Abstract
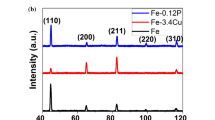
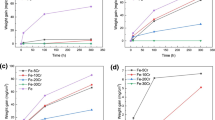
This study was undertaken to investigate the effect of small amounts of copper and copper + nickel additions on the oxidation rate and oxide/metal interface microstructure of iron. Three iron-based alloys were compared: 0.3 wt pct copper, 0.3 wt pct copper-0.1 wt pct nickel, and 0.3 wt pct copper-0.05 wt pct nickel. Alloy samples were oxidized in air at 1150 °C for 60, 300, and 600 seconds. Pure iron oxidized for 300 seconds was used as a reference material. The parabolic oxidation rate for the iron-copper alloy did not differ from that of pure iron, but the parabolic rate for the nickel-containing alloys decreased by a factor of 2. The microstructure of the iron-copper alloy consisted of a thin, copper-rich layer at the oxide/metal interface. Both nickel-containing alloys had perturbed oxide/metal interfaces consisting of alternating solid/liquid regions. The application of ternary alloy interface stability theories show that the perturbed interfaces arise from unequal diffusivities in the solid γ-iron phase. It is suggested that this perturbed interface microstructure causes the observed decrease in oxidation rate, by limiting the iron supply to the oxide.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
PHILIPS is a trademark of Philips Electronic Instruments Corp., Mahwah, NJ.
ThermoCalc is a trademark of Thermo-Calc Software, Stockholm, Sweden.
DICTRA is a trademark of Thermo-Calc Software, Stockholm, Sweden.
References
J.A.T. Jones, B. Bowman, and P.A. Lefrank: The Making, Shaping, and Treating of Steel—Steelmaking and Refining Volume, 11th ed., The AISE Steel Foundation, Pittsburgh, PA, 1998, pp. 525–660
Energetics Inc.: Energy and Environmental Profile of the U.S. Iron and Steel Industry, DOE/EE-0229, United States Department of Energy, Office of Industrial Technologies, Washington, DC, 2000, pp. 10–26
B. Sundman, B. Jansson, and J.-O. Andersson: CALPHAD: Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 1985, vol. 9, pp. 153–90
Q. Chen, and Z. Jin: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26A, pp. 417–26
S. Pötschke, and A.R. Büchner: Steel Res. Int., 2006, vol. 77, pp. 416–22
A. Nicholson, and J.D. Murray: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1965, vol. 203, pp. 1007–18
D.A. Melford: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1962, vol. 200, pp. 290–99
W.J.M. Salter: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1966, vol. 204, pp. 478–88
Handbook of Ternary Alloy Phase Diagrams, P. Villars, A. Prince, and H. Okamoto, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 1995, pp. 9350–91
B. Yalamanchili, P. Power, and J. Nelson: Wire J. Int., 1999, vol. 32, pp. 143–55
S. Akamatsu, T. Senuma, Y. Takada, and M. Hasebe: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1999, vol. 15, pp. 1301–07
S.V. Divinski, F. Hisker, C. Herzig, R. Filipek, and M. Danielewski: Def. Diff. Forum, 2005, vols. 237–240, pp. 50–61
G.L. Fisher: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1969, vol. 207, pp. 1010–16
T. Fukagawa, and H. Fujikawa: Oxid. Met., 1999, vol. 52, pp. 177–94
R.Y. Chen, and W.Y.D. Yuen: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp. 807–16
C. Wagner: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1956, vol. 103, pp. 571–80
H.J. Grabke, V. Leroy, and H. Viefhaus: ISIJ Int., 1995, vol. 35, pp. 95–113
B.A. Webler, and S. Sridhar: ISIJ Int., 2007, vol. 47, pp. 1245–54
H. Abuluwefa, R.I.L. Guthrie, and F. Ajersch: Oxid. Met., 1996, vol. 46, pp. 423–40
W. Rasband: ImageJ, Windows version 1.36, US National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD
R.Y. Chen, and W.Y.D. Yuen: Oxid. Met., 2003, vol. 59, pp. 433–68
K. Schwerdtfeger, and S. Zhou: Steel Res., 2003, vol. 74, pp. 538–48
V.G. Levich: Physicochemical Hydrodynamics, 1st ed., Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1962, p. 87.
L. Himmel, R.F. Mehl, and C.E. Birchenall: Trans. AIME, 1953, vol. 197, pp. 827–43
R.Y. Chen, and W.Y.D. Yuen: Oxid. Met., 2005, vol. 63, pp. 145–68
R.T. Foley: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1962, vol. 109, pp. 1202–06
F.J.J. Van Loo: Prog. Solid State Chem., 1990, vol. 20, pp. 47–99
W.W. Mullins, and R.F. Sekerka: J. Appl. Phys., 1964, vol. 35, pp. 444–51
D.P. Whittle, D.J. Young, and W.W. Smeltzer: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1976, vol. 123, pp. 1073–79
D.E. Coates, and J.S. Kirkaldy: Trans. ASM, 1969, vol. 62, pp. 426–36
J.D. Harrison, and C. Wagner: Acta Metall., 1959, vol. 7, pp. 722–35
J.B. Clark, and F.N. Rhines: Trans. ASM, 1959, vol. 51, pp. 199–221
J.S. Kirklady, and L.C. Brown: Can. Metall. Q., 1963, vol. 2, pp. 89–117
L.E. Wirtz, and M.A. Dayananda: Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 567–75
J.S. Kirkaldy and D.Y. Young: Diffusion in the Condensed State, 1st ed., The Institute of Metals, London, 1987, pp. 163 and 361–400
D.E. Coates, and J.S. Kirkaldy: J. Cryst. Growth, 1968, vols. 3–4, pp. 549–54
K. Majima, and H. Mitani: Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1978, vol. 19, pp. 663–68
Y. Hanatate, K. Majima, and H. Mitani: Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1978, vol. 19, pp. 669–73
K.J. Rönkä, A.A. Kodentsov, P.J.J. Van Loon, J.K. Kivilahti, and F.J.J. Van Loo: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, vol. 27A, pp. 2229–38
A. Borgenstam, L. Höglund, J. Ågren, and A. Engström: J. Phase Equilib. Diffus., 2000, vol. 21, pp. 269–80
B.A. Webler, and S. Sridhar: Def. Diff. Forum, 2008, vols. 273–276, pp. 713–23
N. Imai, N. Komatsubara, and K. Kunishige: ISIJ Int., 1997, vol. 37, pp. 224–31
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Center for Iron and Steelmaking Research, Carnegie Mellon University (Pittsburgh, PA), and the Pennsylvania Infrastructure Technology Alliance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 8, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Webler, B., Yin, L. & Sridhar, S. Effects of Small Additions of Copper and Copper + Nickel on the Oxidation Behavior of Iron. Metall Mater Trans B 39, 725–737 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-008-9196-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-008-9196-9