Abstract
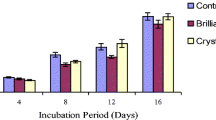
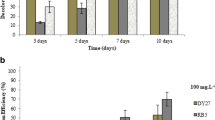
Synthetic textile dyes are among the most dangerous chemical pollutants released in industrial wastewater streams. Recognizing the importance of reducing the environmental impact of these dyes, the ability of the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium to decolorize various textile dyes was investigated. This fungus decolorized 6 of the 14 structurally diverse dyes with varying efficiency (between 14% and 52%). There was no discernable pattern of decolorization even among dyes of the same chemical class, suggesting that attack on the dyes is relatively non-specific. Among the three dyes which showed >40% decolorization, Victoria Blue B (VB) was chosen for further analysis because the ability of the fungus to decolorize VB was nearly independent over a relatively broad concentration range. Blocking lignin peroxidase (LiP) and manganese peroxidase (MnP) production by the fungus did not substantially affect VB decolorization. Inhibition of laccase production by adding various inhibitors to shaken cultures reduced VB decolorization significantly suggesting a role for laccase in VB decolorization. When sodium azide and aminotriazole were used to inhibit endogenous catalase and cytochrome P-450 oxygenase activities, there was 100% and 70% reduction in VB decolorization, respectively. Adding benzoate to trap hydrogen peroxide-derived hydroxyl radicals resulted in 50% decolorization of VB. Boiling the extracellular fluid (ECF) for 30 min resulted in approximately 50% reduction in VB decolorization. Collectively, these data suggest that laccase, and/or oxygenase/oxidase and a heat-stable non-enzymatic factor, but not Lip and MnP, play a role in VB decolorization by P. chrysosporium.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosio ST, Camposakaki GM (2004) Decolorization of reactive azo dyes by Cunninghamella elegans UCP 542 under co-metabolic conditions. Bioresour Technol 91:69–75. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(03)00153-6
Asad S, Amoozegar MA, Pourbabaee AA, Sarbolouki MN, Dastgheib SMM (2007) Decolorization of textile azo dyes by newly isolated halophilic and halotolerant bacteria. Bioresour Technol 98:2082–2088. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.08.020
Banat IM, Nigam P, Singh D, Marchant R (1996) Microbial decolorization of textile-dye containing effluents: a review. Bioresour Technol 58:217–227. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(96)00113-7
Boer CG, Obici L, de Souza CGM, Peralta RM (2004) Decolorization of synthetic dyes by solid state cultures of Lentinula (Lentinus)edodes producing manganese peroxidase as the main ligninolytic enzyme. Bioresour Technol 94:107–112. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2003.12.015
Bonomi F, Kurtz DM, Cui X (1996) Ferroxidase activity of recombinant Desulfovibrio vulgaris rubrerythrin. J Biol Inorg Chem 1:67–72. doi:10.1007/s007750050024
Brandao RL, Castro IM, Passos JB, Nicoli JR, Theveleinen JM (1992) Glucose-induced activation of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase in Fusarium oxysporum. J Genet Microbiol 138:1579–1586
Chen KC, Wu JY, Liou DJ, Hwang SCJ (2003) Decolorization of the textile azo dyes by newly isolated bacterial strains. J Biotechnol 101:57–68. doi:10.1016/S0168-1656(02)00303-6
Dittmer JK, Patel NJ, Dhawale SW, Dhawale SS (1997) Production of multiple laccase isoforms by Phanerochaete chrysosporium grown under nutrient sufficiency. FEMS Microbiol Lett 149:65–70. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1997.tb10309.x
D’Souza TM, Merritt CS, Reddy CA (1999) Lignin-modifying enzymes of the white rot basidiomycete Ganoderma lucidum. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5307–5313
Fabbrini M, Galli C, Gentili P (2002) Comparing the catalytic efficiency of some mediators of laccase. J Mol Catal B Enzym 16:231–240
Forney LJ, Reddy CA, Tien M, Aust SD (1982) The involvement of hydroxyl radical derived from hydrogen peroxide in lignin degradation by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Biol Chem 257(19):11455–11462
Garzillo AMV, Colao MC, Caruso C, Caporale C, Celletti D, Buonocore V (1998) Laccase from white-rot fungus Trametes trogii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49:545–551. doi:10.1007/s002530051211
Hou H, Zhou J, Wang J, Du C, Yan B (2004) Enhancement of laccase production by Pleurotus ostreatus and its use for the decolorization of anthraquinone dye. Process Biochem 39:1415–1419. doi:10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00267-X
Kapdan IK, Kargi F, McMullan G, Marchant R (2000) Effect of environmental conditions on biological decolorization of textile dyestuff by C. versicolor. Enzyme Microb Technol 36:381–387. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(99)00168-4
Marco-Urrea E, Gabarrell X, Sarra M, Caminal G, Vicent T, Reddy CA (2006) Novel aerobic perchloroethylene degradation by the white rot fungus, Trametes versicolor. Environ Sci Technol 40:7796–7802
Marco-Urrea E, Parella T, Gabarrell X, Caminal G, Vicent T, Reddy CA (2008) Mechanistics of trichloroethylene mineralization by the white rot fungus, Trametes versicolor. Chemosphere 70:404–410. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.06.074
Michel FC, Dass SB, Grulke EA, Reddy CA (1991) Role of manganese peroxidases and lignin peroxidases of Phanerochaete chrysosporium in the decolorization of Kraft bleach plant effluent. Appl Environ Microbiol 57(8):2368–2375
Miranda MP, Benito GG, San cristobal N, Nieto CH (1996) Color elimination from molasses wastewater by Aspergillus niger. Bioresour Technol 57:229–235. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(96)00048-X
Mishra SS, Bisaria VS (2006) Production and characterization of laccase from Cyathus bulleri and its use in decolourization of recalcitrant dyes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:646–653. doi:10.1007/s00253-005-0206-4
Palmieri G, Giardina P, Bianco C, Fontanella B, Sannia G (2000) Copper induction of laccase isoenzymes in the ligninolytic fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(3):920–924. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.3.920-924.2000
Raghkumar C, D’Souza TM, Thorn RG, Reddy CA (1999) Lignin-modifying enzymes of Flavodon flavus, a basidiomycete isolated from a coastal marine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(5):2103–2111
Rodriguez CS, Santro R, Cameselle C, Sanroman A (1997) Laccase production in semi-solid cultures of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Biotechnol Lett 19:995–998. doi:10.1023/A:1018495216946
Srinivasan C, D’souza T, Boominathan K, Reddy CA (1995) Demonstration of laccase in the white rot basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium BKM-F-1767. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:4274–4277
Toh YC, Yen JJL, Obbard JP, Ting YP (2003) Decolorisation of azo dyes by white-rot fungi (WRF) isolated in Singapore. Enzyme Microb Technol 33:569–575. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(03)00177-7
Xu F (1996) Oxidation of phenols, anilines, and benzenethiols by fungal Laccases: correlation between activity and redox potentials as well as halide inhibition. Biochemistry 35:7608–7614. doi:10.1021/bi952971a
Yesilada O, Asma D, Cing S (2003) Decolorization of textile dyes by fungal pellets. Process Biochem 38:933–938. doi:10.1016/S0032-9592(02)00197-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gomaa, O.M., Linz, J.E. & Reddy, C.A. Decolorization of Victoria blue by the white rot fungus, Phanerochaete chrysosporium . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24, 2349–2356 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9750-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9750-2