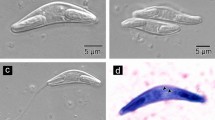
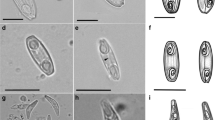
Abstract
Sphaeromyxa spp. are parasites of marine fishes, infecting the gall-bladders or bile ducts. The spores of these species possess characteristic ribbon-like polar filaments, a unique character among myxozoans. This unique character is also a synapomorphy consistent with estimates of phylogeny for this group which forms a lineage distinct from other myxozoans. There are 49 nominal species of Sphaeromyxa Thélohan, 1892 for which a synopsis is provided, reporting spore dimensions, spore shape, locality, and host species. A line drawing is also provided for each species.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aseeva, N. L. (2002a). New species of myxosporeans (Myxozoa, Myxosporea) from sculpins of the northwestern Japan Sea. Acta Parasitologica, 47, 179–189.
Aseeva, N. L. (2002b). [Myxosporidian fauna from the Gadidae in Far Eastern Seas]. Parazitologiia, 36, 167–174 (In Russian).
Auerbach, M. (1909). Bemerkungen über Myxosporidien. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 34, 65–82.
Auerbach, M. (1910). Die Cnidosporidien (Myxosporidien, Actinomyxidien, Microsporidien). Eine Monographische Studie. Leipzig: W. Klinkhardt, 261 pp.
Auerbach, M. (1912). Studien über die Myxosporidien der norwegfischen Seefische und ihre Verbreitung. Zoologische Jahrbücher, Systematik, 34, 1–50.
Awerinzew, S. (1913). Ergebnisse der Untersuchungen über parasitischen Protozoen der tropischen Region Afrikas. III. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 42, 151–156.
Bartošová, P., Fiala, I., & Hypsa, V. (2009). Concatenated SSU and LSU rDNA data confirm the main evolutionary trends within myxosporeans (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) and provide an effective tool for their molecular phylogenetics. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 53, 81–93.
Bartošová-Sojková, P., Kodádková, A., Pecková, H., Kuchta, R., & Reed, C. C. (2015). Morphology and phylogeny of two new species of Sphaeromyxa Thélohan, 1892 (Cnidaria: Myxozoa) from marine fish (Clinidae and Trachichthyidae). Parasitology, 142, 660–674.
Chen, Q. L., & Ma, C. L. (1998). Fauna Sinica. Myxozoa: Myxosporea. Beijing: Science Press (In Chinese).
Davis, H. S. (1917). The Myxosporidia of the Beaufort Region. A systematic and biological study. Bulletin of the United States Bureau of Fisheries, 35, 201–243.
Diamant, A., Whipps, C. M., & Kent, M. L. (2004). A new species of Sphaeromyxa (Myxosporea: Sphaeromyxina: Sphaeromyxidae) in devil firefish, Pterois miles (Scorpaenidae), from the northern Red Sea: morphology, ultrastructure, and phylogeny. Journal of Parasitology, 90, 1434–1442.
Doflein, F. (1898). Studien zur Naturgeschichte der Protozoen. III. Über Myxosporidien. Zoologische Jahrbücher, Abteilung für Anatomie und Ontogenie der Tiere, 11, 281–350.
Dogiel, V. A. (1948). [Parasitic Protozoa of the fish of Peter the Great Bay.] Izvestiya VNIORH (Newsletters of All-Union Scientific Research Institute of Lake and River Fisheries), 27, 17–66 (In Russian).
Donetz, Z. S., & Shulman, S. S. (1973). [On method of studies of mixosporidians (Protozoa, Cnidosporidia).] Parazitologiya, 7, 191–193 (In Russian).
Dunkerly, J. S. (1921). Fish Myxosporidia from Plymouth. Parasitology, 12, 328–333.
Fantham, H. B. (1930). Some parasitic protozoa found in South Africa, XIII. South African Journal of Science, 27, 376–390.
Fiala, I. (2006). The phylogeny of Myxosporea (Myxozoa) based on small subunit ribosomal RNA gene analysis. International Journal for Parasitology, 36, 1521–1534.
Froese, R., & Pauly, D. (Eds) (2015). FishBase. World Wide Web electronic publication. www.fishbase.org, version (04/2015).
Gaevskaya, A. V., & Kovaleva, A. A. (1984). [Addenda to the myxosporidian fauna (Protozoa: Myxosporidia) of fish in North-East Atlantic.] Hydrobiological Journal, 20, 49–53 (In Russian).
