Abstract
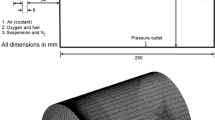
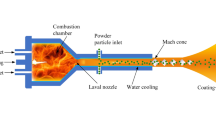
In thermal spray processes, it is demonstrated that substrate shape and location have significant effects on particle in-flight behavior and coatings quality. In the present work, the suspension high-velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) spraying process is modeled using a three-dimensional two-way coupled Eulerian–Lagrangian approach. Flat and cylindrical substrates are placed at different standoff distances, and particles characteristics near the substrates and upon impact are studied. Suspension is a mixture of ethanol, ethylene glycol, and mullite solid powder (3Al2O3·2SiO2) in this study. Suspension droplets with predefined size distribution are injected into the combustion chamber, and the droplet breakup phenomenon is simulated using Taylor analogy breakup model. Furthermore, the eddy dissipation model is used to model the premixed combustion of oxygen–propylene, and non-premixed combustion of oxygen–ethanol and oxygen–ethylene glycol. To simulate the gas phase turbulence, the realizable k–ε model is applied. In addition, as soon as the breakup and combustion phenomena are completed, the solid/molten mullite particles are tracked through the domain. It is shown that as the standoff distance increases the particle temperature and velocity decrease and the particle trajectory deviation becomes more significant. The effect of stagnation region on the particle velocity and temperature is also discussed in detail. The catch rate, which is defined as the ratio of the mass of landed particles to injected particles, is calculated for different substrate shapes and standoff distances in this study. The numerical results presented here is consistent with the experimental data in the literature for the same operating conditions.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Fauchais, G. Montavon, R.S. Lima, and B.R. Marple, Engineering a New Class of Thermal Spray Nano-Based Microstructures from Agglomerated Nanostructured Particles, Suspensions and Solutions: An Invited Review, J. Phys. D, 2011, 44(9), p 093001
P. Fauchais, G. Montavon, and G. Bertrand, From Powders to Thermally Sprayed Coating, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2009, 19, p 56-80
P. Fauchais and G. Montavon, Latest Developments in Suspension and Liquid Precursor Thermal Spraying, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2009, 19, p 226-239
L. Pawlowski, Suspension and Solution Thermal Spray Coatings, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2009, 203, p 2807-2829
A. Klilinger, R. Gadow, G. Mauer, A. Guignard, R. Vaben, and D. Stover, Review of New Developments in Suspension and Solution Precursor Thermal Spray Processes, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2011, 20, p 677-695
J. Oberste Berghaus, J.G. Legoux, C. Moreau, R. Hui, C. Deces-Petit, W. Qu, S. Yick, Z. Wang, R. Maric, and D. Ghosh, Suspension HVOF Spraying of Reduced Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Electrolytes, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2008, 17, p 700-707
S. Moghtadernejad, M. Tembely, M. Jadidi, N. Esmail, and A. Dolatabadi, Shear Driven Droplet Shedding and Coalescence on a Superhydrophobic Surface, Phys. Fluids, 2015, 27, p 032106
M. Jadidi, S. Moghtadernejad, and A. Dolatabadi, A Comprehensive Review on Fluid Dynamics and Transport of Suspension/Liquid Droplets and Particles in High-Velocity Oxygen-Fuel (HVOF) Thermal Spray, Coatings, 2015, 5(4), p 576-645
F.L. Toma, L.M. Berger, D. Jacquet, D. Wicky, I. Villaluenga, Y.R. de Miguel, and J.S. Lindelov, Comparative Study on the Photocatalytic Behaviour of Titanium Oxide Thermal Sprayed Coatings from Powders and Suspensions, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2009, 203, p 2150-2156
A. Killinger, M. Kuhn, and R. Gadow, High-Velocity Suspension Flame Spraying (HVSFS), a New Approach foe Spraying Nanoparticles with Hypersonic Speed, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2006, 201, p 1922-1929
R. Gadow, A. Killinger, and J. Rauch, New Results in High Velocity Suspension Flame Spraying (HVSFS), Surf. Coat. Tech., 2008, 202, p 4329-4336
R. Gadow, A. Killinger, and J. Rauch, Introduction to High-Velocity Suspension Flame Spraying (HVSFS), J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2008, 17, p 655-661
P. Fauchais, R. Etchart-Salas, V. Rat, J.F. Coudert, N. Caron, and K. Wittmann-Teneze, Parameters Controlling Liquid Plasma Spraying: Solutions, Sols, or Suspensions, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2008, 17(1), p 31-59
J. Fazilleau, C. Delbos, V. Rat, J.F. Coudert, P. Fauchais, and B. Pateyron, Phenomena Involved in Suspension Plasma Spraying Part 1: Suspension Injection and Behavior, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 2006, 26(4), p 371-391
L. Pawlowski, The Science and Engineering of Thermal Spray Coatings, 2nd ed., Wiley, Chichester, 2008
C.T. Crowe, M. Sommerfeld, and Y. Tsuji, Multiphase Flows with Droplets and Particles, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1998
M. Taleby and S. Hossainpour, Numerical Investigation of High Velocity Suspension Flame Spraying, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2012, 21, p 1163-1172
