Abstract
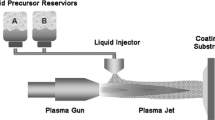
Solution precursor plasma spray (SPPS) synthesis is a simple, single-step, and rapid technique for synthesizing nano-ceramic materials from solution precursors. This innovative method uses molecularly mixed precursors as liquids, avoiding a separate processing method for the preparation of powders and enabling the synthesis of a wide range of metal oxide powders and coatings. Also, this technique is considered to be promising for the formation of non-equilibrium phases in multi-component oxide systems. This short review provides an insight into the important aspects of SPPS, the properties obtained in comparison to conventional plasma spray, and the potential applications of the SPPS process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Fauchais et al., “Developments in Direct Current Plasma Spraying,” Surface & Coatings Technology, 201 (2006), pp. 1908–1921.
J. Karthikeyan et al., “Plasma Spray Synthesis of Nanomaterial Powders and Deposits,” Materials Science and Engineering A, 238 (1997), pp. 275–286.
X. Ma et al., “Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Development by Using Novel Plasma Spray Techniques,” Journal of Fuel Cell Science and Technology, 2 (2005), pp. 190–196.
P.S. Devi et al., “Single-Step Deposition of Eu-Doped Y2O3 Phosphor Coatings through a Precursor Plasma Spraying Technique,” Journal of Materials Research, 17 (2002), pp. 2771–2774.
X.Z. Guo et al., “Synthesis of Yttrium Iron Garnet (YIG) by Citrate-Nitrate Gel Combustion and Precursor Plasma Spray Processes,” Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 295 (2005), pp. 145–154.
T.W. Coyle et al., “Plasma Spray Deposition of Hydroxyapatite Coatings from Sol Precursors,” Materials Science Forum, 539–543 (2007), pp. 1128–1133.
A. Ioncea et al., “Bioactive Coatings Based on Hydroxyapatite,” Key Engineering Materials, 132–136 (1997), pp. 1532–1535.
E. Garcia et al., “Hydroxyapatite Coatings Produced by Plasma Spraying of Organic Based Solution Precursor,” Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings, Advances in Bioceramics and Biocomposites II—A Collection of Papers Presented at the 30th International Conference on Advanced Ceramics and Composites, 27 (2006), pp. 103–110.
F. Gitzhofer, M. Bonneau, and M. Boulos, “Double Doped Ceria Electrolyte Synthesized by Solution Plasma Spraying with Induction Plasma Technology,” Thermal Spray 2001: New Surfaces for a New Millenium, ed. C.C. Berndt, K.A. Khor, and E.F. Lugscheider (Materials Park, OH: ASM International, 2001), pp. 61–68.
V. Viswanathan et al., “High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Solution Precursor Plasma Sprayed Nanoceria Coating on Martensitic Steels,” Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 90 (2007), pp. 870–877.
A.D. Jadhav et al., “Thick Ceramic Thermal Barrier Coatings with High Durability Deposited using Solution-Precursor Plasma Spray,” Materials Science and Engineering A, 405 (2005), pp. 313–320.
L. Xie et al., “Deposition of Thermal Barrier Coatings using the Solution Precursor Plasma Spray Process,” Journal of Materials Science, 39 (2004), pp. 1639–1646.
P.P. Nitin et al., “Towards Durable Thermal Barrier Coatings with Novel Microstructures Deposited by Solution Precursor Plasma Spray,” Acta Materialia, 49 (2001), pp. 2251–2257.
L. Xie et al., “Formation of Vertical Cracks in Solution-Precursor Plasma-Sprayed Thermal Barrier Coatings,” Surface & Coatings Technology, 201 (2006), pp. 1058–1064.
X. Ma et al., “Low Thermal Conductivity Thermal Barrier Coating Deposited by the Solution Plasma Spray Process,” Surface & Coatings Technology, 201 (2006), pp. 4447–4452.
A.D. Jadhav et al., “Low-Thermal-Conductivity Plasma-Sprayed Thermal Barrier Coatings with Engineered Microstructures,” Acta Materialia, 54 (2006), pp. 3343–3349.
L. Xie et al., “Phase and Microstructural Stability of Solution Precursor Plasma Sprayed Thermal Barrier Coatings,” Materials Science and Engineering A, 381 (2004), pp. 189–195.
L. Xie et al., “Deposition Mechanisms of Thermal Barrier Coatings in the Solution Precursor Plasma Spray Process,” Surface and Coatings Technology, 177–178 (2004), pp. 103–107.
A.L. Vasiliev, P.P. Nitin, and X. Ma, “Coatings of Metastable Ceramics Deposited by Solution-Precursor Plasma Spray: I. Binary ZrO2-Al2O3 System,” Acta Materialia, 54 (2006), pp. 4913–4920.
