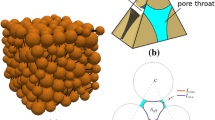
Abstract
We develop a grain-based model for capillarity controlled displacement within 3D fractionally wet porous media. The model is based on a novel local calculation of the position of stable fluid–fluid interfaces in contact with multiple spherical grains of arbitrary contact angles. The interface is assumed to be locally spherical between bulk phases; the interface is assumed to be toroidal between pairs of grains (surfaces of pendular rings). Because the calculation of interface position is entirely local and grain-based, it provides a single, generalized, geometric basis for computing pore-filling events during drainage as well as imbibition with both Melrose events (merging of two interfaces) and Haines events (geometric instability). The model is validated against a series of drainage/imbibition experiments (oil/water) on fractionally wet porous media prepared by mixing oil-wet grains with water-wet grains.





























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Futaisi, A., Patzek, T.W.: Secondary imbibition in NAPL-invaded mixed-wet sediments. J. Contam. Hydrol. 74(1–4), 61–81 (2004)
Amott, E.: Observations relating to the wettability of porous rock. Trans. AIME 216, 156–162 (1959)
Anderson, W.G.: Wettability literature survey.4. Effects of wettability on capillary-pressure. J. Petroleum Technol. 39(10), 1283–1300 (1987a)
Anderson, W.G.: Wettability literature survey. 5. The effects of wettability on relative permeability. J. Petroleum Technol. 39(11), 1453–1468 (1987b)
Bauters, T.W.J., Steenhuis, T.S., DiCarlo, D.A., Nieber, J.L., Dekker, L.W., Ritsema, C.J., Parlange, J.Y., Haverkamp, R.: Physics of water repellent soils. J. Hydrol. 231, 233–243 (2000)
Blunt, M., King, M.J., Scher, H.: Simulation and theory of 2-phase flow in porous-media. Phys. Rev. A 46(12), 7680–7699 (1992)
Blunt, M.J., Scher, H.: Pore-level modeling of wetting. Phys. Rev. E 52(6), 6387–6403 (1995)
Blunt, M.J.: Physically based network modeling of multiphase flow in intermediate-wet porous media. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 20, 117–125 (1998)
Blunt, M.J.: Flow in porous media: pore-network models and multiphase flow. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 6(3), 197–207 (2001)
Blunt, M.J., Jackson, M.D., Piri, M., Valvatne, P.H.: Detailed physics, predictive capabilities and macroscopic consequences for pore-network models of multiphase flow. Adv. Water Resour. 25(8–12), 1069–1089 (2002)
Bradford, S.A., Leij, F.J.: Fractional wettability effects on 2-fluid and 3-fluid capillary pressure–saturation relations. J. Contam. Hydrol. 20(1–2), 89–109 (1995)
Brown, R.J.S., Fatt, I.: Measurements of fractional wettability of oil fields rocks by the nuclear magnetic relaxation method. Fall Meeting of the Petroleum Branch of AIME, Los Angeles (1956)
Bryant, S., Mellor, D., Cade, C.: Physically representative network models of transport in porous media. Aiche J. 39, 387–396 (1993)
Bryant, S.L., King, P.R., Mellor, D.W.: Network model evaluation of permeability and spatial correlation in a real random sphere packing. Transp. Porous Media 11(1), 53–70 (1993)
de Gennes, P.G., Brochard-Wyart, F., Quere, D.: Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena: Drops, Bubbles, Pearls, Waves, 1st edn. Springer, New York (2003)
Donaldson, E.C., Thomas, R.D., Lorenz, P.B.: Wettability determination and its effect on recovery efficiency. SPE J. 9, 13–20 (1969)
Dullien, F.A.L.: Porous media. Fluid Transport and Pore Structure. Academic Press, San Diego (1992)
Gladkikh, M., Bryant, S.: Prediction of imbibition in unconsolidated granular materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 288(2), 526–539 (2005)
Haines, W.B.: Studies in the physical properties of soils. II. A note on the cohesion developed by capillary forces in an ideal soil. J. Agric. Sci. 15, 529–535 (1925)
Han, J., Jin, Y., Willson, C.: Virus retention and transport in chemically heterogeneous porous media under saturated and unsaturated flow conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 1547–1555 (2006)
Heiba, A.A., Davis, H.T., Scriven, L.E.: Effect of wettability on two-phase relative permeabilities and capillary pressures. SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Francisco (1983)
Jerauld, G.R., Hatfield, J.C., Scriven, L.E., Davis, H.T.: Percolation and conduction on voronoi and triangular networks: a case-study in topological disorder. J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 17(9), 1519–1529 (1984a)
Jerauld, G.R., Scriven, L.E., Davis, H.T.: Percolation and conduction on the 3D Voronoi and regular networks: a 2nd case-study in topological disorder. J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 17(19), 3429–3439 (1984b)
Jerauld, G.R., Salter, S.J.: The effect of pore-structure on hysteresis in relative permeability and capillary-pressure: pore-level modeling. Transp. Porous Media 5(2), 103–151 (1990)
Kovscek, A.R., Wong, H., Radke, C.J.: A pore-level scenario for the development of mixed wettability in oil reservoirs. AIChE J. 39(6), 1072–1085 (1993)
Laroche, C., Vizika, O., Kalaydjian, F.: Network modeling as a tool to predict three-phase gas injection in heterogeneous wettability porous media. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 24(2–4), 155–168 (1999)
