Abstract
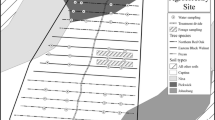
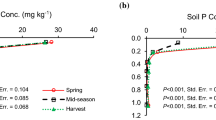
Long-term application of manure can lead to phosphorus accumulation in the soil and increase the risk of P delivery to tile drainage waters. A long-term study (1998–2009) was conducted on eight tile-drained field plots, ranging in size from 0.19 to 0.47 ha, to investigate the effects of long-term surface application of poultry manure on soil phosphorus dynamics and PO4-P loss in tile drainage in Iowa under a corn-soybean rotation system. The experimental treatments included two poultry manure treatments, applied on an N basis at target rates of 168 kg N ha−1 (PM) and 336 kg N ha−1 (PM2), each with three replications, and one chemical fertilizer treatment of urea ammonium nitrate (UAN) at a rate of 168 kg N ha−1 with two replications. Actual manure application rates and estimated plant available N (PAN) varied annually. Bray1-P methods were used to analyze deep core soil samples at five depths (0–15, 15–30, 30–60, 60–90, and 90–120 cm), which were collected in the spring and fall on the half of each plot planted to corn. Tile drainage samples were collected from each actively draining plot equipped throughout the spring and fall drainage season each year, and PO4-P concentrations were analyzed. The results of this study indicated PM2 and PM resulted in a statistically significant increase in topsoil P at 0–30 cm, with no significant movement of P to deeper soil depths. Although an increase in topsoil P levels was observed with poultry manure application, average annual tile drainage P concentrations were not statistically different throughout the study with average PO4-P concentrations of 0.019 ppm with PM2 application and 0.011 and 0.012 ppm for PM and UAN, respectively. Poultry manure application at agronomical recommended application rates may be an environmentally sound fertilizer option for tile drained fine-loamy, calcareous soils under a corn-soybean rotation. However, surface runoff was not evaluated in this study, and high P levels in topsoil could contribute to elevated PO4-P runoff losses.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, P. L., Daniel, T. C., Edwards, D. R., Nichols, D. J., Pote, D. H., & Scott, H. D. (1994). Poultry litter and manure contributions to nitrate leaching through the vadose zone. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 58, 1206–1211.
Addiscott, T. M., Brockie, D., Catt, J. A., Christian, D. G., Harris, G. L., Howse, K. R., Mirza, N. A., & Pepper, T. J. (2000). Phosphate losses through field drains in a heavy cultivated soil. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29, 522–532.
Allen, B. L., & Mallarino, A. P. (2006). Relationships between extractable soil phosphorus and phosphorus saturation after long-term fertilizer or manure application. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 70, 454–463.
American Society of Agricultural Engineers. (2005). ASAE Standard. Manure production and characteristics. D384.2. http://elibrary.asabe.org/standards.asp.
Baker, J. L., & Johnson, H. P. (1981). Nitrate-nitrogen in tile drainage as affected by fertilization. Journal of Environmental Quality, 10, 519–522.
Baker, J. L., Melvin, S. W., Lemke, D. W., Lawlor, P. A., Crumpton, W. G., & Helmers, M. J. (2004). Subsurface drainage in Iowa and the water quality benefits and problem. InProc. 8th Intl. Symp.: Drainage VIII. ASAE Paper No. 701P0304. St. Joseph, Mich.: ASAE.
Bakhsh, A., Kanwar, R. S., & Baker, J. L. (2010). N-application methods and precipitation pattern effects on subsurface drainage nitrate losses and crop yields. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 212, 65–76.
Beauchemin, S., Simard, R. R., & Cluis, D. (1998). Forms and concentrations of phosphorus in drainage water of twenty-seven tile-drained soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 27, 721–728.
Beauchemin, S., Simard, R. R., Bolinder, M. A., Nolin, M. C., & Cluis, D. (2003). Prediction of phosphorus concentration in tile-drainage water from the Montreal Lowlands soils. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 83, 73–87.
Cheatham, M. R. (2003). The impact of poultry manure on water quality using tile drained field plots and lysimeters. MS thesis: Iowa State University.
Chinkuyu, A. J., Kanwar, R. S., Lorimor, J. C., Xin, H., & Bailey, T. B. (2002). Effects of laying hen manure application rate on water quality. Transactions of the ASAE, 45(2), 299–308.