E. Gozali, S. Kamnis, and S. Gu, Numerical Investigation of Combustion and Liquid Feedstock in High Velocity Suspension Flame Spraying Process, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2013, 228, p 176-186
G.I. Taylor, The Shape and Acceleration of a Drop in High-Speed Air Stream, The Scientific Papers of Sir Geoffrey Ingram Taylor, Vol 3, G.K. Batchelor, Ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1963, p 457-464
E. Gozali, M. Mahrukh, S. Gu, and S. Kamnis, Numerical Analysis of Multicomponent Suspension Droplets in High-Velocity Flame Spray Process, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2014, 23, p 940-949
E. Dongmo, A. Killinger, M. Wenzelburger, and R. Gadow, Numerical Approach and Optimization of the Combustion and Gas Dynamics in High Velocity Suspension Flame Spraying (HVSFS), Surf. Coat. Tech., 2009, 203, p 2139-2145
E. Dongmo, R. Gadow, A. Killinger, and M. Wenzelburger, Modeling of Combustion as well as Heat, Mass, and Momentum Transfer During Thermal Spraying by HVOF and HVSFS, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2009, 18, p 896-908
M. Mahrukh, A. Kumar, and S. Gu, Effects of Angular Injection, and Effervescent Atomization on High-Velocity Suspension Flame Spray Process, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2016, 302, p 368-382
M. Jadidi, S. Moghtadernejad, and A. Dolatabadi, Numerical Modeling of Suspension HVOF Spray, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2016, 25, p 451-464
F. Jabbari, M. Jadidi, R. Wuthrich, and A. Dolatabadi, A Numerical Study of Suspension Injection in Plasma-Spraying Process, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2014, 23, p 3-13
M. Jadidi, M. Mousavi, S. Moghtadernejad, and A. Dolatabadi, A Three-Dimensional Analysis of the Suspension Plasma Spray Impinging on a Flat Substrate, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2015, 24, p 11-23
K. Pourang, C. Moreau, and A. Dolatabadi, Effect of Substrate and Its Shape on in-Flight Particle Characteristics in Suspension Plasma Spraying, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2016, 25, p 44-54
E. Dalir, Three-Dimensional Modeling of Arc Voltage Fluctuations in Suspension Plasma Spraying, Master Thesis, Concordia University, Montreal, 2016
A. Farrokhpanah, T.W. Coyle, and J. Mostaghimi, Numerical Study of Suspension Plasma Spraying, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2017, 26, p 12-36
V.R. Srivatsan and A. Dolatabadi, Simulation of Particle–Shock Interaction in a High Velocity Oxygen Fuel Process, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2006, 15, p 481-587
M. Li and P.D. Christofides, Computational Study of Particle In-flight Behavior in the HVOF Thermal Spray Process, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2006, 61, p 6540-6552
M. Li and P.D. Christofides, Multi-Scale Modeling and Analysis of an Industrial HVOF Thermal Spray Process, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2005, 60, p 3649-3669
M. Li, D. Shi, and P.D. Christofides, Diamond Jet Hybrid HVOF Thermal Spray: Gas-Phase and Particle Behavior Modeling and Feedback Control Design, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2004, 43, p 3632-3652
D. Shi, M. Li, and P.D. Christofides, Diamond Jet Hybrid HVOF Thermal Spray: Rule-Based Modeling of Coating Microstructure, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2004, 43, p 3653-3665
ANSYS Inc., ANSYS FLUENT Theory Guide, USA, 2011
J.O. Berghaus and B.R. Marple, High-Velocity Oxy-Fuel (HVOF) Suspension Spraying of Mullite Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2008, 17, p 671-678
S. Gordon, B.J. McBride, Computer Program for Calculation of Complex Chemical Equilibrium Compositions and Applications, NASA Reference Publication No. 1311, Lewis Research Center, Cleveland, OH, October 5 1994
G.E. Lorenzetto and A.H. Lefebvre, Measurements of Drop Size on a Plain-Jet Airblast Atomizer, AIAA J., 1977, 15, p 1006-1010
S. Tanvir and L. Qiao, Surface Tension of Nanofluid-Type Fuels Containing Suspended Nanomaterials, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2012, 7, p 226
M. Li and P.D. Christofides, Modeling and Control of High-Velocity Oxygen-Fuel (HVOF) Thermal Spray: A Tutorial Review, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2009, 18, p 753-768
N. Zuckerman and N. Lior, Jet Impingement Heat Transfer: Physics, Correlations, and Numerical Modeling, Adv. Heat Transfer, 2006, 39, p 565-631
Acknowledgments
This article is based on the work supported by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC). The authors would like to thank Ms. Sara Saberiyan Boroujeni and Dr. Sara Moghtadernejad for their help and scientific feedback in preparing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is an invited paper selected from presentations at the 2017 International Thermal Spray Conference, held June 7-9, 2017, in Düsseldorf, Germany, that has been expanded from the original presentation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jadidi, M., Yeganeh, A.Z. & Dolatabadi, A. Numerical Study of Suspension HVOF Spray and Particle Behavior Near Flat and Cylindrical Substrates. J Therm Spray Tech 27, 59–72 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-017-0656-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-017-0656-0