Lenormand, R., Zarcone, C. Role of roughness and edges during imbibition in square capillaries. 59th Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition of the Society of Petroleum Engineers of AlME, Houston (1984)
Lenormand, R., Zarcone, C., Sarr, A.: Mechanisms of the displacement of one fluid by another in a network of capillary ducts. J. Fluid Mech. 135(OCT), 337–353 (1983)
Lindquist, W.B., Lee, S.M., Coker, D.A., Jones, K.W., Spanne, P.: Medial axis analysis of void structure in three-dimensional tomographic images of porous media. J. Geophys. Res. -Solid, Earth 101(B4), 8297–8310 (1996)
Mason, G., Mellor, D.W.: Simulation of drainage and imbibition in a random packing of equal spheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 176(1), 214–225 (1995)
McDougall, S.R., Sorbie, K.S.: The prediction of waterflood performance in mixed-wet systems from pore-scale modeling and simulation. SPE Symposium on Reservoir Simulation, New Orleans (1993)
Mellor, D.W. Random close packing (RCP) of equal spheres: structure and implications for use as a model porous medium. Open University. Ph.D., Milton Keynes (1989)
Melrose, J.C.: Wettability as related to capillary action in porous media. SPE J. 5, 259–271 (1965)
Mirzaei, M., DiCarlo, D.A.: Prediction of three-phase saturation profiles from two-phase capillary pressure curves as a function of wettability. Int. J. Oil, Gas, Coal Technol. 5(2/3), 123–141 (2012)
Mohanty, K.K., Salter, S.J.: Multiphase flow in porous media: III. Oil mobilization, transverse dispersion, and wettability. SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition San Francisco, CA (1983)
Mohanty, K.K., Davis, H., Scriven, L.E.: Physics of oil entrapment in water-wet rock. SPE Reserv. Eng. 2(1), 113–128 (1987)
Morrow, N.R.: Wettability and its effect on oil-recovery. J. Petroleum Technol. 42(12), 1476–1484 (1990)
Motealleh, S., Bryant, S.L. Predictive model for permeability reduction by small wetting phase saturations. Water Resour. Res. 43, W12S07 (2007)
Motealleh, S.: Mechanistic study of menisci motion within homogeneously and heterogeneously wet porous media. Ph.D. Petroleum engineering. The University of Texas at Austin (2009)
Motealleh, S., Ashouripashaki, M., DiCarlo, D., Bryant, S.L.: Mechanisms of capillary-controlled immiscible fluid flow in fractionally wet porous media. Vadose Zone J. 9(3), 610–623 (2010)
O’Carroll, D.M., Abriola, L.M., Polityka, C.A., Bradford, S.A., Demond, A.H.: Prediction of two-phase capillary pressure–saturation relationships in fractional wettability systems. J. Contam. Hydrol. 77(4), 247–270 (2005)
O’Rourke, J.: Computational Geometry in C. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1998)
Patzek, T.W.: Verification of a complete pore network simulator of drainage and imbibition. SPE J. 6(3), 251–251 (2001)
Piri, M., Blunt, M.J.: Pore-scale modeling of three-phase flow in mixed-wet systems. SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Antonio (2002)
Prodanovic, M., Bryant, S.L.: A level set method for determining critical curvatures for drainage and imbibition. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 304(2), 442–458 (2006)
Salathiel, R.A.: Oil recovery by surface film drainage in mixed-wettability rocks. J. Petroleum Technol. 155, 1216–1224 (1973)
Sharma, M.M., Garough, A., Dunlap, H.F.: Effects of wettability, pore geometry, and stress on electrical conduction in fluid saturated rocks. Log Analyst 32, 511–526 (1991)
Singhal, A. K., Somerton, W. H.: Two-phase flow through a non-circular capillary at low reynolds number. J. Can. Petroleum Technol. 9, 197–205 (1970)
Thane, C.: Geometry and topology of model sediments and their influence on sediment properties. Petroleum Engineering, Austin, The University of Texas at Austin (2006)
Tsakiroglou, C.D., Fleury, M.: Resistivity index of fractional wettability porous media. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 22(4), 253–274 (1999)
Ustohal, P., Stauffer, F., Dracos, T.: Measurement and modeling of hydraulic characteristics of unsaturated porous media with mixed wettability. J. Contam. Hydrol. 33(1–2), 5–37 (1998)
Valvatne, P.H., Blunt, M.J.: Predictive pore-scale modeling of two-phase flow in mixed wet media. Water Resour. Res. 40(7), (2004)
Van Dijke, M.I.J., Sorbie, K.S., McDougall, S.R.: A process-based approach for three-phase capillary pressure and relative permeability relationships in mixed-wet systems. SPE/DOE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa (2000)
Van Dijke, M.I.J., Sorbie, K.S.: Pore-scale modelling of three-phase flow in mixed-wet porous media: multiple displacement chains. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 39(3–4), 201–216 (2003)
Wilkinson, D., Willemsen, J.F.: Invasion percolation: a new form of percolation theory. J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 16(14), 3365–3376 (1983)
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Cynthia Thane and Javad Behseresht for providing the sphere packing and the Delaunay tessellation of the sphere packing. This study was in part supported by Department of Energy Grant DE-FC26-04NT15518.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motealleh, S., Ashouripashaki, M., DiCarlo, D. et al. Unified Model of Drainage and Imbibition in 3D Fractionally Wet Porous Media. Transp Porous Med 99, 581–611 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-013-0201-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-013-0201-7