Abstract
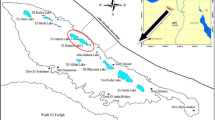
Metal-contaminated sediments in lakes is a global concern that poses toxicological risk to aquatic organisms. This study performed bioassays using the submerged macrophyte, Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara, exposed to contaminated sediments collected from five locations in Dianchi Lake, Yunnan, China. Among the sediments collected, Igeo showed enrichment of As and Cd in Dianchi Lake sediments. In spite of enriched toxic metals at some locations, laboratory bioassays found no significant difference in leaf biomass or leaf photosynthesis rate between the sites. Root biomass and root activity showed significant differences between locations and were negatively correlated with the concentration of As, Cd, Hg, and Pb in sediment but not related to Cr. The above correlations were strongest for Hg and As, respectively. Accumulation of Cd and Pb to leaves of bioassay plants was observed, but this was not evident for As and Cr. Overall, the results indicate that V. natans can be used as a bioassay organism and measures of root toxicity are sensitive to metal concentrations present in Dianchi Lake sediments. Furthermore, the study species holds promise for use as a biomonitor of Cd and Pb sediment metal content.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
11 December 2019
The correct name of the 9th Author is shown in this paper.
11 December 2019
The correct name of the 9th Author is shown in this paper.
References
Al ME, Kaiser K, Williams JR, Dellapenna TM, Louchouarn P, Santschi PH (2018) Centennial record of anthropogenic impacts in Galveston Bay: evidence from trace metals (Hg, Pb, Ni, Zn) and lignin oxidation products. Environ Pollut 237:887–899
Ali B, Vajpayee P, Tripathi RD, Rai UN, Kumar A, Singh N, Behl HM, Singh SP (2000) Mercury bioaccumulation induces oxidative stress and toxicity to submerged Macrophyte Potamogeton crispus L. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 65:573–582
Alloway BJ (2013) Heavy metals in soils: trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability. Springer
Andresen E, Mattusch J, Wellenreuther G, Thomas G, Arroyo Abad U, Kupper H (2013a) Different strategies of cadmium detoxification in the submerged macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum L. Metallomics 5:1377–1386
Andresen E, Opitz J, Thomas G, Stark HJ, Dienemann H, Jenemann K, Dickinson BC, Kupper H (2013b) Effects of Cd & Ni toxicity to Ceratophyllum demersum under environmentally relevant conditions in soft & hard water including a German lake. Aquat Toxicol 142-143:387–402
Andresen E, Kappel S, Stark HJ, Riegger U, Borovec J, Mattusch J, Heinz A, Schmelzer CE, Matouskova S, Dickinson B, Kupper H (2016) Cadmium toxicity investigated at the physiological and biophysical levels under environmentally relevant conditions using the aquatic model plant Ceratophyllum demersum. New Phytol 210:1244–1258
Arts GH, Belgers JD, Hoekzema CH, Thissen JT (2008) Sensitivity of submersed freshwater macrophytes and endpoints in laboratory toxicity tests. Environ Pollut 153:199–206
ATSDR Agency for Toxic Substance and Disease Registry (2017) Substance priority list. https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/spl/index.html. Access 18 March 2019
Bakhat HF, Zia Z, Fahad S, Abbas S, Hammad HM, Shahzad AN, Abbas F, Alharby H, Shahid M (2017) Arsenic uptake, accumulation and toxicity in rice plants: possible remedies for its detoxification: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:9142–9158
Chen J, Hu X, Cao T, Zhang X, Xi Y, Wen X, Su H, de Silva W, Zhu T, Ni L, Xie P (2017) Root-foraging behavior ensures the integrated growth of Vallisneria natans in heterogeneous sediments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:8108–8119
Cheng C (2017) The distribution of heavy metals in Dianchi Lake and ecological risk assessment. Yunnan University, Kunming
Cheng H, Li M, Zhao C, Yang K, Li K, Peng M, Yang Z, Liu F, Liu Y, Bai R, Cui Y, Huang Z, Li L, Liao Q, Luo J, Jia S, Pang X, Yang J, Yin G (2015) Concentrations of toxic metals and ecological risk assessment for sediments of major freshwater lakes in China. J Geochem Explor 157:15–26
CNSMC China National Standardization Management Committee, GAQSIQ General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (2007) The specification for marine monitoring - part 6: organism analysis (GB17378.6–2007), China
Concas S, Ardau C, Bonito MD, Lattanzi P, Vacca A (2015) Field sampling of soil pore water to evaluate the mobile fraction of trace elements in the Iglesiente area (SW Sardinia, Italy). J Geochem Explor 158:82–94
Coquery M, Welbourn P (1994) Mercury uptake from contaminated water and sediment by the rooted and submerged aquatic macrophyte Eriocaulon septangulare. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 26:335–341
Eckley CS, Luxton TP, Goetz J, Mckernan J (2017) Water-level fluctuations influence sediment porewater chemistry and methylmercury production in a flood-control reservoir. Environ Pollut 222:32–41
