Abstract
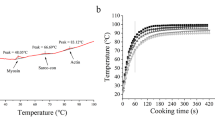
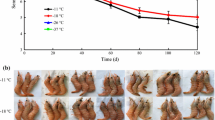
Effect of cooking between 1 and 80 min at 60 to 100 °C on several quality attributes of whole peeled shrimp (Litopenaeus setiferus) (80–90 counts/kg) was studied using an isothermal heating method. Cook loss, area shrinkage, and hardness of shrimp increased with increasing heating time and temperature, following a fractional first-order kinetic model with activation energies (E a ) of 71.0, 53.3, and 29.9 kJ/mol, respectively. Cook loss, area shrinkage, and hardness were positively correlated. The toughness of shrimp muscle increased in the initial period of heating, then decreased in the later period during the treatments. The overall color change (ΔE) increased with increasing treatment time and temperature, and followed a zero kinetic model with an E a of 37.2 kJ/mol. The kinetic parameters obtained from this study can be applied toward understanding and predicting shrimp-quality changes during pasteurization treatments, and further provides insight into the pasteurization conditions required to achieve safe and high-quality shrimp products and potentially other crustacean shellfish and seafood products.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberle, E. D. (2001). Principles of meat science. Kendall Hunt.
Allshouse, J., Buzby, J. C., Harvey, D., & Zorn, D. (2003). International trade and seafood safety. International Trade and Food Safety: Economic Theory and Case Studies (pp. 109–124). Washington DC: United States Department of Agriculture, Economics Research Service.
Allshouse, J. E., Buzby, J., Harvey, D., & Zorn, D. (2004). Seafood safety and trade. USDA.
Bell, J. W., Farkas, B. E., Hale, S. A., & Lanier, T. C. (2001). Effect of thermal treatment on moisture transport during steam cooking of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonas pelamis). Journal of Food Science, 66(2), 307–313.
Belitz, H. D., Grosch, W., & Schieberle, P. (2004). Food chemistry (3rd ed.). Berlin: Springer.
Benjakul, S., Visessanguan, W., Kijroongrojana, K., & Sriket, P. (2008). Effect of heating on physical properties and microstructure of black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) and white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) meats. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 43(6), 1066–1072.
Bertola, N. C., Bevilacqua, A. E., & Zaritzky, N. E. (1994). Heat treatment effect on texture changes and thermal denaturation of proteins in beef muscle. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 18(1), 31–46.
Bozkurt, H., D’Souza, D. H., & Davidson, P. M. (2014). Determination of thermal inactivation kinetics of hepatitis A virus in blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) homogenate. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80(10), 3191–3197.
Buckow, R., Isbarn, S., Knorr, D., Heinz, V., & Lehmacher, A. (2008). Predictive model for inactivation of feline calcivirus, a norovirus surrogate, by heat and high hydrostatic pressure. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74(4), 1030–1038.
Chau, K. V., & Snyder, G. V. (1988). Mathematical-model for temperature distribution of thermally processed shrimp. Transactions of the ASAE, 31(2), 608–612.
Crerar, S. K., Bull, A. L., & Beers, M. Y. (2002). Australia’s imported food program—a valuable source of information on micro-organisms in foods. Communicable diseases intelligence quarterly report, 26(1), 28.
Downing, D.L. 1996. A complete course in canning and related processes 13th ed-Book II: microbiology, packaging, HACCP & ingredients. CTI Publication, Inc.
Erdogdu, F. (1996). Modeling of temperature distribution in shrimp, and measurement of its effect on texture, shrinkage and yield loss. Master of Engineering Thesis, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL.
Erdogdu, F., Balaban, M. O., & Chau, K. V. (1999). Mathematical model to predict yield loss of medium and large tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) during cooking. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 22, 383–394.
Erdogdu, F., & Balaban, M. O. (2000). Thermal processing effects on the textural attributes of previously frozen shrimp. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology, 9, 61–84.
Erdogdu, F., Balaban, M. O., Otwell, W. S., & Garrido, L. (2004). Cook-related yield loss for pacific white (Penaeus vannamei) shrimp previously treated with phosphates: effect of shrimp size and internal temperature distribution. Journal of Food Engineering, 64, 297–300.
Erdogdu, F., Luzuriaga, D. A., Balaban, M. O., & Chau, K. V. (2001). A predictive model on moisture and yield loss in phosphate-treated, cooked tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology, 10(2), 31–45.
FAO (2016). The state of world’s fisheries and aquaculture 2016.
Fennema, O. R. (1996). Food Chemistry 3rd. New York: Marcel Decker.
FDA (2011). Fish and fishery products hazards and controls guidance. US Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition.
