Abstract
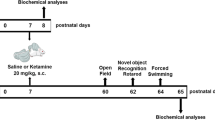
Ketamine is one of general anesthetics and has been commonly used in obstetric and pediatric anesthesia. However, effects of exposure to ketamine on neonatal brain are largely unknown. In this study, we aim to investigate the effect of neonatal exposure of ketamine on spatial memory and long-term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampus of adult rats. One-week-old neonatal rats were separated into ketamine group and control group. Neonatal rats in ketamine group were received intraperitoneal injection of 25 mg/kg (low-dose group, N = 8) or 50 mg/kg ketamine (high-dose group, N = 8). Neonatal Rats in control group received saline injection (N = 8). After 10 weeks, the spatial memory of adult rats was examined by using Morris Water Maze, and LTP in the hippocampus of adult rats was assessed by electrophysiological experiment. We found that exposure of ketamine to neonatal rats, either low-dose or high-dose, had not induced alteration on their adulthood’s escape latency, swimming speed and the percentage of time spent in original quadrant compared with the control. The electrophysiological examination showed that the induction of LTP in hippocampus was significantly reduced in adult rats of ketamine group (either low-dose or high-dose). Our study showed that neonatal exposure of ketamine inhibited the induction of hippocampal LTP without impairing the spatial memory of adult rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akeju O, Davis-Dusenbery BN, Cassel SH, Ichida JK, Eggan K (2014) Ketamine exposure in early development impairs specification of the primary germ cell layers. Neurotoxicol Teratol 43:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ntt.2014.04.001
Bellinger FP, Wilce PA, Bedi KS, Wilson P (2002) Long-lasting synaptic modification in the rat hippocampus resulting from NMDA receptor blockade during development. Synapse 43(2):95–101. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.10020
Berberich S, Jensen V, Hvalby O, Seeburg PH, Kohr G (2007) The role of NMDAR subtypes and charge transfer during hippocampal LTP induction. Neuropharmacology 52(1):77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2006.07.016
Brown EN, Purdon PL, Van Dort CJ (2011) General anesthesia and altered states of arousal: a systems neuroscience analysis. Annu Rev Neurosci 34:601–628. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-060909-153200
Carr ZJ, Torjman MC, Manu K, Dy G, Goldberg ME (2011) Spatial memory using active allothetic place avoidance in adult rats after isoflurane anesthesia: a potential model for postoperative cognitive dysfunction. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 23(2):138–145. https://doi.org/10.1097/ANA.0b013e3182049f19
Chen X, Shu S, Bayliss DA (2009) HCN1 channel subunits are a molecular substrate for hypnotic actions of ketamine. J Neurosci 29(3):600–609. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3481-08.2009
Green SM, Cote CJ (2009) Ketamine and neurotoxicity: clinical perspectives and implications for emergency medicine. Ann Emerg Med 54(2):181–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2008.10.003
Gruart A, Munoz MD, Delgado-Garcia JM (2006) Involvement of the CA3-CA1 synapse in the acquisition of associative learning in behaving mice. J Neurosci 26(4):1077–1087. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2834-05.2006
Huang C, Zhang X, Zheng J, Chen C, Chen Y, Yi J (2014a) Upregulation of miR-137 protects anesthesia-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(8):5000–5007
Huang S, Dai Y, Zhang Z, Hao W, Chen H (2014b) Docosahexaenoic acid intake ameliorates ketamine-induced impairment of spatial cognition and learning ability in ICR mice. Neurosci Lett 580:125–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2014.08.011
Hudetz JA, Iqbal Z, Gandhi SD, Patterson KM, Byrne AJ, Hudetz AG, Warltier DC (2009) Ketamine attenuates post-operative cognitive dysfunction after cardiac surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 53(7):864–872. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2009.01978.x
Ikonomidou C, Bosch F, Miksa M, Bittigau P, Vockler J, Dikranian K, Olney JW (1999) Blockade of NMDA receptors and apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Science 283(5398):70–74
Izumi Y, Zorumski CF (2014) Metaplastic effects of subanesthetic ketamine on CA1 hippocampal function. Neuropharmacology 86:273–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.08.002
Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Hartman RE, Izumi Y, Benshoff ND, Dikranian K, Zorumski CF, Wozniak DF (2003) Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits. J Neurosci 23(3):876–882
Jia Z, Geng L, Xie G, Chu Q, Zhang W (2015) Sevoflurane impairs acquisition learning and memory function in transgenic mice model of Alzheimer’s disease by induction of hippocampal neuron apoptosis. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(9):15490–15497
Liang G, Ward C, Peng J, Zhao Y, Huang B, Wei H (2010) Isoflurane causes greater neurodegeneration than an equivalent exposure of sevoflurane in the developing brain of neonatal mice. Anesthesiology 112(6):1325–1334. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181d94da5
