., Hafezi-Moghadam, A., & Ley, K. (2000). Role of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and fibronectin connecting segment-1 in monocyte rolling and adhesion on early atherosclerotic lesions. Circulation Research, 87, 153–159.
Indenbaum, V., Bin, H., Makarovsky, D., Weil, M., Shulman, L. M., Albeck, M., et al. (2012). In vitro and in vivo activity of AS101 against West Nile virus (WNV). Virus Research, 166, 68–76.
Jack, C., Ruffini, F., Bar-Or, A., & Antel, J. P. (2005). Microglia and multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 81, 363–373.
Jones, J. L., & Coles, A. J. (2010). New treatment strategies in multiple sclerosis. Experimental Neurology, 225, 34–39.
Kalechman, Y., Sredni, B., Weinstein, T., Freidkin, I., Tobar, A., Albeck, M., et al. (2003). Production of the novel mesangial autocrine growth factors GDNF and IL-10 is regulated by the immunomodulator AS101. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 14, 620–630.
King, I. L., Dickendesher, T. L., & Segal, B. M. (2007). Cutting edge: CNS CD11c+ cells from mice with encephalomyelitis polarize Th17 cells and support CD25+ CD4+ T cell-mediated immunosuppression, suggesting dual roles in the disease process. Journal of Immunology, 178, 6695–6699.
King, I. L., Dickendesher, T. L., & Segal, B. M. (2009). Circulating Ly-6C+ myeloid precursors migrate to the CNS and play a pathogenic role during autoimmune demyelinating disease. Blood, 113, 3190–3197.
Kivisakk, P., Imitola, J., Rasmussen, S., Elyaman, W., Zhu, B., Ransohoff, R. M., et al. (2009). Localizing central nervous system immune surveillance: Meningeal antigen-presenting cells activate T cells during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Annals of Neurology, 65, 457–469.
Lassmann, H. (2010). Axonal and neuronal pathology in multiple sclerosis: What have we learnt from animal models. Experimental Neurology, 225, 2–8.
Leussink, V. I., Zettl, U. K., Jander, S., Pepinsky, R. B., Lobb, R. R., Stoll, G., et al. (2002). Blockade of signaling via the very late antigen (VLA-4) and its counterligand vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) causes increased T cell apoptosis in experimental autoimmune neuritis. Acta Neuropathologica, 103, 131–136.
Martinou, J. C., & Youle, R. J. (2011). Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Developmental Cell, 21, 92–101.
McCormack, P. L. (2013). Natalizumab: A review of its use in the management of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Drugs, 73, 1463–1481.
Meuth, S. G., Göbel, K., & Wiendl, H. (2012). Immune therapy of multiple sclerosis—future strategies. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 18, 4489–4497.
Mosser, D. M., & Edwards, J. P. (2008). Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nature Reviews Immunology, 8, 958–969.
Niino, M., Bodner, C., Simard, M. L., Alatab, S., Gano, D., Kim, H. J., et al. (2006). Natalizumab effects on immune cell responses in multiple sclerosis. Annals of Neurology, 59, 748–754.
Noonan, C. W., Williamson, D. M., Henry, J. P., Indian, R., Lynch, S. G., Neuberger, J. S., et al. (2010). The prevalence of multiple sclerosis in 3 US communities. Preventing Chronic Disease, 7, A12.
Okun, E., Arumugam, T. V., Tang, S. C., Gleichmann, M., Albeck, M., Sredni, B., et al. (2007). The organotellurium compound ammonium trichloro(dioxoethylene-0,0′) tellurate enhances neuronal survival and improves functional outcome in an ischemic stroke model in mice. Journal of Neurochemistry, 102, 1232–1241.
Okun, E., Mattson, M. P., & Arumugam, T. V. (2010). Involvement of Fc receptors in disorders of the central nervous system. Neuromolecular Medicine, 12, 164–178.
Prat, A., & Antel, J. (2005). Pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Current Opinion in Neurology, 18, 225–230.
Prendergast, C. T., & Anderton, S. M. (2009). Immune cell entry to central nervous system–current understanding and prospective therapeutic targets. Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders: Drug Targets, 9, 315–327.
Rezai-Zadeh, K., Gate, D., & Town, T. (2009). CNS infiltration of peripheral immune cells: D-Day for neurodegenerative disease? Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology, 4, 462–475.
Shani, A., Tichler, T., Catane, R., Gurwith, M., Rozenszajn, L. A., Gezin, A., et al. (1990). Immunologic effects of AS101 in the treatment of cancer patients. Natural Immunity Cell Growth Regulation, 9, 182–190.
Sheremata, W. A., Minagar, A., Alexander, J. S., & Vollmer, T. (2005). The role of alpha-4 integrin in the aetiology of multiple sclerosis: Current knowledge and therapeutic implications. CNS Drugs, 19, 909–922.
Smyser, G. S. (1973). Counterstaining Golgi-Cox impregnations with luxol fast blue as a myelin stain. Stain Technology, 48, 53–57.
