Summary
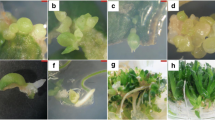
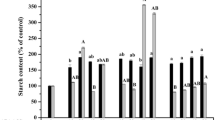
The effects of exogenous applications of ascorbic acid on white spruce somatic embryogenesis were examined. Increasing concentrations of ascorbate (1 µM to 100 µM) in the germination medium enhanced somatic embryo conversion in a linear fashion. At the optimal ascorbate level (100 µM) the number of embryos able to undergo normal conversion, i.e., emergence of both root and shoot, increased from 34% (control) to 58%. The effect of ascorbate had a more pronounced effect on shoot growth than on root emergence; and at 100 µM ascorbate, the percentage of embryos able to produce new leaf primordia increased from 47% (control) to 79%. Root emergence increased slightly from 64% in the control embryos to 74% in the presence of ascorbic acid. The ascorbate-treated embryos were characterized by an enlarged apical region, presumably due to a larger number of leaf primordia produced, and by dark green leaves. When allowed to grow further, these embryos were able to develop into normal plantlets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammirato, P. V. Patterns of development in culture. In: Henke, R. R.; Hughes, K. W.; Constantine, M. J., ed. Tissue culture in forestry and agriculture. New York: Plenum Press; 1985:9–29.
Arrigoni, O.; Bitonti, M. B.; Cozza, R.; Innocenti, A. M.; Liso, R.; Veltri, R. Ascorbic acid effect on pericycle cell line in Allium cepa root. Caryologia 42:213–216; 1989.
Arrigoni, O.; De Gara, L.; Tommasi, F.; Liso, R. Changes in the ascorbate system during seed development of Vicia faba L. Plant Physiol. 99:235–238; 1992.
Attree, S. M.; Fowke, L. C. Somatic embryogenesis and synthetic seeds of conifers. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 35:1–35; 1993.
Carpita, N. C.; Gibeaut, D. M. Structural models of primary cell walls in flowering plants: consistency of molecular structure with the physical properties of the wall during growth. Plant J. 3:1–30; 1993.
Chalupa, V. Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from cultured immature and mature embryos of Picea abies (L.) Karst. Comm. Inst. For. 14:57–63; 1985.
Citterio, S.; Sgorbati, S.; Scippa, S.; Sparvoli, E. Ascorbic acid effect on the onset of cell proliferation in pea root. Physiol. Plant. 92:601–607; 1994.
De Gara, L.; Tommasi, F.; Liso, R.; Arrigoni, O. Il sistema dell’acido ascorbico in Vicia faba L. Boll. Soc. Ital. Biol. Sper. 63:551–558; 1987.
Durzan, D. J. Physiological states and metabolic phenotypes in embryonic development. In: Bonga, J. M.; Durzan, D. J., ed. Cell and tissue culture in forestry. Vol. 2. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Martinus-Nijhoff Publishers; 1987:405–439.
Hakman, I.; Fowke, L. C.; von Arnold, S.; Eriksson, T. The development of somatic embryos in tissue cultures initiated from immature embryos of Picea abies (Norway spruce). Plant Sci. 38:53–59; 1985.
Hosie, R. C. Native trees of Canada. 8th ed. Don Mills: Fitzhenry and Whiteside; 1979:64.
Innocenti, A. M.; Bitonti, M. B.; Arrigoni, O.; Liso, R. The size of the quiescent center in roots Allium cepa L. grown with ascorbic acid. New Phytol. 114:507–509; 1990.
Joy, R. W., IV; Patel, K. R.; Thorpe, T. A. Ascorbic acid enhancement of organogenesis in tobacco. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 13:219–228; 1988.
Joy, R. W., IV; Yeung, E. C.; Kong, L.; Thorpe, T. A. Development of white spruce somatic embryos: I. Storage product deposition. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 27:32–41; 1991.
Kerk, N. M.; Feldman, L. J. A biochemical model for the initiation and the maintenance of the quiescent center: implications for organization of root meristems. Development 121:2825–2833; 1995.
Kong, L.; Attree, S. M.; Evan, D. E.; Binarova, P.; Yeung, E. C.; Fowke, L. C. Somatic embryogenesis in white spruce: studies of embryo development and cell biology. In: Jain, M.; Gupta, P. K.; Newton, R. J., ed. Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, Vol. 2. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1998:1–20.
Kong, L.; Yeung, E. C. Development of white spruce somatic embryos: II. Continual shoot meristem development during germination. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 28:125–131; 1992.
Liso, R.; Calabrese, G.; Bitonti, M. B.; Arrigoni, O. Relationship between ascorbic acid and cell division. Exp. Cell Res. 150:314–320; 1984.
Liso, R.; Innocenti, A. M.; Bitonti, M. B.; Arrigoni, O. Ascorbic acid-induced progression of quiescent cells from G1 to S phase. New Phytol. 110:469–471; 1988.
Lu, C.-Y.; Thorpe, T. A. Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration in cultured immature embryos of Picea glauca. J. Plant Physiol. 128:297–302; 1987.
Merkle, S. A.; Parrot, W. A.; Williams, E. G. Applications of somatic embryogenesis and embryo cloning. In: Bhojwani, S. S., ed. Plant tissue culture: applications and limitations. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishing, Inc.; 1990:67–101.
Miyake, C.; Asada, K. Thylakoid-bound ascorbate peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts and photoreduction of its primary oxidation product, monodehydroascorbate radicals in the thylakoids. Plant Cell Physiol. 33:541–553; 1992.
Nagmani, R.; Bonga, J. M. Embryogenesis in subcultured callus of Larix decidua. Can. J. For. Res. 15:1088–1091; 1985.
Noctor, G.; Foyer, C. H. Ascorbate and glutathione: keeping active oxygen under control. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Mol. Biol. 49:249–279; 1998.
Quinn, J.; Simon, J. E.; Janick, J. Zygotic and somatic embryos in borage: histology. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 114:516–520; 1989.
Roberts, D. R.; Stutton, B. C.; Flinn, B. S. Synchronous and high frequency germination of interior spruce somatic embryos following partial drying at high relative humidity. Can. J. Bot. 68:1086–1090; 1990.
Smirnoff, N. The function and metabolism of ascorbic acid in plants. Ann. Bot. 78:661–669; 1996.
Tommasi, F.; De Gara, L. Correlazione tra la presenza dell’acido ascorbico e comparsa dell’attivita’ ascorbico perossidasica in embrioni di Avena sativa L. Boll. Soc. Ital. Biol. Sper. 66:357–364; 1990.
Thorpe, T. A. Organogenesis in vitro: structural, physiological, and biochemical aspects. Int. Rev. Cytol. Suppl. 11A:71–111; 1980.
Thorpe, T. A.; Joy, R. W., IV; Leung, D. W. M. Starch turnover in shootforming tobacco callus. Physiol. Plant. 66:58–62; 1986.
Tsao, C. S. An overview of ascorbic acid chemistry and biochemistry. In: Packer, L.; Fuchs, J., ed. Vitamin C in health and disease. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc.; 1997:25–58.
von Arnold, S.; Eriksson, T. In vitro studies on adventitious shoot formation in Pinus contorta. Can. J. Bot. 59:870–874; 1981.
Zar, J. H. Biostatistical analysis. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, Inc.; 1974.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stasolla, C., Yeung, E.C. Ascorbic acid improves conversion of white spruce somatic embryos. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 35, 316–319 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-999-0041-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-999-0041-x