Franklin, C. E., Crockford, T., Johnston, I. A., & Kamunde, C. (1994). The thermostability of haemoglobins from the hot-spring fish, Oreochromis alcalicus grahami: Comparisons with antarctic and temperate species. Journal of Thermal Biology, 19(4), 277–280.
Gaze, J. E., Boyd, A. R., & Shaw, H. L. (2006). Heat inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes Scott A on potato surfaces. Journal of Food Engineering, 76, 27–31.
Gibson, K. E., & Schwab, K. J. (2011). Thermal inactivation of human norovirus surrogates. Food and Environmental Virology, 3, 74–77.
Gillett, R. (2008). Global study of shrimp fisheries. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Haefner, J. W. (2005). Modeling biological systems: principles and applications. Springer Science & Business Media.
Haard, N. F. (1992). Biochemistry and chemistry of color and color change in seafoods. Advances in seafood biochemistry: Composition and quality, 305–360.
Hastings, R. J., Rodger, G. W., Park, R., Matthews, A. D., & Anderson, E. M. (1985). Differential scanning calorimetry of fish muscle: the effect of processing and species variation. Journal of Food Science, 50(2), 503–506.
Kemp, R. M., North, M. F., & Leath, S. R. (2009). Component heat capacities for lamb, beef and pork at elevated temperatures. Journal of Food Engineering, 92(3), 280–284.
Kong, F., Tang, J., Lin, M., & Rasco, B. (2008). Thermal effects on chicken and salmon muscles: Tenderness, cook loss, area shrinkage, collagen solubility and microstructure. LWT-food Science and Technology, 41(7), 1210–1222.
Kong, F. B., Tang, J. M., Rasco, B., Crapo, C., & Smiley, S. (2007a). Quality changes of salmon (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha) muscle during thermal processing. Journal of Food Science, 72(2), S103–S111.
Kong, F., Tang, J., Rasco, B., & Crapo, C. (2007b). Kinetics of salmon quality changes during thermal processing. Journal of Food Engineering, 83(4), 510–520.
Limbo, S., & Piergiovanni, L. (2006). Shelf life of minimally processed potatoes: part 1. Effects of high oxygen partial pressures in combination with ascorbic and citric acids on enzymatic browning. Postharvest Biology and Technology., 39(3), 254–264.
Lopez, A. (1987). A complete course in canning and related processes: packaging, aseptic processing, ingredients. The Canning Trade, Baltimore, US: CTI Publications.
Ma, C. Y., & Harwalkar, V. R. (1991). Thermal analysis of food proteins. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, 35, 317–366.
Ma, L. Y., Deng, J. C., Ahmed, E. M., & Adams, J. P. (1983). Canned shrimp texture as a function of its heat history. Journal of Food Science, 48(2), 360–363.
Martens, H., & Vold, E. (1976). DSC studies of muscle tissue protein denaturation. In congress documentation; proceedings of the European meeting of meat research workers.
Martens, H., Stabursvik, E., & Martens, M. (1982). Texture and colour changes in meat during cooking related to thermal denaturation of muscle proteins. Journal of Texture Studies, 13(3), 291–309.
Mizuta, S., Yamada, Y., Miyagi, T., & Yoshinaka, R. (1999). Histological changes in collagen related to textural development of prawn meat during heat processing. Journal of Food Science, 64(6), 991–995.
Murakami, E. G. (1994). Thermal processing affects properties of commercial shrimp and scallops. Journal of Food Science, 59, 237–241.
Muriana, F. J., Ruiz-Gutierrez, V., Gallardo-Guerrero, M. L., & Minguez-Mosquera, M. I. (1993). A study of the lipids and carotenoprotein in the prawn, Penaeus japonicus. The Journal of Biochemistry, 114(2), 223–229.
National Marine Fisheries Service (US) (Ed.). (2016). Fisheries of the United States: 2014. Government Printing Office.
Niamnuy, C., Devahastin, S., & Soponronnarit, S. (2007). Quality changes of shrimp during boiling in salt solution. Journal of Food Science, 72(5), 289–297.
Niamnuy, C., Devahastin, S., & Soponronnarit, S. (2008). Changes in protein compositions and their effects on physical changes of shrimp during boiling in salt solution. Food Chemistry, 108(1), 165–175.
Nunak, N., & Schleining, G. (2011). Instrumental textural changes in raw white shrimp during iced storage. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology, 20(4), 350–360.
Olsen, S. J., MacKinnon, L. C., Goulding, J. S., Bean, N. H., & Slutsker, L. (2000). Surveillance for foodborne-disease outbreaks—United States, 1993–1997. MMWR. CDC Surveillance Summaries, 49(1), 1–62.