Sredni, B. (2012). Immunomodulating tellurium compounds as anti-cancer agents. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 22, 60–69.
Sredni, B., Albeck, M., Tichler, T., Shani, A., Shapira, J., Bruderman, I., et al. (1995). Bone marrow-sparing and prevention of alopecia by AS101 in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with carboplatin and etoposide. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 13, 2342–2353.
Sredni, B., Caspi, R. R., Klein, A., Kalechman, Y., Danziger, Y., Ben Ya’akov, M., et al. (1987). A new immunomodulating compound (AS-101) with potential therapeutic application. Nature, 330, 173–176.
Sredni, B., Gal, R., Cohen, I. J., Dazard, J.-E., Givol, D., Gafter, U., et al. (2004a). Hair growth induction by the Tellurium immunomodulator AS101: Association with delayed terminal differentiation of follicular keratinocytes and ras-dependent up-regulation of KGF expression. FASEB Journal, 18, 400–402.
Sredni, B., Geffen-Aricha, R., Duan, W., Albeck, M., Shalit, F., Lander, H. M., et al. (2007). Multifunctional tellurium molecule protects and restores dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease models. FASEB Journal, 21, 1870–1883.
Sredni, B., Tichler, T., Shani, A., Catane, R., Kaufman, B., Strassmann, G., et al. (1996). Predominance of TH1 response in tumor-bearing mice and cancer patients treated with AS101. Journal of National Cancer Institute, 88, 1276–1284.
Sredni, B., Weil, M., Khomenok, G., Lebenthal, I., Teitz, S., Mardor, Y., et al. (2004b). Ammonium trichloro(dioxoethylene-o, o’)tellurate (AS101) sensitizes tumors to chemotherapy by inhibiting the tumor interleukin 10 autocrine loop. Cancer Research, 64, 1843–1852.
Steinman, L. (2005). Blocking adhesion molecules as therapy for multiple sclerosis: Natalizumab. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 4, 510–518.
Steinman, L. (2009). A molecular trio in relapse and remission in multiple sclerosis. Nature Reviews Immunology, 9, 440–447.
Strassmann, G., Kambayashi, T., Jacob, C. O., & Sredni, D. (1997). The immunomodulator AS-101 inhibits IL-10 release and augments TNF alpha and IL-1 alpha release by mouse and human mononuclear phagocytes. Cellular Immunology, 176, 180–185.
Susin, S. A., Zamzami, N., & Kroemer, G. (1998). Mitochondria as regulators of apoptosis: Doubt no more. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1366, 151–165.
Swanborg, R. H. (1995). Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in rodents as a model for human demyelinating disease. Clinical Immunology and Immunopathology, 77, 4–13.
Theien, B. E., Vanderlugt, C. L., Nickerson-Nutter, C., Cornebise, M., Scott, D. M., Perper, S. J., et al. (2003). Differential effects of treatment with a small-molecule VLA-4 antagonist before and after onset of relapsing EAE. Blood, 102, 4464–4471.
van der Laan, L. J., van der Goes, A., Wauben, M. H., Ruuls, S. R., Döpp, E. A., De Groot, C. J., et al. (2002). Beneficial effect of modified peptide inhibitor of alpha4 integrins on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 67, 191–199.
Wayner, E. A., Garcia-Pardo, A., Humphries, M. J., McDonald, J. A., & Carter, W. G. (1989). Identification and characterization of the T lymphocyte adhesion receptor for an alternative cell attachment domain (CS-1) in plasma fibronectin. The Journal of cell biology, 109, 1321–1330.
Yednock, T. A., Cannon, C., Fritz, L. C., Sanchez-Madrid, F., Steinman, L., & Karin, N. (1992). Prevention of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by antibodies against alpha 4 beta 1 integrin. Nature, 356, 63–66.
Yusuf-Makagiansar, H., Anderson, M. E., Yakovleva, T. V., Murray, J. S., & Siahaan, T. J. (2002). Inhibition of LFA-1/ICAM-1 and VLA-4/VCAM-1 as a therapeutic approach to inflammation and autoimmune diseases. Medicinal Research Reviews, 22, 146–167.
Zhu, B., Bando, Y., Xiao, S., Yang, K., Anderson, A. C., Kuchroo, V. K., et al. (2007). CD11b+ Ly-6C(hi) suppressive monocytes in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Journal of Immunology, 179, 5228–5237.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Aging.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jun-Ho Lee and Meital Halperin-Sheinfeld have contributed equally to acquisition and analysis of data in this study.
Mark P. Mattson, Benjamin Sredni and Dennis D. Taub made equal contributions as senior authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JH., Halperin-Sheinfeld, M., Baatar, D. et al. Tellurium Compound AS101 Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by VLA-4 Inhibition and Suppression of Monocyte and T Cell Infiltration into the CNS. Neuromol Med 16, 292–307 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8277-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8277-3