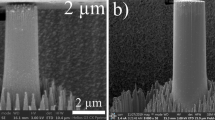
Abstract
The deformation behavior of the epitaxial TiN/MgO (001) thin film/substrate system was studied through in-situ nanoindentation in a transmission electron microscope (TEM). The required sample geometry was prepared using Ga+ focused ion beam (FIB) etching. During room-temperature indentation, both the TiN film and the MgO substrate deformed through the motion of dislocations. The result was a localized hemispherical plastic zone in the TiN film directly under the indentation contact area, forming an 8° tilt boundary. These results show directly that small-scale plasticity in TiN can occur at room temperature through the motion of dislocations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.E. Sundgren, A. Rockett, and J.E. Greene, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 6, 2770 (1986).
For example, W.S. Williams, Progress in Solid State Chemistry (New York: Pergamon Press, 1971), pp. 57–118.
W.S. Williams, Proprietes Thermodynamiques, Physiques et Structurales des Derives Semi-metalliques (Paris, editions du Centre National de la Rechereche Scientifique, 1967), pp. 181–189.
M. Oden, H. Ljungcrantz, and L. Hultman, J. Mater. Res. 12, 2134 (1997).
W.S. Williams, J. Appl. Phys. 35, 1329 (1964).
L.E. Toth, Transition Metal Carbides and Nitrides (New York, Academic Press, 1971), p. 5.
J.S. Chun, I. Petrov, and J.E. Greene, J. Appl. Phys. 86, 3633 (1999).
H. Holleck, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 4, 2661 (1986).
E.A. Stach, Microsc. Microanal. 7, 507 (2001).
A.M. Minor, J.W. Morris, and E.A. Stach, Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 1625 (2001).
A.M. Minor, E.T. Lilleodden, E.A. Stach, and J.W. Morris, Jr., J. Electron. Mater. 31, 958 (2002).
B.W. Karr, I. Petrov, P. Desjardins, D.G. Cahill, and J.E. Greene, Surf. Coating Technol. 94–95, 403 (1997).
B.W. Karr, I. Petrov, D.G. Cahill, and J.E. Greene, Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 1703 (1997).
B.W. Karr, D.G. Cahill, I. Petrov, and J.E. Greene, Phys. Rev. B 61, 16137 (2000).
R. Menzel, K. Gartner, W. Wesch, and H. Hobert, J. Appl. Phys. 88, 5658 (2000).
S. Rubanov and P.R. Munroe, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 20, 1181 (2001).
J. Ziegler, TRIM, http://www.srim.org
H. Ljungcrantz, M. Oden, L. Hultman, J.E. Greene, and J.-E. Sundgren, J. Appl. Phys. 80, 6725 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minor, A.M., Stach, E.A., Morris, J.W. et al. In-situ nanoindentation of epitaxial TiN/MgO (001) in a transmission electron microscope. J. Electron. Mater. 32, 1023–1027 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-003-0084-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-003-0084-4