EPD EPD (2012) Soil-determination of total phosphorus by alkali fusion-Mo-Sb anti spectrophotometric method (HJ632-2011), China, 1–8 pp
EPD EPD (2014) Soil quality - determination of total nitrogen - modified Kjeldahl method (HJ717–2014), China
Ghrefat HA, Aburukah Y, Rosen MA (2011) Application of geoaccumulation index and enrichment factor for assessing metal contamination in the sediments of Kafrain Dam, Jordan. Environ Monit Assess 178:95–109
Giddings JM, Arts G, Hommen U (2013) The relative sensitivity of macrophyte and algal species to herbicides and fungicides: an analysis using species sensitivity distributions. Integr Environ Assess Manag 9:308–318
Gu J, Xu Z, Jin H, Ning X, He H, Yu J, Jeppesen E, Li K (2016) Response of Vallisneria natans to increasing nitrogen loading depends on sediment nutrient characteristics. Water 8:563
Guilizzoni P (1991) The role of heavy metals and toxic materials in the physiological ecology of submersed. Aquat Bot 41:87–109
Gupta M, Chandra P (1994) Lead accumulation and toxicity in Vallisneria spiralis (L.) and Hvdrilla vertieillata (lf) Royle. J Environ Sci Health A 29:503–516
Gupta M, Chandra P (1998) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of mercury in rooted-submerged macrophyte Vallisneria spiralis. Environ Pollut 103:327–333
Gupta M, Tripathi BD, Rai PK, Chandra P (1998) Role of glutathione and phytochelatin in Hydrilla verticillata (I.f.) Royle and Vallisneria spiralis L. under mercury stress. Chemosphere 37:785–800
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Jiang HS, Zhang Y, Yin L, Li W, Jin Q, Fu W, Zhang T, Huang W (2018) Diurnal changes in photosynthesis by six submerged macrophytes measured using fluorescence. Aquat Bot 149:33–39
Juncos R, Campbell L, Arcagni M, Daga R, Rizzo A, Arribere M, Ribeiro Guevara S (2017) Variations in anthropogenic silver in a large Patagonian lake correlate with global shifts in photographic processing technology. Environ Pollut 223:685–694
Khan I, Ahmad A, Iqbal M (2009) Modulation of antioxidant defence system for arsenic detoxification in Indian mustard. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:626–634
Kroflic A, Germ M, Golob A, Stibilj V (2018) Does extensive agriculture influence the concentration of trace elements in the aquatic plant Veronica anagallis aquatica? Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 150:123–128
Lai WL, Zhang Y, Chen ZH (2012) Radial oxygen loss, photosynthesis, and nutrient removal of 35 wetland plants. Ecol Eng 39:24–30
Lewis MA (1995) Use of freshwater plants for phytotoxicity testing: a review. Environ Pollut 87:19–336
Lewis M, Thursby G (2018) Aquatic plants: test species sensitivity and minimum data requirement evaluations for chemical risk assessments and aquatic life criteria development for the USA. Environ Pollut 238:270–280
Li HB, Yu S, Li GL, Deng H, Xu B, Ding J, Gao JB, Hong YW, Wong MH (2013) Spatial distribution and historical records of mercury sedimentation in urban lakes under urbanization impacts. Sci Total Environ 445-446:117–125
Li B, Gu B, Yang Z, Zhang T (2018a) The role of submerged macrophytes in phytoremediation of arsenic from contaminated water: a case study on Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:224–231
Li Y, Zhou S, Zhu Q, Li B, Wang J, Wang C, Chen L, Wu S (2018b) One-century sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution in western Taihu Lake, China. Environ Pollut 240:709–716
Liu H, Cao Y, Li W, Zhang Z, Jeppesen E, Wang W (2017) The effects of cadmium pulse dosing on physiological traits and growth of the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria spinulosa and phytoplankton biomass: a mesocosm study. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:15308–15314
Lv S, Yang B, Kou Y, Zeng J, Wang R, Xiao Y, Li F, Lu Y, Mu Y, Zhao C (2018) Assessing the difference of tolerance and phytoremediation potential in mercury contaminated soil of a non-food energy crop, Helianthus tuberosus L. (Jerusalem artichoke). Peer J 6:1–18
Macdonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Mallick N, Mohn FH (2003) Use of chlorophyll fluorescence in metal-stress research: a case study with the green microalga Scenedesmus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 55:64–69
Manahan SE, Manahan SE (2001) Fundamentals of environmental chemistry. Lewis Publishers 163-163 pp
NFB NFB (1999) Determination of organic matter in forest soil and calculatin carbon-nitrogen ratio, pp 1–4
Peng K, Luo C, Lou L, Li X, Shen Z (2008) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals by the aquatic plants Potamogeton pectinatus L. and Potamogeton malaianus Miq. and their potential use for contamination indicators and in wastewater treatment. Sci Total Environ 392:22–29
Qian Y, Gallagher FJ, Feng H, Wu M (2012) A geochemical study of toxic metal translocation in an urban brownfield wetland. Environ Pollut 166:23–30
Qian Y, Gallagher FJ, Feng H, Wu M, Zhu Q (2014) Vanadium uptake and translocation in dominant plant species on an urban coastal brownfield site. Sci Total Environ 476-477:696–704
