Abstract
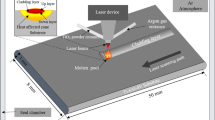
Laser cladding of metal matrix composite coatings (MMCs) has become an effective and economic method to improve the wear resistance of mechanical components. The clad quality characteristics such as clad height, carbide fraction, carbide dissolution, and matrix hardness in MMCs determine the wear resistance of the coatings. These clad quality characteristics are influenced greatly by the laser cladding processing parameters. In this study, American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) 420 + 20% vanadium carbide (VC) was deposited on mild steel with a high powder direct diode laser. The Taguchi-based Grey relational method was used to optimize the laser cladding processing parameters (laser power, scanning speed, and powder feed rate) with the consideration of multiple clad characteristics related to wear resistance (clad height, carbide volume fraction, and Fe-matrix hardness). A Taguchi L9 orthogonal array was designed to study the effects of processing parameters on each response. The contribution and significance of each processing parameter on each clad characteristic were investigated by the analysis of variance (ANOVA). The Grey relational grade acquired from Grey relational analysis was used as the performance characteristic to obtain the optimal combination of processing parameters. Based on the optimal processing parameters, the phases and microstructure of the laser-cladded coating were characterized by using x-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Xi, D. Liu, and D. Han, Surf. Coat. Technol. 202, 2577 (2008).
C.E. Pinedo and W.A. Monteiro, Surf. Coat. Technol. 179, 119 (2004).
M. Zhong and W. Liu, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part C 224, 1041 (2010).
S. Liu, P. Farahmand, and R. Kovacevic, Opt. Laser Technol. 64, 363 (2014).
P. Farahmand, S. Liu, Z. Zhang, and R. Kovacevic, Ceram. Int. 40, 15421 (2014).
J.J. Candel, V. Amigó, J.A. Ramos, and D. Busquets, Surf. Coat. Technol. 204, 3161 (2010).
H. Yan, J. Zhang, P. Zhang, Z. Yu, C. Li, P. Xu, and Y. Lu, Surf. Coat. Technol. 232, 362 (2013).
N. Altinkök, JOM 66, 909 (2014).
H.F. El-Labban, E.R.I. Mahmoud, and H. Al-Wadai, J. Manuf. Process. 20, 190 (2015).
X.H. Wang, M. Zhang, L. Cheng, S.Y. Qu, and B.S. Du, Tribol. Lett. 34, 177 (2009).
J. Nurminen, J. Näkki, and P. Vuoristo, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 27, 472 (2009).
Q. Wu, W. Li, N. Zhong, G. Wu, and H. Wang, Mater. Des. 49, 10 (2013).
X.H. Wang, L. Cheng, M. Zhang, S.Y. Qu, B.S. Du, and Z.D. Zou, Surf. Eng. 25, 211 (2009).
S. Ilo, C. Just, and F. Xhiku, Mater. Des. 33, 459 (2012).
Y. Dongxia, L. Xiaoyan, H. Dingyong, N. Zuoren, and H. Hui, Opt. Laser Technol. 44, 2020 (2012).
A.N. Haq, P. Marimuthu, and R. Jeyapaul, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 37, 250 (2008).
J.L. Lin and C.L. Lin, Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manuf. 42, 237 (2002).
Y.S. Tarng, S.C. Juang, and C.H. Chang, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 128, 1 (2002).
R.S. Pawade and S.S. Joshi, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 56, 46 (2011).
X. Cao, M. Xiao, M. Jahazi, J. Fournier, and M. Alain, Mater. Manuf. Process. 23, 413 (2008).
I. Smurov, M. Doubenskaia, and A. Zaitsev, Surf. Coat. Technol. 220, 112 (2013).
S. Zanzarin, S. Bengtsson, and A. Molinari, J. Laser Appl. 27, S29209 (2015).
L. John and J.K. Damian, Welding Metallurgy and Weldability of Stainless Steels, 1st ed. (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2005), pp. 63–67.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially support by the National Science Foundation (Grant IIP-1034652). The authors also would like to thank the research engineer, Andrew Socha, for his help in the execution of experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Kovacevic, R. Multiresponse Optimization of Laser Cladding Steel + VC Using Grey Relational Analysis in the Taguchi Method. JOM 68, 1762–1773 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-1942-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-1942-x