Cooperband, L. R., & Good, L. W. (2002). Biogenic phosphate minerals in manure: implications for phosphorus loss to surface waters. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(23), 5075–5082.
Daigh, A. L., Brye, K. R., Sharpley, A. N., Miller, D. M., West, C. P., & Brahana, V. J. (2009). Five-year change in soil profile chemical properties as affected by broiler litter application rate. Soil Science, 174(10), 531–542.
Daniel, T. C., Sharpley, A. N., Edwards, D. R., Wedepohl, R., & Lemunyon, J. L. (1994). Minimizing surface water eutrophication from agriculture by phosphorus management. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 49(2), 30–38.
Dinnes, D. L., Karlen, D. L., Jaynes, D. B., Kaspar, T. C., Hatfield, J. L., Colvin, T. S., & Cambardella, C. A. (2002). Nitrogen management strategies to reduce nitrate leaching in tile-drained midwestern soils. Agronomy Journal, 94(1), 153–171.
Dou, Z., Ramberg, C. F., Toth, J. D., Wang, Y., Sharpley, A. N., Boyd, S. E., Chen, C. R., Williams, D., & Xu, Z. H. (2009). Phosphorus speciation and sorption-desorption characteristics in heavily manured soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 73, 93–101.
Edwards, D. R., & Daniel, T. C. (1992). Environmental impacts of on-farm poultry waste disposal—a review. Bioresource Technology, 41(1), 9–33.
Edwards, D. R., Moore, P. A., Jr., Daniel, T. C., & Srivastava, P. (1995). Poultry litter-treated length effects on quality of runoff from fescue plots. Transactions of the ASAE, 39, 105–110.
Fang, F., Brezonik, P. L., Mulla, D. J., & Hatch, L. K. (2002). Estimating runoff phosphorus losses from calcareous soils in the Minnesota River basin. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31(6), 1918–1929.
Gartley, K. L., Sims, J. T., Olsen, C. T., & Chu, P. (2002). Comparison of soil test extractants used in Mid-Atlantic United States. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 33, 873–895.
Gollehon, N., Caswell, M., Ribaudo, M., Kellogg, R., Lander, C., & Letson, D. (2001). Confined animal production and manure nutrients. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Agriculture Indormation Bulletin No. 771. http://purl.umn.edu/33763.
Harmel, R. D., Harmel, B., & Patterson, M. C. (2008). On-farm agro-economic effects of fertilizing cropland with poultry litter. Journal of Applied Poultry Research, 17(4), 545–555.
Harmel, R. D., Smith, D. R., Haney, R. L., & Dozier, M. (2009). Nitrogen and phosphorus runoff from cropland and pasture fields fertilized with poultry litter. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 64(6), 400–412.
Harmel, R. D., Haney, R. L., & Smith, D. R. (2011). Effects of annual turkey litter application on surface soil quality of a Texas blackland vertisol. Soil Science, 176(5), 227–236.
Iowa State University Extension. (2008). Using manure nutrients for crop production. PMR 1003. Available at: https://store.extension.iastate.edu/Product/Using-Manure-Nutrients-for-Crop-Production.
Kanwar, R. S., Baker, J. L., & Baker, D. G. (1988). Tillage and split N fertilization effects on subsurface drainage water quality and crop yields. Transactions of the ASABE, 31(2), 453–460.
Moore, P. A., Daniel, T. C., Sharpley, A. N., & Wood, C. W. (1995). Poultry manure management—environmentally sound options. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 50, 321–327.
Mozaffari, M., & Sims, J. T. (1994). Phosphorus availability and sorption in an Atlantic coastal-plain watershed dominated by animal-based agriculture. Soil Science, 157(2), 97–107.
Mozaffari, M., & Sims, J. T. (1996). Phosphorus transformations in poultry litter amended soils of the Atlantic coastal plain. Journal of Environmental Quality, 25, 1357–1365.
NASS-USDA. (2010). 2010 Agricultural Statistics. Available at: http://www.nass.usda.gov/Publications/Ag_Statistics/2010/.
Nguyen, H. Q., Kanwar, R. S., Hoover, N. L., Dixon, P., Hobbs, J., Pederson, C., & Soupir, M. L. (2013). Long-term effects of poultry manure application on nitrate leaching in tile drain water. Transactions of the ASABE, 56(1), 91–101.
Owens, L. B., & Shipitalo, M. J. (2006). Surface and subsurface phosphorus losses from fertilized pasture systems in Ohio. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35, 1101–1109.