Georgévitch, J. (1916a). Note sur les Myxosporidies recuellis à Roscoff. Bulletin de la Société Zoologique de France, 41, 86–95.
Georgévitch, J. (1916b). Note sur les Myxosporidies des poisons de la baie de Villefranche et de Monaco. Bulletin de L’Institut Océanographique de Monaco, no. 322.
Gracia, M. P., Maillo, P. A., Amigo, J. M., & Salvado, H. (1997). Ultrastructural study of Sphaeromyxa balbianii, Thélohan 1892 (Myxozoa, Myxosporea: Bivalvulida), a parasite of Cepola macrophthalma, Linnaeus 1758. Acta Protozoologica, 36, 171–179.
Hewitt, G. C., & Hine, P. M. (1972). Checklist of parasites of New Zealand fishes and of their hosts. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 6, 69–114.
Hsieh, S. R., & Gong, X. N. (1993). [Three new species of myxosporidian from fishes.] In: Transactions of researches on fish diseases (No. 1). Edited by Department of Fish Diseases, Institute of Hydrobiology, Academia Sinica. Beijing: China Ocean Press, pp. 87–90 (In Chinese with English abstract).
Jameson, A. P. (1913). A note on some Myxosporidia collected at Monaco. Bulletin de L’Institut Océanographique de Monaco, no. 273.
Jameson, A. P. (1929). Myxosporidia from Californian fishes. Journal of Parasitology, 16, 59–68.
Kalavati, C., & MacKenzie, K. (1999). The genera Ceratomyxa Thélohan, 1892, Leptotheca Thélohan, 1895 and Sphaeromyxa Thélohan, 1892 (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) in gadid fish of the northeast Atlantic. Systematic Parasitology, 43, 209–216.
Kalavati, C., & Vaidehi, J. (1991). Two new species of myxosporidians from fishes of Chilka Lake: genus Sphaeromyxa Thélohan and genus Zschokkella Auerbach. Uttar Pradesh Journal of Zoology, 11, 146–150.
Karatayev, A. K., & Iskov, M. P. (1984). [New Myxosporidia species from Black Sea sand-smelt Atherina mochon pontica.] Vestnik Zoologii, 1, 59–60 (In Russian).
Karlsbakk, E., Einen, A. C., & Bartošová, P. (2013). Sphaeromyxa artedielli sp. n. (Myxozoa: Sphaeromyxidae), a parasite of sculpins (Cottidae) in northern Norway. Folia Parasitologica, 60, 425–432.
Khan, R. A., Bowering, W. R., Burgeois, C., Lear, H. P., & Pippy, J. H. (1986). Myxosporean parasites of marine fish from the continental shelf of Newfoundland and Labrador. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 64, 2218–2226.
Kovaleva, A. A., & Gaevskaya, A. V. (1982). [New data on Myxosporidia from the South-western Atlantic fishes.] Parazitologiya, 16, 353–359 (In Russian).
Kovaleva, A. A., Velev, P., & Vladev, P. (1993). [New data on myxosporidians (Cnidospora: Myxosporea) fauna from commercial fishes of the Atlantic coast of Africa.] In: Ecology and resources of commercial fishes of the eastern Atlantic. Kaliningrad: Atlantic Research Institute of Fisheries and Oceanography, pp. 174–193 (In Russian).
Kpatcha, T. K., Diebakate, C., & Toguebaye, B. S. (1996). Myxosporidia (Myxozoa, Myxosporea) of the genera Sphaeromyxa Thélohan, 1892, Myxidium Bütschli, 1882, Zschokkella Auerbach, 1910, Bipteria Kovaljova, Zubtchenko & Krasin, 1983 and Leptotheca Thélohan, 1895 parasites of fish from the coast of Senegal (West Africa). Journal of African Zoology, 110, 309–317.
Kristmundsson, A., & Freeman, M. A. (2013). Sphaeromyxids form part of a diverse group of myxosporeans infecting the hepatic biliary systems of a wide range of host organisms. Parasites & Vectors, 6, 51.
Kudo, R. R. (1919). Studies on Myxosporidia. Illinois Biological Monographs, 5, 1–265.
Kudo, R. R. (1921). On the effect of some fixatives upon Myxosporidian spores. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 40, 161–167.
Laird, M. (1953). The Protozoa of New Zealand intertidal zone fishes. Transactions of the Royal Society of New Zealand, 81, 79–143.
