Abstract
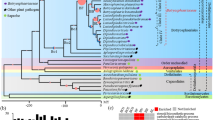
Tristratiperidium microsporum gen. et sp. nov. (Xylariales) is introduced to accommodate a taxon isolated from dead leaves of Arundo plinii, collected in Italy. The sexual and asexual morphs are described and illustrated and compared with similar taxa. Phylogenetic analysis of combined Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) and Large Subunit (LSU) rRNA sequence data show the relationships of T. microsporum with other genera in the Xylariales. Tristratiperidium microsporum clusters with the hyphomycete Subramaniomyces fusisaprophyticus in the order Xylariales, in the clade comprising Apiosporaceae, Hyponectriaceae, Melogrammataceae, and Pseudomassariaceae. The phylogenetic relationships of T. microsporum and allied fungi are discussed and its placement in the Xylariales genera incertae sedis is suggested.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr ME (1990) Podromus to nonlichenized, pyrenomycetous members of class Hymenoascomycetes. Mycotaxon 39:43–184
Bhat DJ, Kendrick B (1993) Twenty-five new conidial fungi from the Western Ghats and the Andaman Islands (India). Mycotaxon 49:19–90
Bhat DJ, Sutton BC (1985) New and interesting hyphomycetes from Ethiopia. Trans Br Mycol Soc 85:107–122
Chomnunti P, Hongsanan S, Aguirre-Hudson B, Tian Q, Peršoh D, Dhami MK, Alias AS, Xu J, Liu X, Stadler M, Hyde KD (2014) The sooty moulds. Fungal Divers 66:1–36. doi:10.1007/s13225-014-0278-5
Daranagama DA, Camporesi E, Tian Q, Liu X, Chamyuang S, Stadler M, Hyde KD (2015) Anthostomella is polyphyletic comprising several genera in Xylariaceae. Fungal Divers 73:203–238. doi:10.1007/s13225-015-0329-6
Duong LM, Lumyong S, Hyde KD, Jeewon R (2004) Emarcea castanopsidicola gen. et sp. nov. from Thailand, a new xylariaceous taxon based on morphology and DNA sequences. Stud Mycol 50:253–260
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh340
Eriksson OE, Baral HO, Currah RS, Hansen K, Kurtzman CP, Rambold G, Laessøe T (2003) Outline of Ascomycota. Myconet 9:1–89
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis. program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hawksworth DL, Lodha BC (1983) Helicogermslita, a new stromatic xylariaceous genus with a spiral germ slit from India. Trans Br Mycol Soc 81:91–96
Hawksworth DL, Kirk P, Sutton BC, Pegler DN (1995) Ainsworth & Bisby’s Dictionary of the Fungi, 8th edn. CAB International, Oxon
Hernandez–Restrepo M, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW (2015) Taxonomic and phylogenetic re-evaluation of Microdochium, Monographella and Idriella. Persoonia 36:57–82. doi:10.3767/003158516X688676
Index Fungorum (2015) http://www.indexfungorum.org/Names/Names.asp. Accessed 26 Aug 2015
Jaklitsch WM, Voglmayr H (2012) Phylogenetic relationships of five genera of Xylariales and Rosasphaeria gen. nov. (Hypocreales). Fungal Divers 52:75–98. doi:10.1007/s13225-011-0104-2
Jayasiri SC, Hyde KD, Ariyawansa HA, Bhat J, Buyck B, Cai L, Dai YC, Abd-Elsalam KA, Ertz D, Hidayat I, Jeewon R, Jones EBG, Bahkali AH, Karunarathna SC, Liu JK, Luangsa-ard JJ, Lumbsch HT, Maharachchikumbura SSN, McKenzie EHC, Moncalvo JM, Ghobad-Nejhad M, Nilsson H, Pang KA, Pereira OL, Phillips AJL, Raspé O, Rollins AW, Romero AI, Etayo J, Selçuk F, Stephenson SL, Suetrong S, Taylor JE, Tsui CKM, Vizzini A, Abdel-Wahab MA, Wen TC, Boonmee S, Dai DQ, Daranagama DA, Dissanayake AJ, Ekanayaka AH, Fryar SC, Hongsanan S, Jayawardena RS, Li WJ, Perera RH, Phookamsak R, de Silva NI, Thambugala KM, Tian Q, Wijayawardene NN, Zhao RL, Zhao Q, Kang JC, Promputtha I (2015) The Faces of Fungi database: fungal names linked with morphology, phylogeny and human impacts. Fungal Divers. doi:10.1007/s13225-015-0351-8
Jong SC, Davis EE (1973) Stromatic Neurosporas. Mycologia 65:458–464
