Abstract
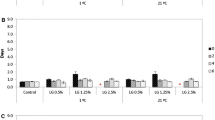
To improve the application of essential oils as natural antimicrobial preservatives, the objective of the present study was to determine physical, antimicrobial, and biophysical properties of eugenol after nanoencapsulation by sodium caseinate (NaCas). Emulsions were prepared by mixing eugenol in 20.0 mg/mL NaCas solution at an overall eugenol content of 5.0–137.9 mg/mL using shear homogenization. Stable emulsions were observed up to 38.5 mg/mL eugenol, which had droplet diameters of smaller than 125 nm at pH 5–9 after ambient storage for up to 30 days. The encapsulated eugenol had similar minimal inhibitory and minimal bactericidal concentrations as free eugenol against Escherichia coli O157:H7 ATCC 43895, Listeria monocytogenes Scott A, and Salmonella Enteritidis but showed better inhibition of E. coli O157:H7 than free eugenol during incubation at 37 °C for 48 h. After 20 min interaction at 21 °C, bacteria treated with encapsulated eugenol had a greater reduction of intracellular ATP and a greater increase of extracellular ATP than free eugenol, suggesting the enhanced permeation of eugenol after nanoencapsulation. However, such overall trend was not observed when examining bacterial morphology and uptake of crystal violet, suggesting the possible membrane adaptation. Findings from this study showed the feasibility of preparing nanoemulsions with high loading of eugenol using NaCas.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Burt, Int. J. Food Microbiol. 94, 223 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.03.022
K. Ziani, Y. Chang, L. McLandsborough, D.J. McClements, J. Agric. Food Chem. 59, 6247 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf200450m
C. Beristain, H. Garcıa, E. Vernon-Carter, LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 34, 398 (2001)
D.A. Rodea-González, J. Cruz-Olivares, A. Román-Guerrero, M.E. Rodríguez-Huezo, E.J. Vernon-Carter, C. Pérez-Alonso, J. Food Eng. 111, 102 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2012.01.020
C. Liolios, O. Gortzi, S. Lalas, J. Tsaknis, I. Chinou, Food Chem. 112, 77 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.05.060
M.-J. Choi, A. Soottitantawat, O. Nuchuchua, S.-G. Min, U. Ruktanonchai, Food Res. Int. 42, 148 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2008.09.011
S. Gaysinsky, T.M. Taylor, P.M. Davidson, B.D. Bruce, J. Weiss, J. Food Prot. 70, 2631 (2007). https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-70.11.2631
Q. Ma, P.M. Davidson, Q. Zhong, Int. J. Food Microbiol. 166, 77 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.06.017
E.N. Frankel, S.-W. Huang, R. Aeschbach, E. Prior, J. Agric. Food Chem. 44, 131 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf950374p
Y. Zhang, Q.X. Zhong, Food Hydrocoll 33, 1 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.02.009
K. Pan, Q. Zhong, S.J. Baek, J. Agric. Food Chem. 61, 6036 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf400752a
H.Q. Chen, Y. Zhang, Q.X. Zhong, J. Food Eng. 144, 93 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2014.07.021
J. Xue, Q. Zhong, J. Agric. Food Chem. 62, 9900 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5034366
K. Pan, H. Chen, P.M. Davidson, Q. Zhong, J. Agric. Food Chem. 62, 1649 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf4055402
K.P. Devi, S.A. Nisha, R. Sakthivel, S.K. Pandian, J. Ethnopharmacol. 130, 107 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2010.04.025
H. Chen, P.M. Davidson, Q. Zhong, App. Environ. Microbiol. 80, 907 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03010-13
M. Oussalah, S. Caillet, M. Lacroix, J. Food Prot. 69, 1046 (2006). https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-69.5.1046
M. Srinivasan, H. Singh, P.A. Munro, J. Agric. Food Chem. 44, 3807 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf960135h
NIST. NIST WEBbook (http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry), last Accessed on Dec. 6, 2017
N. Terjung, M. Loffler, M. Gibis, J. Hinrichs, J. Weiss, Food Funct. 3, 290 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2FO10198J
S.F. Hosseini, M. Zandi, M. Rezaei, F. Farahmandghavi, Carbohydr. Polym. 95, 50 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.02.031
K. Pan, Y. Luo, Y. Gan, S.J. Baek, Q. Zhong, Soft Matter 10, 6820 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4SM00239C
R. van der Lee et al., Chem. Rev. 114, 6589 (2014)
H. Bouzid, M. Rabiller-Baudry, L. Paugam, F. Rousseau, Z. Derriche, N.E. Bettahar, J. Membrane Sci. 314, 67 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2008.01.028
E. Dickinson, Food Hydrocoll 23, 1473 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2008.08.005
S. Hemaiswarya, M. Doble, Phytomedicine 16, 997 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2009.04.006
K. Knobloch, A. Pauli, B. Iberl, H. Weigand, N. Weis, J. Essent. Oil Res. 1, 119 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1080/10412905.1989.9697767
A. Gill, R. Holley, Int. J. Food Microbiol. 108, 1 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.10.009
M. Rohmer, in Comprehensive natural products II: Chemistry and Biology, edited by L. Mander, and H.-W. Liu (Newnes, 2010), pp. 517
X. Hui, G. Yan, F.-L. Tian, H. Li, W.-Y. Gao, Med. Chem. Res. 26, 442 (2016)
H.A. Bladen, S.E. Mergenhagen, J. Bacteriol. 88, 1482 (1964)
M. Kong, X.G. Chen, K. Xing, H.J. Park, Int. J. Food Microbiol. 144, 51 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.09.012
J. Xue, P.M. Davidson, Q. Zhong, Int. J. Food Microbiol. 210, 1 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.06.003
T. Ohta, K. Nagano, M. Yoshida, P. Natl, Acad. Sci. 83, 2071 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.83.7.2071
J.-Y. Lee, Y.-S. Kim, D.-H. Shin, J. Agric. Food Chem. 50, 2193 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf011175a
J. Sikkema, J. De Bont, B. Poolman, Microbiol. Rev. 59, 201 (1995)
P.D. Cani, A. Everard, Trend. Endocrinol. Met. 26, 273 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2015.03.009
R.V. Stahelin, W. Cho, Biochemistry 40, 4672 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0020325
M. Sokolovski, T. Sheynis, S. Kolusheva, R. Jelinek, BBA-Biomembranes 1778, 2341 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.07.001
T. Hira, H. Hara, F. Tomita, Y. Aoyama, Exp. Biol. Med. 228, 850 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1177/15353702-0322807-11
F. Nazzaro, F. Fratianni, L. De Martino, R. Coppola, V. De Feo, Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 6, 1451 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6121451
Y.M. Zhang, C.O. Rock, Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 222 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1839
R.Y. Chiou, R.D. Phillips, P. Zhao, M.P. Doyle, L.R. Beuchat, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 2204 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.4.2204-2210.2004
F. Foglia, A.F. Drake, A.E. Terry, S.E. Rogers, M.J. Lawrence, D.J. Barlow, BBA-Biomembranes 1808, 1574 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.02.012
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank Dr. Yangchao Luo for assisting SEM experiments. This work was supported by The University of Tennessee, the USDA NIFA Hatch Project 223984 and TEN02010-03476, and Dairy Research Institute (Rosemont, IL, USA). Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the view of the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 215 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Pan, K. & Zhong, Q. Eugenol Nanoencapsulated by Sodium Caseinate: Physical, Antimicrobial, and Biophysical Properties. Food Biophysics 13, 37–48 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-017-9509-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-017-9509-0