Ofstad, R., Kidman, S., Myklebust, R., & Hermansson, A. M. (1993). Liquid holding capacity and structural changes during heating of fish muscle: cod (Gadus morhua L.) and salmon (Salmo salar). Food Structure, 12(2), 163–174.
Ovissipour, M., Rasco, B., Tang, J., & Sablani, S. S. (2013). Kinetics of quality changes in whole blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) during pasteurization. Food Research International, 53(1), 141–148.
Paquotte, P., & Lem, A. (2008). Seafood markets and trade: a global perspective and an overview of EU Mediterranean countries. Options Mediterrané ennes, 62, 43–55.
Peng, J., Tang, J., Barrett, D. M., Sablani, S. S., Anderson, N., & Powers, J. R. (2017). Thermal pasteurization of ready-to-eat foods and vegetables: critical factors for process design and effects on quality. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 57(14), 2970–2995.
Rizvi, A. F., & Tong, C. H. (1997). Fractional conversion for determining texture degradation kinetics of vegetables. Journal of Food Science, 62(1), 1–7.
Sajeev, M. S., Manikantan, M. R., Kingsly, A. R. P., Moorthy, S. N., & Sreekumar, J. (2004). Texture analysis of taro (Colocasia esculenta L. Schott) cormels during storage and cooking. Journal of Food Science, 69(7), 315–321.
Schanda, J, ed. (2007). Colorimetry: understanding the CIE system. Wiley.
Schmidt G. R. (1988). Processing. In: Cross HR, Overby A. J, (eds). World animal science. Vol. B3, Meat science, milk science and technology. London: Elsevier Science Publishers. p 83–114.
Schubring, R. (2009). Comparative study of DSC pattern, colour and texture of shrimps during heating. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 95(3), 749–757.
Skipnes, D., Johnsen, S. O., Skåra, T., Sivertsvik, M., & Lekang, O. (2011). Optimization of heat processing of farmed Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) muscle with respect to cook loss, water holding capacity, color, and texture. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology, 20(3), 331–340.
Skipnes, D., Østby, M. L., & Hendrickx, M. E. (2007). A method for characterising cook loss and water holding capacity in heat treated cod (Gadus morhua) muscle. Journal of Food Engineering, 80(4), 1078–1085.
Skipnes, D., Van der Plancken, I., Van Loey, A., & Hendrickx, M. E. (2008). Kinetics of heat denaturation of proteins from farmed Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Journal of Food Engineering, 85(1), 51–58.
Sriket, P., Benjakul, S., Visessanguan, W., & Kijroongrojana, K. (2007). Comparative studies on chemical composition and thermal properties of black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) and white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) meats. Food Chemistry, 103(4), 1199–1207.
Straadt, I. K., Rasmussen, M., Andersen, H. J., & Bertram, H. C. (2007). Aging-induced changes in microstructure and water distribution in fresh and cooked pork in relation to water-holding capacity and cooking loss—a combined confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) and low-field nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation study. Meat Science, 75(4), 687–695.
Thorne, S. (1986). The history of food preservation. Barnes and Noble Books.
Tornberg, E. (2005). Effects of heat on meat proteins—implications on structure and quality of meat products. Meat Science, 70(3), 493–508.
Trout, G. R. (1988). Techniques for measuring water-binding capacity in muscle foods—a review of methodology. Meat Science, 23(4), 235–252.
US National Fisheries Institute (2017). Top 10 list for seafood consumption. http://www.aboutseafood.com/about/about-nfi-6/.
Wallace, B. J., Guzewich, J. J., Cambridge, M., Altekruse, S., & Morse, D. L. (1999). Seafood-associated disease outbreaks in New York, 1980–1994. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 17(1), 48–54.
Wang, Y., Lau, M. H., Tang, J., & Mao, R. (2004). Kinetics of chemical marker M-1 formation in whey protein gels for developing sterilization processes based on dielectric heating. Journal of Food Engineering, 64(10), 111–118.
Wright, D. J., Leach, I. B., & Wilding, P. (1977). Differential scanning calorimetric studies of muscle and its constituent proteins. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 28(6), 557–564.
Whisler, R. L., & Daniel, R. (1985). Carbohydrates in OR Fenenema (ed.) food chemistry.
Yam, K. L., & Papadakis, S. E. (2004). A simple digital imaging method for measuring and analyzing color of food surfaces. Journal of Food Engineering, 61(1), 137–142.
Funding
The author thanks the Chinese Scholarship Council for support for his studies at Washington State University, the Washington State Agricultural Experiment Station and USDA AFRI CAPS project (grant number 2016-68003-24840) for financial supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Tang, J., Rasco, B. et al. Kinetics of Quality Changes of Shrimp (Litopenaeus setiferus) During Pasteurization. Food Bioprocess Technol 11, 1027–1038 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2073-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2073-x