Abstract
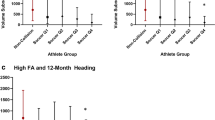
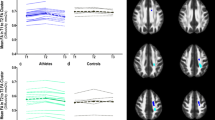
Soccer is the most popular sport in the world. Soccer players are at high risk for repetitive subconcussive head impact when heading the ball. Whether this leads to long-term alterations of the brain’s structure associated with cognitive decline remains unknown. The aim of this study was to evaluate cortical thickness in former professional soccer players using high-resolution structural MR imaging. Fifteen former male professional soccer players (mean age 49.3 [SD 5.1] years) underwent high-resolution structural 3 T MR imaging, as well as cognitive testing. Fifteen male, age-matched former professional non-contact sport athletes (mean age 49.6 [SD 6.4] years) served as controls. Group analyses of cortical thickness were performed using voxel-based statistics. Soccer players demonstrated greater cortical thinning with increasing age compared to controls in the right inferolateral-parietal, temporal, and occipital cortex. Cortical thinning was associated with lower cognitive performance as well as with estimated exposure to repetitive subconcussive head impact. Neurocognitive evaluation revealed decreased memory performance in the soccer players compared to controls. The association of cortical thinning and decreased cognitive performance, as well as exposure to repetitive subconcussive head impact, further supports the hypothesis that repetitive subconcussive head impact may play a role in early cognitive decline in soccer players. Future studies are needed to elucidate the time course of changes in cortical thickness as well as their association with impaired cognitive function and possible underlying neurodegenerative process.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BIS:
-
Barrett Impulsivity Score
- BESS:
-
Balance error scoring system
- ROCF:
-
Rey osterrieth complex figure
- RSHI:
-
Repetitive subconcussive head impact
- TMT A:
-
Trailmaking Test A
- TMT B:
-
Trailmaking Test B
References
Bailes, J. E., Petraglia, A. L., Omalu, B. I., Nauman, E., & Talavage, T. (2013). Role of subconcussion in repetitive mild traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurosurgery, 119(5), 1235–1245.
Bell, D. R., Guskiewicz, K. M., Clark, M. A., & Padua, D. A. (2011). Systematic review of the balance error scoring system. Sports Health, 3(3), 287–295.
Boden, B. P., Kirkendall, D. T., & Garrett Jr., W. E. (1998). Concussion incidence in elite college soccer players. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 26(2), 238–241.
Bowie, C. R., & Harvey, P. D. (2006). Administration and interpretation of the trail making test. Nature Protocols, 1(5), 2277–2281.
Ekblom, B. (1986). Applied physiology of soccer. Sports Medicine, 3(1), 50–60.
Fjell, A. M., Westlye, L. T., Amlien, I., et al. (2009). High consistency of regional cortical thinning in aging across multiple samples. Cerebral Cortex, 19(9), 2001–2012.
Jordan, S. E., Green, G. A., Galanty, H. L., Mandelbaum, B. R., & Jabour, B. A. (1996). Acute and chronic brain injury in United States national team soccer players. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 24(2), 205–210.
Koerte, I. K., Ertl-Wagner, B., Reiser, M., Zafonte, R., & Shenton, M. E. (2012). White matter integrity in the brains of professional soccer players without a symptomatic concussion. JAMA, 308(18), 1859–1861.
Koerte, I. K., Lin, A. P., & Muehlmann M., et al. (2015a) Altered neurochemistry in former professional soccer players without a history of concussion. Journal of Neurotrauma. doi:10.1089/neu.2014.3715.
Koerte, I. K., Lin, A. P., Willems, A., et al. (2015b) A review of neuroimaging findings in repetitive brain trauma. Brain Pathol, 25(3), 318–349. doi:10.1111/bpa.12249
Lipton, M. L., Kim, N., Zimmerman, M. E., et al. (2013). Soccer heading is associated with white matter microstructural and cognitive abnormalities. Radiology, 268(3), 850–857.
Patton, J. H., Stanford, M. S., & Barratt, E. S. (1995). Factor structure of the barratt impulsiveness scale. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 51(6), 768–774.
Rieder, C., & Jansen, P. (2011). No neuropsychological consequence in male and female soccer players after a short heading training. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 26(7), 583–591.
Rutherford, A., Stephens, R., Fernie, G., & Potter, D. (2009). Do UK university football club players suffer neuropsychological impairment as a consequence of their football (soccer) play? Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 31(6), 664–681.
Salat, D. H., Buckner, R. L., Snyder, A. Z., et al. (2004). Thinning of the cerebral cortex in aging. Cerebral Cortex, 14(7), 721–730.
Shin, M. S., Park, S. Y., Park, S. R., Seol, S. H., & Kwon, J. S. (2006). Clinical and empirical applications of the Rey-osterrieth complex figure test. Nature Protocols, 1(2), 892–899.
Sowell, E. R., Peterson, B. S., Kan, E., et al. (2007). Sex differences in cortical thickness mapped in 176 healthy individuals between 7 and 87 years of age. Cerebral Cortex, 17(7), 1550–1560.
Storsve, A. B., Fjell, A. M., Tamnes, C. K., et al. (2014). Differential longitudinal changes in cortical thickness, surface area and volume across the adult life span: regions of accelerating and decelerating change. The Journal of Neuroscience, 34(25), 8488–8498.
Straume-Naesheim, T. M., Andersen, T. E., Dvorak, J., & Bahr, R. (2005). Effects of heading exposure and previous concussions on neuropsychological performance among norwegian elite footballers. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 39(Suppl 1), i70–i77.
Tremblay, S., De Beaumont, L., Henry, L. C., et al. (2013). Sports concussions and aging: a neuroimaging investigation. Cerebral Cortex, 23(5), 1159–1166.
Tysvaer, A., & Storli, O. (1981). Association football injuries to the brain. A preliminary report. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 15(3), 163–166.
Zhang, M. R., Red, S. D., Lin, A. H., Patel, S. S., & Sereno, A. B. (2013). Evidence of cognitive dysfunction after soccer playing with ball heading using a novel tablet-based approach. PloS One, 8(2), e57364.
Funding
This study was supported by the Else Kröner-Fresenius Stiftung, Germany (IK). This work was also partially funded by grants from The Department of Defense (X81XWH-07-CC-CSDoD; RZ, MES) and a VA Merit Award (MES). Michael Mayinger was supported by the Petraeic Legate foundation, Germany.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Compliance with ethical standards
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible institutional committee on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, and the applicable revisions. Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants prior to inclusion in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koerte, I.K., Mayinger, M., Muehlmann, M. et al. Cortical thinning in former professional soccer players. Brain Imaging and Behavior 10, 792–798 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9442-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9442-0