Abstract
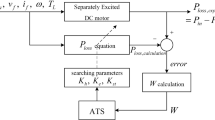
This paper considers minimization of resistive and frictional power dissipation in a separately excited DC motor based incremental motion drive (IMD). The drive is required to displace a given, fixed load through a definite angle in specified time, with minimum energy dissipation in the motor windings and minimum frictional losses. Accordingly, an energy optimal (EO) control strategy is proposed in which the motor is first accelerated to track a specific speed profile for a pre-determined optimal time period. Thereafter, both armature and field power supplies are disconnected, and the motor decelerates and comes to a halt at the desired displacement point in the desired total displacement time. The optimal time period for the initial acceleration phase is computed so that the motor stores just enough energy to decelerate to the final position at the specified displacement time. The parameters, such as the moment of inertia and coefficient of friction, which depend on the load and other external conditions, have been obtained using system identification method. Comparison with earlier control techniques is included. The results show that the proposed EO control strategy results in significant reduction of energy losses compared to the existing ones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. K. Lai, K. K. Shyu. A Novel Motor Drive Design for Incremental Motion System via Sliding-mode Control Method. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 499–507, 2005.
J. Tal, S. Kahne. Control and Component Selection for Incremental Motion Systems. Automatica, vol. 9, pp. 501–507, 1973.
C. C. Chan, R. Zhang, K. T. Chau, J. Z. Jiang. Optimal Efficiency Control of PM Hybrid Motor Drives for Electrical Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, vol. 1, pp. 363–368, 1997.
J. Holtz, L. Springob. Identification and Compensation of Torque Ripple in High Precision Permanent Magnet Motor Drives. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 309–320, 1996.
P. Pillay, R. Krishnan. Modeling, Simulation, and Analysis of Permanent-magnet Motor Drives — Part 1: The Permanent-magnet Synchronous Motor Drive. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 274–279, 1989.
G. Zhang, A. Schmidhofer, A. Schmid. Efficiency Optimisation at DC Drives for Small Electrical Vehicles. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, IEEE Press, vol. 2, pp. 1150–1155, 2003.
E. E. EI-kholy, S. S. Shokralla, A. H. Morsi, S. A. EIAbsawy. Improved Performance of Rolling Mill Drives Using Hybrid Fuzzy-PI Controller. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems, IEEE Press, vol. 2, pp. 1010–1015, 2003.
T. Egami, J. Wang, T. Tsuchiya. Efficiency Optimized Speed Control System Synthesis Method Based on Improved Optimal Regulator Theory — Application to Separately Excited DC Motor System. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. IE-32, no. 4, pp. 372–380, 1985.
A. Kusko, D. Galler. Control Means for Minimization of Losses in AC and DC Motor Drives. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. IA-19, no. 4, pp. 561–570, 1983.
S. Murtuza, N. Narasimhamurthi, S. T. Dilodovico. DC Servo Control-academic and Real. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, IEEE Press, vol. 3, pp. 2036–2037, 1995.
R. N. Danbury. Servomechanisms for Incremental Motion: Power Dissipation Considerations. Mechatronics, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 25–36, 1994.
A. M. Trzynadlowski. Energy Optimization of a Certain Class of Incremental Motion DC Drives. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 60–66, 1988.
F. J. Zheng, G. Cook. Energy Optimal Control for Steel Rolling. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. IE-32, no. 4, pp. 388–392, 1985.
J. C. Brierley, R. E. Colyer, A. M. Trzynadlowski. The “SOAR” Method for Computer Aided Design of Energyoptimal Positioning DC Drive Systems. In Proceedings of Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, IEEE Press, vol. 1, pp. 464–467, 1989.
E. R. Pinch. Optimal Control and the Calculus of Variations, Oxford University Press Inc., New York, USA, 1993.
I. J. Nagrath, M. Gopal. Control Systems Engineering, New Age International Ltd., New Delhi, India, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Milan A. Sheta received the bachelor degree in electrical engineering from Vyavasayi Vidya Pratishthan Engineering College, Rajkot, Gujarat, India in 2002, and the M. Tech. degree in systems and control engineering at the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, India, in 2005.
Vivek Agarwal received the bachelor degree in physics from St. Stephen’s college, Delhi University, USA, the Master degree in electrical Engineering from the Indian Institute of Science, India, and the Ph.D. degree in the Depterment of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Victoria, Canada in 1994. He worked for Statpower Technologies, Burnaby, Canada, as a research engineer. In 1995, he joined the Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, India, where he is currently a professor. He is a senior member of IEEE, fellow of IETE, and a life member of ISTE.
His research interests include power electronics, modeling and simulation of new power converter configurations, intelligent and hybrid control of power electronic systems, power quality, EMI/EMC, and conditioning of energy from non-conventional energy sources.
Paluri S. V. Nataraj received the Ph.D. degree in process dynamics and control from Indian Institute of Technology Madras, India in 1987. He is a faculty of the systems and control engineering at Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, India.
His research interests include robust control, process automation, nonlinear system analysis and control, and reliable computing.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheta, M.A., Agarwal, V. & Nataraj, P.S.V. A new energy optimal control scheme for a separately excited DC motor based incremental motion drive. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 6, 267–276 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-009-0267-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-009-0267-4