Qian Y, Gallagher F, Deng Y, Wu M, Feng H (2017) Risk assessment and interpretation of heavy metal contaminated soils on an urban brownfield site in New York metropolitan area. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:23549–23558
Richter AK, Frossard E, Brunner I (2007) Polyphenols in the woody roots of Norway spruce and European beech reduce TTC. Tree Physiol 27:155–160
Saygideger S, Dogan M (2004) Lead and cadmium accumulation and toxicity in the presence of EDTA in Lemna minor L. and Ceratophyllum demersum L. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 73:182–189
Shao X (2003) Study of spatial distribution of heavy metal element in the sediment of Dianchi Lake, Yunnan, Nanjing Normal University
Shri M, Kumar S, Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK, Mallick S, Misra P, Shukla D, Mishra S, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD, Tuli R (2009) Effect of arsenic on growth, oxidative stress, and antioxidant system in rice seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1102–1110
Singh KP, Mohan D, Sinha S, Dalwani R (2004) Impact assessment of treated/untreated wastewater toxicants discharged by sewage treatment plants on health, agricultural, and environmental quality in the wastewater disposal area. Chemosphere 55:227–255
Sivaci A, Sivaci ER, Sokmen M (2007) Changes in antioxidant activity, total phenolic and abscisic acid constituents in the aquatic plants Myriophyllum spicatum L. and Myriophyllum triphyllum Orchard exposed to cadmium. Ecotoxicology 16:423–428
Soana E, Naldi M, Bartoli M (2012) Effects of increasing organic matter loads on pore water features of vegetated ( Vallisneria spiralis L.) and plant-free sediments. Ecol Eng 47:141–145
Tamas L, Zelinova V (2017) Mitochondrial complex II-derived superoxide is the primary source of mercury toxicity in barley root tip. J Plant Physiol 209:68–75
Tripathi RD, Singh R, Tripathi P, Dwivedi S, Chauhan R, Adhikari B, Trivedi PK (2014) Arsenic accumulation and tolerance in rootless macrophyte Najas indica are mediated through antioxidants, amino acids and phytochelatins. Aquat Toxicol 157:70–80
Wang J, Yu D (2007) Influence of sediment fertility on morphological variability of Vallisneria spiralis L. Aquat Bot 87:127–133
Wang C, Sun Q, Wang L (2009) Cadmium toxicity and phytochelatin production in a rooted-submerged macrophyte Vallisneria spiralis exposed to low concentrations of cadmium. Environ Toxicol 24:271–278
Wang Z, Yao L, Liu G, Liu W (2014) Heavy metals in water, sediments and submerged macrophytes in ponds around the Dianchi Lake, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 107:200–206
Xing W, Wu H, Hao B, Liu G (2013) Metal accumulation by submerged macrophytes in eutrophic lakes at the watershed scale. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:6999–7008
Xing W, Bai G, Wu H, Liu H, Liu G (2017) Effect of submerged macrophytes on metal and metalloid concentrations in sediments and water of the Yunnan Plateau lakes in China. J Soils Sediments 17:2566–2575
Yang J, Chen L, Steele JC, Chen RS, Meng XZ (2016) An extended study on historical mercury accumulation in lake sediment of Shanghai: the contribution of socioeconomic driver. Environ Pollut 219:612–619
Yi Y, Yang Z, Zhang S (2011) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ Pollut 159:2575–2585
Zhang X, Huang G, Bian X, Zhao Q (2013) Effects of root interaction and nitrogen fertilization on the chlorophyll content, root activity, photosynthetic characteristics of intercropped soybean and microbial quantity in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil Environ 59:80–88
Zhao P, Zhu Y, Wang W (2010) Evaluation and improvement of spectrophotometric assays of TTC reduction: maize (Zea mays) embryo as an example. Acta Physiol Plant 32:815–819
Zheng N, Wang Q, Liang Z, Zheng D (2008) Characterization of heavy metal concentrations in the sediments of three freshwater rivers in Huludao City, Northeast China. Environ Pollut 154:135–142
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Professor Nanlan Peng for metal analysis.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Joint Grant of Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department – Yunnan University Major Project (2018FY001-007), the National Natural Science Foundation of China for Young Scientist (Grant No. 3170040), and the Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Yunnan for Young Scientist (Grant No. 2017FD066) and Yunnan Science and Technology Major Project (2018BC002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, Y., Cheng, C., Drouillard, K. et al. Bioaccumulation and growth characteristics of Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara after chronic exposure to metal-contaminated sediments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 20510–20519 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05347-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05347-z