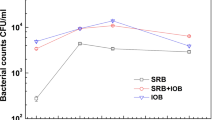
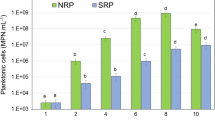
Abstract
This work investigates microbiologically influenced corrosion of API 5L X52 linepipe steel by a sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) consortium. The SRB consortium used in this study was cultivated from a sour oil well in Louisiana, USA. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis indicated that the mixed bacterial consortium contained three phylotypes: members of Proteobacteria (Desulfomicrobium sp.), Firmicutes (Clostridium sp.), and Bacteroidetes (Anaerophaga sp.). The biofilm and the pits that developed with time were characterized using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). In addition, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), linear polarization resistance (LPR) and open circuit potential (OCP) were used to analyze the corrosion behavior. Through circuit modeling, EIS results were used to interpret the physicoelectric interactions between the electrode, biofilm and solution interfaces. The results confirmed that extensive localized corrosion activity of SRB is due to a formed biofilm in conjunction with a porous iron sulfide layer on the metal surface. X-ray diffraction (XRD) revealed semiconductive corrosion products predominantly composed of a mixture of siderite (FeCO3), iron sulfide (Fe x S y ), and iron (III) oxide-hydroxide (FeOOH) constituents in the corrosion products for the system exposed to the SRB consortium.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.J. Little and J.S. Lee, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, 2007
R. Bhola, S.M. Bhola, B. Mishra, and D.L. Olson, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion and Its Mitigation: A Review, Mater. Sci. Res. India, 2010, 7(2), p 407–412
R. Javaherdashti, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion: An Engineering Insight, Springer, London, 2008
W.A. Hamilton, Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Anaerobic Corrosion, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 1985, 39, p 195–217
M. Bethencourt, F. Botana, and M. Cano, Biocorrosion of Carbon Steel Alloys by an Hydrogenotrophic Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium Desulfovibrio Capillatus Isolated from a Mexican Oil Field Separator, Corros. Sci., 2006, 48, p 2417–2431
M. Madigan, Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 12th ed., Pearson Benjamin Cummings, San Francisco, 2009
F.M. AlAbbas, C. Williamson, S.M. Bhola, J.R. Spear, D.L. Olson, B. Mishra, and A.E. Kakpovbia, Influence of Sulfate Reducing Bacterial Biofilm on Corrosion Behavior of Low-Alloy, High-Strength Steel (API-5L X80), Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2013, 78, p 34–42
NACE Standard TM0194-2004, Field Monitoring of Bacterial Growth in Oil and Gas Systems, NACE, Houston, TX, 2004
P.J. Antony, R.K. Singh, R. Mohanram, K. Pradeep, and R. Raman, Influence of Thermal Aging on Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria (SRB)-Influenced Corrosion Behaviour of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel, Corros. Sci., 2008, 50, p 1858–1864
D.J. Lane, 16S/23S rRNA Sequencing, Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics, E. Stackebrandt and M. Goodfellow, Ed., Wiley, Chichester, 1991, p 115–175
J.W. Sahl, N. Fairfield, J. Kirk Harris, D. Wettergreen, W.C. Stone, and J.R. Spear, Novel Microbial Diversity Retrieved by Autonomous Robotic Exploration of the World’s Deepest Vertical Phreatic Sinkhole, Astrobiology, 2010, 10(2), p 201–213
E. Brent and P. Green, Base-Calling of Automated Sequencer Traces Using Phred. II. Error Probabilities, Genome Res., 1998, 8(3), p 186–194
E. Brent, L. Hillier, M.C. Wendl, and P. Green, Base-Calling of Automated Sequencer Traces Using Phred. I. Accuracy Assessment, Genome Res., 1998, 8(3), p 175–185
D.N. Frank, XplorSeq: A Software Environment for Integrated Management and Phylogenetic Analysis of Metagenomic Sequence Data, BMC Bioinformatics, 2008, 9(1), p 420
P. Elmar, J. Peplies, and F. Oliver Glöckner, SINA: Accurate High-Throughput Multiple Sequence Alignment of Ribosomal RNA Genes, Bioinformatics, 2012, 28(14), p 1823–1829
P. Elmar, C. Quast, K. Knittel, B.M. Fuchs, W. Ludwig, J. Peplies, and F. Oliver Glöckner, SILVA: A Comprehensive Online Resource for Quality Checked and Aligned Ribosomal RNA Sequence Data Compatible with ARB, Nucleic Acids Res., 2007, 35(21), p 7188–7196
W. Ludwig, S. Oliver, W. Ralf, R. Lothar, M. Harald, Yadhukumar, B. Arno, et al. ARB: A Software Environment for Sequence Data, Nucleic Acids Res., 2004, 32(4), p 1363–1371
D.A. Benson, K.M. Ilene, D.J. Lipman, J. Ostell, and D.L. Wheeler, GenBank, Nucleic Acids Res., 2005, 33, p D34–D38
S.F. Altschul, W. Gish, W. Miller, E.W. Myers, and D.J. Lipman, Basic Local Alignment Search Tool, J. Mol. Biol., 1990, 215(3), p 403–410
A. Stamatakis, RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum Likelihood-Based Phylogenetic Analyses with Thousands of Taxa and Mixed Models, Bioinformatics, 2006, 22(21), p 2688–2690