Maharachchikumbura SS, Hyde KD, Jones EBG, McKenzie EHC, Huang SK, Abdel-Wahab MA, Daranagama DA, Dayarathne M, D’souza MJ, Goonasekara ID, Hongsanan S, Jayawardena RS, Kirk PM, Konta S, Liu JK, Liu ZY, Norphanphoun C, Pang KL, Perera RH, Senanayake IC, Shang Q, Shenoy BD, Xiao YP, Bahkali AH, Kang JC, Somrothipol S, Suetrong S, Wen TC, Xu JC (2015) Towards a natural classification and backbone tree for Sordariomycetes. Fungal Divers 72:199–301. doi:10.1007/s13225-015-0331-z
Mani Varghese KI, Rao VG (1980) Forest microfungi. I. Subramaniomyces, a new genus of Hyphomycetes. Kavaka 7:83–85
Müller E, Von Arx JA (1973) Pyrenomycetes: Meliolales, Coronophorales, Sphaeriales. In: Ainsworth GC, Sparrow FK, Sussman AS (eds) The fungi: an advanced treatise. Volume IVA. A taxonomic review with keys: Ascomycetes and Fungi Imperfecti. Academic, London
Munk A (1953) The system of the Pyrenomycetes. Dan Bot Ark 15:1–163
Nylander JAA (2004) MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University, Uppsala
Page RDM (1996) TREEVIEW: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Seifert K, Morgan-Jones G, Gams W, Kendrick B (2011) The Genera of Hyphomycetes. [CBS Biodiversity Series 9]. CBS KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht
Senanayake IC, Maharachchikumbura SSN, Hyde KD, Bhat JD, Jones EBG, Mckenzie EHC, Dai DQ, Daranagama DA, Dayarathne MC, Goonasekara ID, Konta S, Li WJ, Shang QJ, Stadler M, Wijayawardene NN, Xiao YP, Norphanphoun C, Li QR, Liu XZ, Bahkali AH, Kang JC, Wang Y, Wen TC, Xu JC, Camporesi E (2015) Towards unraveling relationships in Xylariomycetidae (Sordariomycetes). Fungal Divers 73:73–144. doi:10.1007/s13225-015-0340-y
Silvestro D, Michalak I (2012) raxmlGUI: a graphical front end for RAxML. Org Divers Evol 12:335–337. doi:10.1007/s13127-011-0056-0
Smith GJD, Liew ECY, Hyde KD (2003) The Xylariales: a monophyletic order containing 7 families. Fungal Divers 13:185–218
Stamatakis A, Alachiotis N (2010) Time and memory efficient likelihood-based tree searches on phylogenomic alignments with missing data. Bioinformatics 26:132–139
Tang AMC, Jeewon R, Hyde KD (2009) A re-evaluation of the evolutionary relationships within the Xylariaceae based on ribosomal and protein-coding gene sequences. Fungal Divers 34:127–155
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Triebel D, Peršoh D, Wollweber H, Stadler M (2005) Phylogenetic relationships among Daldinia, Entonaema and Hypoxylon as inferred from ITS nrDNA sequences. Nova Hedwigia 80:25–3
Zhang N, Castlebury LA, Miller AN, Huhndorf SM, Schoch CL, Seifert KA, Rossman AY, Roger JD, Kohlmeyer J, Sung GH (2006) An overview of the systematics of the Sordariomycetes based on a four-gene phylogeny. Mycologia 98:1076–1087
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the financial support and postgraduate scholarship provided by State Key Laboratory of Mycology, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing and the Mushroom Research Foundation, Chiang Mai, Thailand. The authors gratefully thank Dr. Shaun Pennycook from Landcare Research University of Auckland, New Zealand for nomenclature advice on the proposed names. The authors extend their sincere appreciations to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for its funding this Prolific Research group (PRG-1436-09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Section Editor: Gerhard Rambold
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daranagama, D.A., Camporesi, E., Liu, X.Z. et al. Tristratiperidium microsporum gen. et sp. nov. (Xylariales) on dead leaves of Arundo plinii . Mycol Progress 15, 8 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-015-1151-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-015-1151-y