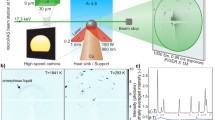
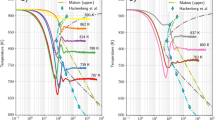
Abstract
Beam-based additive manufacturing (AM) typically involves high cooling rates in a range of 103–104 K/s. Therefore, new techniques are required to understand the non-equilibrium evolution of materials at appropriate time scales. Most technical alloys have not been optimized for such rapid solidification, and microstructural, phase, and elemental solubility behavior can be very different. In this work, the combination of complementary in situ synchrotron micro-x-ray diffraction (microXRD) and small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) studies with laser-based heating and rapid cooling is presented as an approach to study alloy behavior under processing conditions similar to AM techniques. In rapidly solidified Ti-48Al, the full solidification and phase transformation sequences are observed using microXRD with high temporal resolution. The high cooling rates are achieved by fast heat extraction. Further, the temperature- and cooling rate-dependent precipitation of sub-nanometer clusters in an Al-Cu-Mg alloy can be studied by SAXS. The sensitivity of SAXS on the length scales of the newly formed phases allows their size and fraction to be determined. These techniques are unique tools to help provide a deeper understanding of underlying alloy behavior and its influence on resulting microstructures and properties after AM. Their availability to materials scientists is crucial for both in-depth investigations of novel alloys and also future production of high-quality parts using AM.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.A. Dantzig and M. Rappaz, Solidification, 1st ed. (Lausanne: EPFL Press, 2009).
P. Li, V.I. Nikitin, E.G. Kandalova, and K.V. Nikitin, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 332, 371 (2002).
P. Ma, K. Prashanth, S. Scudino, Y. Jia, H. Wang, C. Zou, Z. Wei, and J. Eckert, Metals 4, 28 (2014).
R.M. Srivastava, J. Eckert, W. Löser, B.K. Dhindaw, and L. Schultz, Mater. Trans. 43, 1670 (2002).
Y. Li and D. Gu, Mater. Des. 63, 856 (2014).
A. Hussein, L. Hao, C. Yan, and R. Everson, Mater. Des. 52, 638 (2013).
D. Gu, Y.-C. Hagedorn, W. Meiners, G. Meng, R.J.S. Batista, K. Wissenbach, and R. Poprawe, Acta Mater. 60, 3849 (2012).
R. Chou, J. Milligan, M. Paliwal, and M. Brochu, JOM 67, 590 (2015).
J.L. Fife, M. Rappaz, M. Pistone, T. Celcer, G. Mikuljan, and M. Stampanoni, J. Synchrotron Radiat. 19, 352 (2012).
C. Kenel and C. Leinenbach, J. Alloys Compd. 637, 242 (2015).
W. De Nolf, F. Vanmeert, and K. Janssens, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 47, 1107 (2014).
C. Kenel, D. Grolimund, J.L. Fife, V.A. Samnson, S. Van Petegem, H. Van Swygenhoven, and C. Leinenbach, Scr. Mater. 114, 117 (2016).
Y.-W. Kim, JOM 46, 30 (1994).
H. Clemens, W. Wallgram, S. Kremmer, V. Güther, A. Otto, and A. Bartels, Adv. Eng. Mater. 10, 707 (2008).
P. Bartolotta, J. Barret, T. Kelly, and R. Smashey, JOM 49, 48 (1997).
C. McCullough, J. Valencia, C. Levi, and R. Mehrabian, Acta Metall. 37, 1321 (1989).
J. Liu, P. Staron, S. Riekehr, A. Stark, N. Schell, N. Huber, A. Schreyer, M. Müller, and N. Kashaev, Intermetallics 62, 27 (2015).
T. Sentenac, Y. Le Maoultt, G. Rolland, and M. Devy, IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 52, 46 (2003).
P. Schloth, J.N. Wagner, J.L. Fife, A. Menzel, J.-M. Drezet, and H. Van Swygenhoven, Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 101908 (2014).
P. Schloth, A. Menzel, J.L. Fife, J.N. Wagner, H. Van Swygenhoven, and J.-M. Drezet, Scr. Mater. 108, 56 (2015).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Paul Scherrer Institut for providing beamtime at the cSAXS and microXAS beamlines of the Swiss Light Source. They also thank the TOMCAT beamline at the Swiss Light Source for providing the laser system.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kenel, C., Schloth, P., Van Petegem, S. et al. In Situ Synchrotron X-Ray Diffraction and Small Angle X-Ray Scattering Studies on Rapidly Heated and Cooled Ti-Al and Al-Cu-Mg Alloys Using Laser-Based Heating. JOM 68, 978–984 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1774-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1774-0