Laveran, A., & Mesnil, F. (1900). Sur une Myxosporidie des voies biliaires de l’Hippocampe (Sphaeromyxa sabrazesi nov. sp.). Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Séances et Mémoires de la Société de Biologie, Paris, 52, 380–382.
Li, L. X., & Nie, D. S. (1973). Myxosporidia. In: [An illustrated guide to the fish diseases and causative pathogenic fauna and flora in the Hubei Province.] Beijing: Science Press, pp. 57–91 (In Chinese).
Lom, J., & Noble, E. R. (1984). Revised classifications of class Myxosporea Bütschli, 1881. Folia Parasitologica, 31, 193–205.
Lom, J. (1970). Protozoa causing diseases in marine fishes. In Snieszko, S. F. (Ed.), A Symposium of the American Fisheries Society on Diseases of Fishes and Shellfishes (pp. 101–123). Washington DC: American Fisheries Society.
Lom, J. (2004). Morphology and ultrastructure of Sphaeromyxa noblei sp. n. (Myxozoa), parasite of Heteroclinus whiteleggii (Pisces) from Australian New South Wales coast. Folia Parasitologica, 51, 19–26.
Lom, J., & Dykova, I. (1992). Protozoan parasites of fishes. Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Science, 26. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Lubat, V., Radujković, B., Marques, A., & Bouix, G. (1989). Parasites des poissons marins du Montenegro: Myxosporidies. Acta Adriatica, 30, 31–50.
Miroshnichenko, A. I. (1984). [Myxosporidians of fish of Crimea.] Vestnik Zoologii, 6, 16–22 (In Russian).
Morrison, N. D., & Pratt, I. (1973). Sphaeromyxa maiyai sp. n. (Protozoa: Myxosporidea), coelozoic parasite of the Pacific tomcod Microgadus proximus. Journal of Protozoology, 20, 214–217.
Moser, M., & Noble, E. R. (1977). Three genera of myxosporida (Protozoa) in macrourid fishes. International Journal for Parasitology, 7, 93–96.
Naidenova, N. N. (1970). [Parasitofauna of fishes from family Gobiidae from the Azov Sea.] Biologiya Morya, 20, 84–113 (In Russian).
Noble, E. R. (1939). Myxosporidia from tide pool fishes of California. Journal of Parasitology, 25, 359–364.
Noble, E. R. (1941). On the distribution relationships between California tide pool fishes and their myxosporidian (protozoan) parasites. Journal of Parasitology, 27, 409–415.
Parisi, B. (1912). Primo contributo alla distribuzione geografica dei missosporidi in Italia. Atti della Società Italiana di Scienze Naturali e del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale in Milano, 50, 283–290.
Parker, J. D., & Warner, M. C. (1970). Effects of fixation, dehydration and staining on dimensions of myxosporidian and microsporidian spores. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 6, 448–456.
Pogoreltseva, T. P. (1964). [Data for the study of parasitic protozoans of fish in the Black Sea.] Problemy Parazitologii: Trudy Ukrainskogo Respublikanskogo Obchestva Parazitologov, 3, 16–29 (In Russian).
Polyanskii, Y. I. (1955). [The parasitology of fish of Northern marine waters of the USSR: Parasites of the fish of the Barents Sea.] Trudy Zoologicheskogo Instituta Akademii Nauk USSR (Transactions of the Zoological Institute of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR), 19, 5–170 (In Russian).
Pronin, N. M., Fleischer, G. W., Baldanova, D. R., & Pronina, S. V. (1997). Parasites of the recently established round goby (Neogobius melanostomus) and tubenose goby (Proterorhinus marmoratus) (Cottidae) from the St. Clair River and Lake St. Clair, Michigan. USA. Folia Parasitologica, 44, 1–6.
Sarkar, N. K. (1984). A new myxosporidan Sphaeromyxa hareni sp. n. (Myxozoa: Myxididae) from an Indian marine teleost Tachysurus platystomus (Day). Acta Protozoologica, 23, 183–186.
Sarkar, N. K. (1999). Ortholinea gadusiae sp. n. and Sphaeromyxa opisthopterae sp. n. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) from the clupeid fish of the Bay of Bengal, West Bengal. India. Acta Protozoologica, 38, 145–153.
Sarkar, N. K. (2004). On some new coelozoic Myxosporidia (Myxozoa : Myxosporea) from some teleost fishes of west Bengal, India. Journal of Environment and Sociobiology, 1, 35–48.