E.P. Nawrocki, Structural RNA Homology Search and Alignment Using Covariance Models, Washington University, Saint Louis, MO, 2009
N.D. Pattengale, M. Alipour, O.R.P. Bininda-Emonds, B.M.E. Moret, and A. Stamatakis, How Many Bootstrap Replicates are Necessary?, J. Comput. Biol., 2010, 17(3), p 337–354
D.A. Jones and P.S. Amy, A Thermodynamic Interpretation of Microbiologically Influenced, Corrosion, 2002, 8(8), p 938–945
C. Xua, Y. Zhanga, B. Chenga, and W. Zhub, Pitting Corrosion Behavior of 316L Stainless Steel in the Media of Sulphate-Reducing and Iron-Oxidizing Bacteria, Mater. Charact., 2008, 59(3), p 245–255
ASTM G1-03, Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimens, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 2009, p 17–23
J.Y. Leu, T.C. McGovern, A.R. Porter, and W.A. Hamilton, The Same Species of Sulphate-Reducing Desulfomicrobium Occur in Different Oil Field Environments in the North Sea, Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 1999, 29, p 246–252
G. Voordouw, J.K. Voordouw, and T.R. Jack, Identification of Distinct Communities of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria in Oil Fields by Reverse Sample Genome Probing, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1992, 58, p 3542–3552
H. Dahle, F. Garshol, M. Madsen, and N. Birkeland, Microbial Community Structure Analysis of Produced Water from a High-Temperature North Sea Oil-Field, Biomed. Life Sci., 2008, 9, p 37–49
D. Enning, H. Venzlaff, J. Garrelfs, H.T. Dinh, V. Meyer, K. Mayrhofer, A.W. Hassel, M. Stratmann, and F. Widdel, Marine Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Cause Serious Corrosion of Iron Under Electroconductive Biogenic Mineral Crust, Environ. Microbiol., 2012, 14(7), p 1772–1787
H. Castaneda and X.D. Benetton, SRB-Biofilm Influenced in Active Corrosion Sites Formed at the Steel-Electrolyte Interface When Exposed to Artificial Seawater Conditions, Corros. Sci., 2008, 50(4), p 1169–1183
D. Cetin and L. Aksu, Corrosion Behavior of Low-Alloy Steel in the Presence of Desulfotomaculum sp, Corro. Sci., 2009, 51, p 1584–1588
H. Venzlaff, D. Enning, J. Srinivasan, K.J.J. Mayrhofer, A.W. Hassel, H.F. Widdel, and M. Stratmann, Accelerated Cathodic Reaction in Microbial Corrosion of Iron Due to Direct Electron Uptake by Sulphate Reducing Bacteria, Corros. Sci., 2013, 66, p 88–96
F.M. AlAbbas, J.R. Spear, A. Kakpovbia, N.M. Balhareth, D.L. Olson, and B. Mishra, Bacterial Attachment to Metal Substrate and Its Effects on Microbiologically-Influenced Corrosion in Transporting Hydrocarbon Pipelines, J. Pipeline Eng., 2012, 2(1), p 63–72
R.G.J. Edyvean, Hydrogen Sulphide—A Corrosive Metabolite, Int. Biodeterior., 1991, 27, p 109–120
F. Kuanga, J. Wang, L. Yana, and D. Zhanga, Effects of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria on the Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel, Electrochim. Acta, 2007, 52, p 6084–6088
T. Liu, H. Liu, Y. Hu, L. Zhou, and B. Zheng, Growth Characteristics of Thermophile Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and its Effect on Carbon Steel, Mater. Corros., 2009, 60(3), p 218–224
W. Lee, Z. Lewandowski, P.H. Nielsen, and W.A. Hamilton, Role of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria in Corrosion of Mild Steel: A Review, Biofouling, 1995, 8, p 165–194
R.A. King and J.D. Miller, Corrosion by Sulfate Reducing Bacteria, Nature, 1971, 233, p 491–492
E. Robert, R. Hill, and R. Abbaschian, Physical Metallurgy Principles, 3rd ed., PWS-Kent Publication, Boston, 1992
ASM Handbook Volume 13 A, Corrosion: Fundamentals, Testing and Protection, ASM International, Materials Park, OH
O.R. Monroy, M.H. Gayosso, N. Ordaz, G. Olivares, and C.J. Ramírez, Corrosion of API, XL 52 Steel in Presence of Clostridium Celerecrescens, Mater. Corros., 2011, 62(9), p 878–883
S.M. Bhola, R. Bhola, B. Mishra, and D.L. Olson, Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopic Characterization of the Oxide Film Formed over Low Modulus Ti-35.5Nb-7.3Zr-5.7Ta Alloy in Phosphate Buffer Saline at Various Potentials, J. Mater. Sci., 2010, 45(22), p 6179–6186
S.M. Bhola, R. Bhola, L. Jain, B. Mishra, and D.L. Olson, Corrosion Behavior of Mild Carbon Steel in Ethanolic Solutions, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2011, 20(3), p 409–416
J.F.D. Stott, What Progress in the Understanding of Microbially Induced Corrosion Has Been Made in the Last 25 Years? A Personal Viewpoint, Corrosion Sci., 1993, 35(1-4), p 667–673
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge and appreciate the Saudi Aramco and Inspection Department Management for their continual support for this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
AlAbbas, F.M., Williamson, C., Bhola, S.M. et al. Microbial Corrosion in Linepipe Steel Under the Influence of a Sulfate-Reducing Consortium Isolated from an Oil Field. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 22, 3517–3529 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-013-0627-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-013-0627-7