A.L. Vasiliev and N.P. Padture, “Coatings of Metastable Ceramics Deposited by Solution-Precursor Plasma Spray: II. Ternary ZrO2-Y2O3-Al2O3 System,” Acta Materialia, 54 (2006), pp. 4921–4928.
W.G. Mao et al., “Modeling of Residual Stresses Variation with Thermal Cycling in Thermal Barrier Coatings,” Mechanics of Materials, 38 (2006), pp. 1118–1127.
A.G. Evans, M.Y. He, and J.W. Hutchinson, “Mechanics-Based Scaling Laws for the Durability of Thermal Barrier Coatings,” Progress in Materials Science, 46 (2001), pp. 249–271.
A.G. Evans et al., “Mechanisms Controlling the Durability of Thermal Barrier Coatings,” Progress in Materials Science, 46 (2001), pp. 505–553.
X. Liangde et al., “Deposition of Thermal Barrier Coatings using the Solution Precursor Plasma Spray Process,” Journal of Materials Science, 39 (2004), pp. 1639–1646.
K. Bobzin, E. Lugscheider, and R. Nickel, “Modeling and Simulation in the Production Process Control and Material Property Calculation of Complex Structured EB-PVD TBCs,” Computational Materials Science, 39 (2007), pp. 600–610.
X. Ning et al., “Modification of Microstructure and Electrical Conductivity of Plasma-Sprayed YSZ Deposit through Post-Densification Process,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, 428 (2006), pp. 98–105.
A.D. Jadhav et al., “Low-Thermal-Conductivity Plasma-Sprayed Thermal Barrier Coatings with Engineered Microstructures,” Acta Materialia, 54 (2006), pp. 3343–3349.
L. Xie et al., “Identification of Coating Deposition Mechanisms in the Solution-Precursor Plasma-Spray Process using Model Spray Experiments,” Materials Science and Engineering A, 362 (2003), pp. 204–212.
S. Sampath et al., “Substrate Temperature Effects on Splat Formation, Microstructure Development and Properties of Plasma Sprayed Coatings Part I: Case Study for Partially Stabilized Zirconia,” Materials Science and Engineering A, 272 (1999), pp. 181–188.
L. Xie et al., “Phase and Microstructural Stability of Solution Precursor Plasma Sprayed Thermal Barrier Coatings,” Materials Science and Engineering A, 381 (2004), pp. 189–195.
S. Guo and Y. Kagawa, “Effect of Thermal Exposure on Hardness and Young’s Modulus of EB-PVD Yttria-Partially-Stabilized Zirconia Thermal Barrier Coatings,” Ceramics International, 32 (2006), pp. 263–270.
N.P. Padture et al., “Towards Durable Thermal Barrier Coatings with Novel Microstructures Deposited by Solution Precursor Plasma Spray,” Acta Materialia, 49 (2001), pp. 2251–2257.
A. Jadhav et al., “Thick Ceramic Thermal Barrier Coatings with High Durability Deposited Using Solution-Precursor Plasma Spray,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, 405 (2005), pp. 313–320.
M. Gell et al., “Mechanisms of Spallation of Solution Precursor Plasma Spray Thermal Barrier Coatings,” Surface & Coatings Technology, 188–189 (2004), pp. 101–106.
A.L. Vasiliev, N.P. Padture, and X. Ma, “Coatings of Metastable Ceramics Deposited by Solution-Precursor Plasma Spray: I. Binary ZrO2-Al2O3 System,” Acta Materialia, 54 (2006), pp. 4913–4920.
J. Li et al., “Phase Structure and Luminescence Properties of Eu3+-Doped TiO2 Nanocrystals Synthesized by Ar/O2 Radio Frequency Thermal Plasma Oxidation of Liquid Precursor Mists,” Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 110 (2006), pp. 1121–1127.
L. Xie et al., “Deposition Mechanisms of Thermal Barrier Coatings in the Solution Precursor Plasma Spray Process,” Surface and Coatings Technology, 177–178 (2001), pp. 103–107.
A. Ozturk and B.M. Cetegen, “Modeling of Plasma Assisted Formation of Precipitates in Zirconium Containing Liquid Precursor Droplets,” Materials Science and Engineering A, 384 (2004), pp. 331–351.
A. Ozturk and B.M. Cetegen, “Modeling of Axially and Transversely Injected Precursor Droplets into a Plasma Environment,” International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 48 (2005), pp. 4367–4383.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brinley, E., Babu, K.S. & Seal, S. The solution precursor plasma spray processing of nanomaterials. JOM 59, 54–59 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-007-0090-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-007-0090-8