Liu L, Wong TP, Pozza MF, Lingenhoehl K, Wang Y, Sheng M, Wang YT (2004) Role of NMDA receptor subtypes in governing the direction of hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Science 304(5673):1021–1024. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1096615
Lynch MA (2004) Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol Rev 84(1):87–136. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00014.2003
Morgan CJ, Curran HV, Independent Scientific Committee on Drugs (2012) Ketamine use: a review. Addiction 107(1):27–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2011.03576.x
Paule MG, Li M, Allen RR, Liu F, Zou X, Hotchkiss C, Wang C (2011) Ketamine anesthesia during the first week of life can cause long-lasting cognitive deficits in rhesus monkeys. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33(2):220–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ntt.2011.01.001
Ribeiro PO, Silva HB, Tome AR, Cunha RA, Antunes LM (2014a) Hippocampal long-term potentiation in adult mice after recovery from ketamine anesthesia. Lab Anim (NY) 43(10):353–357. https://doi.org/10.1038/laban.571
Ribeiro PO, Tome AR, Silva HB, Cunha RA, Antunes LM (2014b) Clinically relevant concentrations of ketamine mainly affect long-term potentiation rather than basal excitatory synaptic transmission and do not change paired-pulse facilitation in mouse hippocampal slices. Brain Res 1560:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.03.004
Rudolph U, Antkowiak B (2004) Molecular and neuronal substrates for general anaesthetics. Nat Rev Neurosci 5(9):709–720. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1496
Sinner B, Graf BM (2008) Ketamine. Handb Exp Pharmacol 182:313–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74806-9_15
Slikker W Jr, Zou X, Hotchkiss CE, Divine RL, Sadovova N, Twaddle NC, Wang C (2007) Ketamine-induced neuronal cell death in the perinatal rhesus monkey. Toxicol Sci 98(1):145–158. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfm084
Snyder GL, Galdi S, Hendrick JP, Hemmings HC Jr (2007) General anesthetics selectively modulate glutamatergic and dopaminergic signaling via site-specific phosphorylation in vivo. Neuropharmacology 53(5):619–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.07.008
Soriano SG, Liu Q, Li J, Liu JR, Han XH, Kanter JL, Ibla JC (2010) Ketamine activates cell cycle signaling and apoptosis in the neonatal rat brain. Anesthesiology 112(5):1155–1163. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181d3e0c2
Squire LR (1992) Memory and the hippocampus: a synthesis from findings with rats, monkeys, and humans. Psychol Rev 99(2):195–231
Su PH, Chang YZ, Chen JY (2010) Infant with in utero ketamine exposure: quantitative measurement of residual dosage in hair. Pediatr Neonatol 51(5):279–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-9572(10)60054-X
Volianskis A, Bannister N, Collett VJ, Irvine MW, Monaghan DT, Fitzjohn SM, Collingridge GL (2013) Different NMDA receptor subtypes mediate induction of long-term potentiation and two forms of short-term potentiation at CA1 synapses in rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol 591(4):955–972. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2012.247296
Wang DS, Orser BA (2011) Inhibition of learning and memory by general anesthetics. Can J Anaesth 58(2):167–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12630-010-9428-8
Wang C, Slikker W Jr (2008) Strategies and experimental models for evaluating anesthetics: effects on the developing nervous system. Anesth Analg 106(6):1643–1658. https://doi.org/10.1213/ane.ob013e3181732c01
Wang RR, Jin JH, Womack AW, Lyu D, Kokane SS, Tang N, Chen J (2014) Neonatal ketamine exposure causes impairment of long-term synaptic plasticity in the anterior cingulate cortex of rats. Neuroscience 268:309–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.03.029
Williams NR, Schatzberg AF (2016) NMDA antagonist treatment of depression. Curr Opin Neurobiol 36:112–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2015.11.001
Yamamura T, Harada K, Okamura A, Kemmotsu O (1990) Is the site of action of ketamine anesthesia the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor? Anesthesiology 72(4):704–710
Zhao T, Li Y, Wei W, Savage S, Zhou L, Ma D (2014) Ketamine administered to pregnant rats in the second trimester causes long-lasting behavioral disorders in offspring. Neurobiol Dis 68:145–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2014.02.009
Zou X, Patterson TA, Divine RL, Sadovova N, Zhang X, Hanig JP, Wang C (2009) Prolonged exposure to ketamine increases neurodegeneration in the developing monkey brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 27(7):727–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2009.06.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, D., Gan, J., Tan, T. et al. Neonatal exposure of ketamine inhibited the induction of hippocampal long-term potentiation without impairing the spatial memory of adult rats. Cogn Neurodyn 12, 377–383 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-018-9474-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-018-9474-4