Abstract
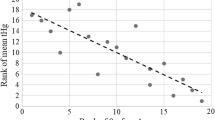
Mercury concentrations in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) bass were compared among five reservoirs in South Carolina. Three of these reservoirs (Lake Russell, Lake Thurmond, and Lake Marion) are accessible to the public and two (L-Lake and Par Pond) are located on the U.S. Department of Energy's Savannah River Site (SRS), which is closed to public access. Age-adjusted mercury concentrations were significantly higher in SRS bass compared to the offsite reservoirs. In addition, mercury concentrations were significantly higher in bass from Par Pond compared to L-Lake and in bass from Lakes Russell and Thurmond compared to Lake Marion. No mercury concentrations in excess of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration action level (1.0 mg⋅kg−1) were found in any bass from the public-accessible reservoirs. However, the majority of fish from these reservoirs had mercury concentrations that fall into or exceed the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency consumption category of “no more than one per week". In addition, most fish from these reservoirs had mercury levels in excess of those believed to be detrimental to sensitive avian species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burger, J., Gaines, K. F., Boring, C. S., Stephens, Jr. W. L., Snodgrass, J. and Gochfeld, M.: 2001, ‘Mercury and selenium in fish from the Savannah River: Species, trophic level, and locational differences’, Environ. Res. Sect. A 87, 108–118.
Castro, M. S., McLaughlin, E. N., Davis, S. L. and Morgan, R. P.: 2002, ‘Total mercury concentrations in lakes and fish of western Maryland, USA’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 42, 454– 462.
Chan, H. M., Scheuhammer, A. M., Ferran, A., Loupelle, C., Holloway, J. and Weech, S.: 2003, ‘Impacts of mercury on freshwater fish-eating wildlife and humans’, Human Ecol. Risk Assess. 9, 867–883.
Dupre, T. P., Granier, T. J., Keife, S., Marino, R., O'Rourke, S., Partridge, C., Schultz, D. L., Mandhare, K. and Beck, J. N.: 1999, ‘Variation of mercury concentration in fish taken from Lake Bouef, southeastern Louisiana’, Microchem. J. 61, 156–164.
Eisler, R.: 1987, ‘Mercury hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: A synoptic review’, U.S. Fish Wild. Serv. Biol. Rep. 85, 90 pp.
Facemire, C. T., Augspurger, T., Bateman, D., Brim, M., Conzelman, P., Delchamps, S., Douglas, E., Inmon, L., Looney, K., Lopez, F., Masson, G., Morrison, D., Morse, N. and Robison, A.: 1995, ‘Impacts of mercury contamination in the southeastern United States’, Water Air Soil Pollut. 80, 923–926.
Foster, E. P., Drake, D. L. and DiDomenico, G.: 2000, ‘Seasonal changes and tissue distribution of mercury in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) from Dorena Reservoir, Oregon’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 38, 78–82.
Huggett, D. B., Steevens, J. A., Allgood, J. C., Lutken, C. B., Grace, C. A. and Benson, W. H.: 2001, ‘Mercury in sediment and fish from North Mississippi lakes’ Chemosphere 42, 923–929.
Jagoe, C. H., Bryan, Jr. A. L., Brant, H. A., Murphy, T. M. and Brisbin, Jr. I. L.: 2002, ‘Mercury in bald eagle nestlings from South Carolina, USA’, J. Wildl. Dis. 38, 706–712.
Kvartek, E. J., Carlton, W. H., Denham, M., Eldridge, L. and Newman, M. C.: 1994, ‘Assessment of mercury in the Savannah River Site Environment’, Report WSRC-TR-94-0218ET, Westinghouse Savannah River Company, Aiken SC.
Lange, T. R., Royals, H. E. and Connor, L. L.: 1993, ‘Influence of water chemistry on mercury concentration in largemouth bass from Florida lakes’, Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 122, 74–84.
Lange, T. R., Royals, H. E. and Connor, L. L.: 1994, ‘Mercury accumulation in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) in a Florida lake’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 27, 466–471.
Linder, G. and Grillitsch, B.: 2000, ‘Ecotoxicology of metals’, in: D. W. Sparling, G. Linder and C. A. Bishop (eds), Ecotoxicology of amphibians and reptiles, SETAC Press, Pensacola, FL, pp. 325–408.
Morel, F. M., Kraepiel, A. M. L. and Amyot, M.: 1998, ‘The chemical cycle and bioaccumulation of mercury’, Ann. Rev. Ecol. Systematics 29, 543–566.
Mueller, K. W. and Serdar, D. M.: 2002, ‘Total mercury concentrations among fish and crayfish inhabiting different trophic levels in Lake Whatcom, Washington’, J. Freshwater Ecol. 71: 621–633.
NADP: 2000–2004, National Atmospheric Deposition Programs, Annual Summaries, Illinois State Water Survey, Champaign, IL, napd.sws.uiuc.edu.
Neumann, R. M. and Ward, S. M.: 2000, ‘Bioaccumulation and biomagnification of mercury in two warmwater fish communities’, J. Freshwater Ecol. 14, 487–498.
Park, J. G. and Curtis, L. R.: 1997, ‘Mercury distribution in sediments and bioaccumulation by fish in two Oregon reservoirs: Point source and nonpoint source impacted systems’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 33, 423–429.
Sokal, R. R. and Rohlf, F. J.: 1987, ‘Introduction to biostatistics’, W. H. Freeman, New York, 363 pp.
South Carolina Department of Health and Environmental Control (SCDHEC): 2005, ‘South Carolina fish consumption advisories’, http://www.scdhec.net/water/fish/advisories.htm.
Sugg, D. W., Chesser, R. K., Brooks, J. A. and Grasman, B. T.: 1995, ‘The association of DNA damage to concentrations of mercury and radiocesium in largemouth bass’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 14, 661–668.
US EPA: 2000, Guidance for Assessing Chemical Contaminant Data for Use in Fish Advisories, Volume 2: Risk Assessment and Fish Consumption Limits, Third Edition’, Office of Water, November 2000, EPA-823-B-00-008.
US EPA: 2004, Technical Memorandum Origin of 1 Meal/Week Noncommercial Fish Consumption Rate in National Advisory for Mercury, Office of Water, National Fish and Wildlife Contamination Program, http://www.epa.gov/ost/fishadvice/1-meal-per-week.pdf.
Wiener, J. G. and Spry, D. J.: 1996, ‘Toxicological significance of mercury in freshwater fish’, in W. N. Beyer, G. H. Heinz and A. W. Redmon-Norwood (eds), Environmental contaminants in wildlife: Interpreting tissue concentrations, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 927–340.
Yanochko, G. M., Jagoe, C. H. and Brisbin, Jr. I. L.: 1997, ‘Tissue mercury concentrations in alligators (Alligator mississippiensis) from the Florida Everglades and the Savannah River Site, South Carolina’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 32, 323–328.
Yeardley, Jr. R. B., Lazorchak, J. M. and Paulsen, S. G.: 1998, ‘Elemental fish tissue contamination in northeastern U.S. lakes: Evaluation of an approach to regional assessment’, Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 17, 1875–1884.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peles, J.D., Glenn, T.C., Brant, H.A. et al. Mercury Concentrations in Largemouth BASS (Micropterus Salmoides) from Five South Carolina Reservoirs. Water Air Soil Pollut 173, 151–162 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-9034-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-9034-5