Abstract
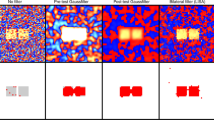
With the rapid development of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) technology, the spatial resolution of fMRI data is continuously growing. This provides us the possibility to detect the fine-scale patterns of brain activities. The established univariate and multivariate methods to analyze fMRI data mostly focus on detecting the activation blobs without considering the distributed fine-scale patterns within the blobs. To improve the sensitivity of the activation detection, in this paper, multivariate statistical method and univariate statistical method are combined to discover the fine-grained activity patterns. For one voxel in the brain, a local homogenous region is constructed. Then, time courses from the local homogenous region are integrated with multivariate statistical method. Univariate statistical method is finally used to construct the interests of statistic for that voxel. The approach has explicitly taken into account the structures of both activity patterns and existing noise of local brain regions. Therefore, it could highlight the fine-scale activity patterns of the local regions. Experiments with simulated and real fMRI data demonstrate that the proposed method dramatically increases the sensitivity of detection of fine-scale brain activity patterns which contain the subtle information about experimental conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogawa S, Lee T, Kay A, et al. Brain magnetic resonance imaging with contrast dependent on blood oxygenation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1990, 87(24): 9868–9872
Kwong K, Belliveau J, Chesler D, et al. Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of human brain activity during primary sensory stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1992, 89(12): 5675–5679
Petersson K, Nichols T, Poline J, et al. Statistical limitations in functional neuroimaging I. non-inferential methods and statistical models. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 1999, 354(1387): 1240–1260
Petersson K, Nichols T, Poline J, et al. Statistical limitations in functional neuroimaging II, signal detection and statistical inference. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 1999, 354(1387): 1261–1281
Friston K, Holmes A, Worsley K, et al. Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: A general linear approach. Hum Brain Mapp, 1995, 2(4): 189–210
Friston K, Holmes A, Poline J, et al. Analysis of fMRI time-series revisited. NeuroImage, 1995, 2(1): 45–53
Friston K, Josephs O, Zarahn E, et al. To smooth or not to smooth? Bias and efficiency in fMRI time-series analysis. NeuroImage, 2000, 12(2): 196–208
Kriegeskorte N, Goebel R, Bandettini P. Information-based functional brain mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2006, 103(10): 3863–3868
Bandettini P. Functional MRI today. Int J Psychophysiol, 2007, 63(2): 138–145
Friston K, Frith C, Liddle P, et al. Functional connectivity: The principal component analysis of large (PET) data sets. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 1993, 13(1): 5–14
McKeown M, Makeig S, Brown G, et al. Analysis of fMRI data by blind separation into independent spatial components. Hum Brain Mapp, 1998, 6(3): 160–188
Formisano E, Esposito F, Kriegeskorte N, et al. Spatial independent component analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging time-series: characterization of the cortical components. Neurocomputing, 2002, 49(1–4): 241–254
Calhoun V, Adali T, Pearlson G, et al. Spatial and temporal independent component analysis of functional MRI data containing a pair of task-related waveforms. Hum Brain Mapp, 2001, 13(1): 43–53
Duann J, Jung T, Kuo W, et al. Single-trial variability in event-related BOLD signals. NeuroImage, 2002, 15(4): 823–835
Strother S, Anderson J, Hansen L, et al. The quantitative evaluation of functional neuroimaging experiments: the NPAIRS data analysis framework. NeuroImage, 2002, 15(4): 747–771
Turner R. How much cortex can a vein drain? Down stream dilution of activation-related cerebral blood oxygenation changes. NeuroImage, 2002, 16(4): 1062–1067
Andersen A H, Gash D M, Avison M J. Principal component analysis of the dynamic response measured by fMRI: A generalized linear systems framework. Magn Reson Imaging, 1999, 17(6): 795–815
Worsley K, Poline J, Friston K, et al. Characterizing the response of PET and fMRI data using multivariate linear models. NeuroImage, 1998, 6(4): 305–319
McIntosh A, Chau W, Protzner A. Spatiotemporal analysis of event-related fMRI data using partial least squares. NeuroImage, 2004 23(2): 764–775
Tononi G, McIntosh A, Russell D, et al. Functional clustering: identifying strongly interactive brain regions in neuroimaging data. NeuroImage, 1998, 7(2): 133–149
Katanoda K, Matsuda Y, Sugishita M, et al. A spatial-temporal regression model for the analysis of functional MRI data. NeuroImage, 2002, 17(3): 1415–1428
Zang Y, Jiang T, Lu Y, et al. Regional homogeneity approach to fMRI data analysis. NeuroImage, 2004, 22(1): 394–400
Morel J, Solimini S. Variational Methods in Image Segmentation. Basel: Birkhauser Publishing, Inc, 1995
Lu Y, Jiang T, Zang Y, et al. Region growing method for the analysis of functional MRI data. NeuroImage, 2003, 20(1): 455–465
Bellec P, Perlbarg V, Jbabdi S, et al. Identification of large-scale networks in the brain using fMRI. NeuroImage, 2006, 29(4): 1231–1243
Friston K J, Fletcher P, Josephs O, et al. Event-related fMRI: characterizing differential responses. NeuroImage, 1998, 7(1): 30–40
Langer N. Tutorial in biostatistics: statistical approaches to human brain mapping by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Stat Med, 1996, 15(4): 389–428
Sorenson J, Wang X. ROC methods for evaluation of fMRI techniques. Magn Reson Med, 1996, 36(5): 737–744
Skudlarski P, Constable R T, Gore J C. ROC analysis of statistical methods used in functional MRI: individual subjects. NeuroImage, 1999, 9(3): 311–329
Nichols T, Holmes A. Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: a primer with examples. Hum Brain Mapp, 2000, 15(1): 1–25
Efron B, Tibshirani R. An Introduction to the Bootstrap. New York: Chapman Hall, 1993. 202–219
Genovese C, Lazar N, Nichols T. Thresholding of statistical maps in functional neuroimaging using the false discovery rate. NeuroImage, 2002, 15(4): 870–878
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Chair Professors of Changjiang Scholars Program and CAS Hundred Talents Program, National Program on Key Basic Research Projects (Grant No. 2006CB705700), National High-Tech R&D Program of China (Grant No.2006AA04Z216), National Key Technology R&D Program (Grant No. 2006BAH02A25), Joint Research Fund for Overseas Chinese Young Scholars (Grant No.30528027), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.30600151, 30500131 and 60532050), and Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (Grant Nos. 4051002 and 4071003)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhen, Z., Tian, J. & Zhang, H. Adaptive integration of local region information to detect fine-scale brain activity patterns. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 51, 1980–1989 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0124-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0124-7