Sarkar, N. K., & Majumder, S. K. (1983). Myxosporidian Sphaeromyxa dighae sp. n. (Myxozoa: Myxidiidae) from the gallbladder of Hilsa ilisha (Clupeidae). Acta Protozoologica, 22, 257–260.
Schröder, O. (1907). Beitrage aur Entwicklungsgeschichte der Myxosporidien. Sphaeromyxa sabrazesi Laveran et Mesnil. Archiv für Protistenkunde, 9, 359–381.
Schröder, O. (1910). Ueber die anlage der sporocyste (pansporoblast) bei Sphaeromyxa sabrazesi Laveran et Mesnil. Archiv für Protistenkunde, 19, 1–5.
Sears, B. F., Anderson, P., & Greiner, E. C. (2011). A new species of myxosporean (Sphaeromyxidae), a parasite of lined seahorses, Hippocampus erectus, from the Gulf of Mexico. Journal of Parasitology, 97, 713–716.
Shulman, S. S. (1966). [Myxosporidia fauna of the USSR.] Moscow-Leningrad: Nauka, 504 pp (In Russian).
Su, X., & White, R. W. G. (1994). New myxosporeans (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) from marine fishes of Tasmania, Australia. Acta Protozoologica, 33, 251–259.
Thélohan, P. (1892). Observations sur les myxosporidies etéssai de classification de ces organismes. Bulletin de la Société Philomatique de Paris, 4, 165–178.
Thélohan, P. (1895). Recherches sur les Myxosporidies. Bulletin Scientifique de la France et de la Belgique, 26, 100–394.
Timi, J. T., & Sardella, N. H. (1998). Myxosporeans and coccidians parasitic on engraulid fishes from the coasts of Argentina and Uruguay. Parasite, 5, 331–339.
Tripathi, Y. R. (1953). Studies on parasites of Indian fishes. I. Protozoa Myxosporidia together with a check list of parasitic protozoa described from Indian fishes. Records of the Indian Museum, 50, 63–88.
Uspenskaya, A. V. (1972). [The fine structure of the polar capsule in a myxosporidian Sphaeromyxa cottidarum.] Tsitologiya, 14, 779–782 (In Russian).
Whipps, C. M., & Kent, M. L. (2006). Phylogeography of the cosmopolitan marine parasite Kudoa thyrsites (Myxozoa: Myxosporea). Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 53, 364–373.
Whipps, C. M., & Font, W. F. (2013). Interaction of two myxozoan parasites from naked goby Gobiosoma bosc, in Lake Pontchartrain, Louisiana. Journal of Parasitology, 99, 441–447.
WoRMS Editorial Board (2015). World Register of Marine Species. Available from http://www.marinespecies.org at VLIZ. Accessed 11 April 2015.
Yurakhno, V. M. (1988). [New data on fish Myxosporea of the Black Sea.] Parazitologiya, 22, 521–524 (In Russian).
Yurakhno, V. M. (1993). [New data of the fauna of Myxosporidians from fishes of the Black Sea.] Parazitologiya, 27, 320–326 (In Russian).
Zhukov, E. V. (1964). [On the parasite fauna of the fishes of the Chukotsk peninsula and the adjoining seas. III. The parasitic Protozoa of marine and freshwater fishes.] Parazitologiceskij. Sbornik, 22, 224–263 (In Russian).
Acknowledgments
CMW is thankful to the SUNY-ESF and the Oregon State University library staff (particularly Ruth Owens at ESF) for obtaining several original manuscripts, some of which were very difficult to locate. Also thanks to many colleagues who provided manuscripts or were instrumental in locating manuscripts; namely, Geoff Grossel, Chaganti Kalavati, Egil Karlsbakk, Cecile Reed, Vladimir Voronin, and Jinyong Zhang. Some line drawings were provided by Pavla Bartošová-Sojková and Alena Kodádková (S. clini and S. limnocapitis), and Mark Freeman (S. lycodi), and we thank them greatly for these high quality figures.
Funding
This work was partially supported by funding from the Chinese Natural Sciences Fund (no. 31471980) to YZ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whipps, C.M., Zhao, Y. Synopsis of the species of the genus Sphaeromyxa Thélohan, 1892 (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida: Variisporina: Sphaeromyxidae). Syst Parasitol 92, 81–99 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-015-9591-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-015-9591-y