Poirier, S. C., Whalen, J. K., & Michaud, A. R. (2012). Bioavailable phosphorus in fine-sized sediments transported from agricultural fields. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 76(1), 258–267.
Qi, Z., Helmers, M. J., Malone, R. W., & Thorp, K. R. (2011). Simulating long-term impacts of winter rye cover crop on hydrologic cycling and nitrogen dynamics for a corn-soybean crop system. Transactions of the ASABE, 54(5), 1575–1588.
SAS Institute. (2009). Statistical analysis software, Ver. 9.2. Cary: SAS Institute.
Sauer, T. J., Daniel, T. C., Nichols, D. J., West, C. P., Moore, P. A., & Wheeler, G. L. (2000). Runoff water quality from poultry litter-treated pasture and forest sites. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29, 515–521.
Sawyer, J. E., Mallarino, A. P., Killhorn, R., & Barnhart, S. K. (2002). General guide for crop nutrient recommendations in Iowa. Publ. Pm-1688 (Rev.) Iowa State Univ. Ext., Ames. Available at: https://store.extension.iastate.edu/Product/A-General-Guide-for-Crop-Nutrient-and-Limestone-Recommendations-in-Iowa.
Sharpley, A. N., Meisinger, J. J., Breeuwsma, A., Sims, T., Daniel, T. C., & Schepers, J. S. (1998). Impacts of animal manure management on ground and surface water quality. In J. Hatfield (Ed.), Effective management of animal waste as a soil resource (pp. 173–242). Chelsea: Ann Arbor Press.
Shepherd, M. A. (1993). Poultry manure and nitrate leaching. World’s Poultry Science Journal, 49(2), 171–172.
Shipitalo, M. J., Nuutinen, V., & Butt, K. R. (2004). Interaction of earthworm burrows and cracks in a clayey, subsurface-drained, soil. Applied Soil Ecology, 26, 209–217.
Shreve, B. R., Moore, P. A., Jr., Miller, D. M., Daniel, T. C., & Edwards, D. R. (1995). Long-term phosphorus solubility in soils receiving poultry litter treated with aluminum, calcium and iron amendments. Communication on Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 27(11&12), 2493–2510.
Sims, J. T., Simard, R. R., & Joern, B. C. (1998). Phosphorus losses in agricultural drainage: historical perspective and current research. Journal of Environmental Quality, 27(2), 277–293.
Sims, J. T., Maquire, R. O., Leytem, A. B., Gartley, K. L., & Pautler, M. C. (2002). Evaluation of Mehlich 3 as an agri-environmental soil phosphorus test for the Mid-Atlantic United States of America. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 66(6), 2016–2032.
Smith, M. C., White, J. W., Coale, & Frank, J. (2009). Evaluation of phosphorus source coefficients as predictors of runoff phosphorus concentrations. Journal of Environmental Quality, 38(2), 587–597.
U.S. EPA. (2000). Ambient water quality criteria recommendations, information supporting the development of state and tribal nutrient criteria, Rivers and Streams in Nutrient Ecoregion VI. Office of Water 4304, EPA 822-B-00-017.
United States Department of Agriculture – Soil Conservation Service. (1981). Soil Survey of Boone County, Iowa. Available at: http://soildatamart.nrcs.usda.gov/manuscripts/IA015/0/boone.pdf.
von Wandruszka, R. (2006). Phosphorus retention in calcareous soils and the effect of organic matter on its mobility. Geochemical Transactions, 7, 6. doi:10.1186/1467-4866-7-6.
Wood, B. H., Wood, C. W., Yoo, K. H., Yoon, K. S., & Delaney, D. P. (1999). Seasonal surface runoff losses of nutrients and metals from soils fertilized with broiler litter and commercial fertilizer. Journal of Environmental Quality, 28, 1210–1218.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support provided by the Vietnam Education Foundation, the Iowa Egg Council, the Leopold Center for Sustainable Agriculture, and Iowa Agriculture and Home Economics Experiment Station to conduct this study. They would also like to thank Lendie Follett with the Iowa State University Statistics Department and Loren Shiers for chemical analysis of water samples in Water Quality Laboratory of Agriculture and Biosystems Engineering Department at Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoover, N.L., Kanwar, R., Soupir, M.L. et al. Effects of Poultry Manure Application on Phosphorus in Soil and Tile Drain Water Under a Corn-Soybean Rotation. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 138 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2403-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2403-9