Abstract
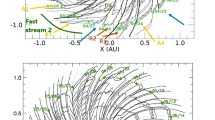
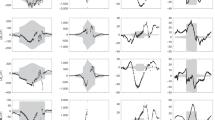
We address the problem of calculating the transverse magnetic field in the solar wind outside of the hypothetical sphere that is called the source surface where the solar wind originates. This calculation must overcome a widely used fundamental assumption about the source surface – the field is normally required to be purely radial at the source surface. Our model rests on the fact that a change in the radial field strength at the source surface is a change in the field line density. Surrounding field lines must move laterally to accommodate this field line density change. As the outward wind velocity drags field lines past the source surface, this lateral component of motion produces a tilt, implying there is a transverse component to the field. An analytic method of calculating the lateral translation speed of the field lines is developed. We apply the technique to an interval of approximately two Carrington rotations at the beginning of 2011 using 2-h averages of data from the Helioseismic Magnetic Imager instrument onboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory spacecraft. We find that the value of the transverse magnetic field is dominated on a global scale by the effects of high-latitude concentrations of field lines that are buffeted by supergranular motions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschuler, M.D., Newkirk, G. Jr.: 1969, Magnetic fields and the structure of the solar corona. I: Methods of calculating coronal fields. Solar Phys. 9, 131. ADS .
Bogdan, T.J., Low, B.C.: 1986, The three-dimensional structure of magnetostatic atmospheres. II – Modeling the large-scale corona. Astrophys. J. 306, 271. DOI . ADS .
Gilbert, J.A., Zurbuchen, T.H., Fisk, L.A.: 2007, A new technique for mapping open magnetic flux from the solar surface into the heliosphere. Astrophys. J. 663, 583. DOI . ADS .
Gonzalez, W.D., Tsurutani, B.T., Clúa de Gonzalez, A.L.: 1999, Interplanetary origin of geomagnetic storms. Space Sci. Rev. 88, 529. DOI . ADS .
Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Hayashi, K., Sun, X., Schou, J., Couvidat, S., et al.: 2014, The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) vector magnetic field pipeline: Overview and performance. Solar Phys. 289, 3483. DOI . ADS .
Horbury, T.S., Balogh, A.: 2001, Evolution of magnetic field fluctuations in high-speed solar wind streams: Ulysses and Helios observations. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 15929. DOI . ADS .
Jackson, B.V., Hick, P.P., Buffington, A., Yu, H.-S., Bisi, M.M., Tokumaru, M., Zhao, X.: 2015, A determination of the north–south heliospheric magnetic field component from inner corona closed-loop propagation. Astrophys. J. Lett. 803, L1. DOI . ADS .
Jokipii, J.R., Kota, J.: 1989, The polar heliospheric magnetic field. Geophys. Res. Lett. 16, 1. DOI . ADS .
Jokipii, J.R., Parker, E.N.: 1968, Random walk of magnetic lines of force in astrophysics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 21, 44. DOI . ADS .
Liu, Y., Hoeksema, J.T., Scherrer, P.H., Schou, J., Couvidat, S., Bush, R.I., Duvall, T.L., Hayashi, K., Sun, X., Zhao, X.: 2012, Comparison of line-of-sight magnetograms taken by the Solar Dynamics Observatory/Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager and Solar and Heliospheric Observatory/Michelson Doppler Imager. Solar Phys. 279, 295. DOI . ADS .
Schatten, K.H.: 1971, Current sheet magnetic model for the solar corona. Cosmic Electrodyn. 2, 232. ADS .
Schatten, K.H., Wilcox, J.M., Ness, N.F.: 1969, A model of interplanetary and coronal magnetic fields. Solar Phys. 6, 442. ADS .
Scherrer, P.H., Bogart, R.S., Bush, R.I., Hoeksema, J.T., Kosovichev, A.G., Schou, J., et al.: 1995, The Solar Oscillations Investigation – Michelson Doppler Imager. Solar Phys. 162, 129. ADS .
Schulz, M., Frazier, E.N., Boucher, D.J. Jr.: 1978, Coronal magnetic-field model with non-spherical source surface. Solar Phys. 60, 83. DOI . ADS .
Stern, D.P.: 1966, The motion of magnetic field lines. Space Sci. Rev. 6, 147. DOI . ADS .
Title, A.M., Schrijver, C.J.: 1998, The Sun’s magnetic carpet. In: Donahue, R.A., Bookbinder, J.A. (eds.) Cool Stars, Stellar Systems, and the Sun, ASP Conf. Ser. 154, 345. ADS .
Tran, T.: 2009, Improving the predictions of solar wind speed and interplanetary magnetic field at the Earth. Ph.D. thesis, Univ. California Los Angeles.
Ulrich, R.K., Boyden, J.E.: 2006, Carrington coordinates and solar maps. Solar Phys. 235, 17.
Ulrich, R.K., Evans, S., Boyden, J.E., Webster, L.: 2002, Mount Wilson synoptic magnetic fields: Improved instrumentation, calibration, and analysis applied to the 2000 July 14 flare and to the evolution of the dipole field. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 139, 259. ADS
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.R.: 1990, Solar wind speed and coronal flux-tube expansion. Astrophys. J. 355, 726. ADS .
Warmuth, A., Mann, G.: 2005, A model of the Alfvén speed in the solar corona. Astron. Astrophys. 435, 1123. DOI . ADS .
Zhang, X.-Y., Moldwin, M.B.: 2014, The source, statistical properties, and geoeffectiveness of long-duration southward interplanetary magnetic field intervals. J. Geophys. Res. 119, 658. DOI . ADS .
Zhao, X., Hoeksema, J.T.: 1994, A coronal magnetic field model with horizontal volume and sheet currents. Solar Phys. 151, 91. DOI . ADS .
Zhao, X., Hoeksema, J.T.: 1995, Prediction of the interplanetary magnetic field strength. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 19. DOI . ADS .
Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2007, A new view of the coupling of the Sun and the heliosphere. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 45, 297. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgements
We thank Jack Harvey for several helpful suggestions including bringing the perceptive quote from Zurbuchen to our attention. We thank Chen Shi for uncovering an error in the sign of \(B_{\theta}\) in our original equations. This error is corrected in the current paper. The HMI images used in preparation of this article are courtesy of NASA/SDO and the science team. This research has been supported by NASA through award NNX15AF39G to Predictive Science, Inc. and subaward to UCLA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below are the links to the electronic supplementary material.
11207_2016_882_MOESM2_ESM.mp4
This video shows the series of hybrid photospheric maps like that in Figure 4. The maps are stationary relative to the central meridian as seen by HMI while the solar longitudes are shifted each frame. (MP4 17.8 MB)
11207_2016_882_MOESM3_ESM.mp4
This video shows the projection from above the south pole of the maps seen in Figure 5 and the video of Figure 10. Note that the solar coordinates are stationary in this video while the observed portion of the solar surface moves around the circular image. (MP4 18.1 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulrich, R.K., Tran, T. Generation of a North/South Magnetic Field Component from Variations in the Photospheric Magnetic Field. Sol Phys 291, 1059–1076 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-016-0882-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-016-0882-5