Abstract
Aims
This paper assessed the effect that the vertical stratification of nutrients in conservation cropping systems of Australia has on phosphorus (P) and nitrogen (N) fertiliser use efficiency.
Methods
Intact soil cores from two long-term tillage experiments, located on a Vertosol and on a Calcarosol were used to assess if tillage system (zero tillage - ZT vs conventional tillage - CT) and soil water influence fertiliser use efficiency (using 33P and 15 N) of wheat under controlled growth conditions.
Results
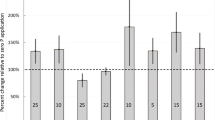
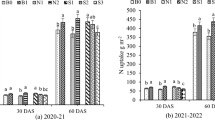
Adding P increased shoot growth and P uptake on the Calcarosol, provided the surface remained moist and N was applied. The percentage of plant P derived from fertiliser (Pdff) was greater on the Calcarosol regardless of tillage practice. Pdff increased when the soil remained wet or when N was added. The percentage of N derived from fertiliser (%Ndff) was not affected by tillage practice on the Vertosol but when the soil surface was allowed to dry, it was significantly greater under ZT than CT on the Calcarosol. Adding P increased N fertiliser recovery but tillage practice had no effect.
Conclusion
The effect of tillage practice on P and N fertiliser use efficiency depends on soil and topsoil water status.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adcock D, McNeill AM, McDonald GK, Armstrong RD (2007) Subsoil constraints to crop production on neutral and alkaline soils in south-eastern Australia: a review of current knowledge and management strategies. Aust J Exp Agric 47:1245–1261
Allen DG, Jeffery RC (1990) Methods of analysis of phosphorus in western Australian soils. Report of investigation No. 37. Chemistry Centre of Western Australia, East Perth, p 7
Alston AM (1976) Effects of depth of fertiliser placement on wheat growth under three water regimes. Aust J Agric Res 27:1–10
Anderson WK, Angus JF (2011) Agronomy and cropping practices in semi-arid conditions in Australia. In: Bonjean AP, Angus W, Van Ginkel M (eds) The world wheat book, vol 2. A History of wheat breeding, Lavoisier, pp 563–605
Armstrong RD, Halpin NV, McCosker K, Standley J (1995) Effect of tillage practise and fallowing on the nitrogen economy of grain sorghum in central Queensland. Aust J Agric Res 47:81–95
Barber SA (1995) Soil nutrient bioavailability: a mechanistic approach, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Bertrand I, McLaughlin MJ, Holloway R, Armstrong R, McBeath T (2006) Changes in P bioavailability induced by the application of liquid and powder sources of P, N and Zn fertilizers in alkaline soils. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 74(1):27–40
Chan KY, Mead JA, Roberts WP (1987) Poor early growth of wheat under direct drilling. Aust J Agric Res 38:791–800
Colwell JD (1965) An automatic procedure for the determination of Phosphorus in sodium hydrogen carbonate extracts of soils. Chemistry Industry. pp. 893–895
Cornish P (1987) Effects of direct drilling on the phosphorus uptake and fertiliser requirements of wheat. Aust J Agric Res 38:775–790
Dunbabin VM, Armstrong RD, Officer SJ, Norton RM (2009) Identifying fertiliser management strategies to maximise nitrogen and phosphorus acquisition by wheat in two contrasting soils from Victoria. Aust J Soil Res 47:74–90
Gates CT, Jones DB, Muller WJ, Hicks JS (1981) The interaction between nutrients and tillage methods on wheat and weed development. Aust J Agric Res 32:227–241
Grant CA, Lafond, (1994) The effects of tillage systems and crop rotations on soil chemical properties of a black Chernozemic soil. Can J Soil Sci 74:301–307
Grant CA, Flaten DN, Tomasiewicz DJ, Sheppard SC (2001) The importance of early season phosphorus nutrition. Can J Plant Sci 81(2):211–224
Haynes RJ, Knight TL (1989) Comparison of soil chemical propoerties, enzyme activities, levels of biomass N and aggregate stability in the soil profile under conventional and no-tillage in Cantebury, New Zealand. Soil Tillage Res 14:197–208
Holford I, Doyle A, Leckie C (1992) Nitrogen response characteristics of wheat protein in relation to yield responses and their interactions with phosphorus. Aust J Agric Res 43(5):969–986
Isbell RF (1996) The Australia soil classification. CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne
Jing J, Rui Y, Zhang F, Rengel Z, Shen J (2010) Localised application of phosphorus and ammonium improves growth of maize seedlings by stimulating root proliferation and rhizosphere acidification. Field Crop Res 119:355–364
Kirkegaard JA (1995) A review of trends in wheat yield responses to conservation cropping in Australia. Aust J Exp Agric 35:835–848
Klute A (1986) Water retention: laboratory methods. In: Klute A (ed) ‘Methods of soil analysis. Part 1. Physical and mineralogical methods, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madiso
Latta J, O’Leary GJ (2003) Long-term comparison of rotation and fallow tillage systems of wheat in Australia. Field Crop Res 83:173–190
Llewellyn RS, D’Emden FH, Kuehne G (2012) Extensive use of no-tillage in grain growing regions of Australia. Field Crop Res 132:204–212
Lombi E, McLaughlin MJ, Johnson C, Armstrong RD, Holloway RE (2004) Mobility, solubility and lability of fluid and granular forms of P fertiliser in calcareous and non-calcareous soils under laboratory conditions. Plant Soil 269:25–34
Mason S, McNeill A, McLaughlin MJ, Zhang H (2010) Prediction of wheat response to an application of phosphorus under field conditions using diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) and extraction methods. Plant Soil 337:243–258
McBeath TM, McLaughlin MJ, Kirby JK, Armstrong RD (2012) The effect of soil water status on fertiliser, topsoil and subsoil phosphorus utilisation by wheat. Plant Soil 358:337–348
Newton PJ (2001) Effects of long term stubble management on yield and nitrogen-uptake efficiency of wheat topdressed with urea in north-eastern Victoria. Aust J Exp Agric 41:1167–1178
O’Leary GJ, Connor DJ (1997) Stubble retention and tillage in a semi-arid environment: 2. Soil mineral nitrogen accumulation during fallow. Field Crop Res 52:221–229
Pittelkow CM, Liang X, Linquist BA, van Groenigen KJ, Lee J, Lundy ME, van Gestel N, Six J, Venterea RT, van Kessel C (2014) Productivity limits and potential of the principles of conservation agriculture. Nature. doi:10.1038/nature 13809
Rasmussen PE, Rohde CR (1991) Tillage, soil depth, and precipitation effects on wheat response to nitrogen. Soil Sci Soc Am J 55:121–124
Rayment GE, Lyons D (2011) Soil chemical methods – Australasia. CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne, p 192
Schwab GJ, Whitney DA, Kilgore GL, Sweeney DW (2006) Tillage and phosphorus management effects on crop production in soils with phosphorus stratification. Agron J 98:430–435
Searle PL (1984) The Bertholet or indophenol reaction and its use in the analytical chemistry of nitrogen. Analyst 109:549–568
Singh DK, Sale PWG, Routley RR (2005) Increasing phosphorus supply in subsurface soil in northern Australia: rationale for deep placement and the effects with various crops. Plant Soil 269:35–44
Strong WM, Barry G (1980) The availability of soil and fertiliser phosphorus to wheat and rape at different water regimes. Aust J Soil Res 18:353–62
Strong WM, Cooper JE (1980) Recovery of nitrogen by wheat from various depths in a cracking clay soil. Aust J Exp Agric Anim Hus 20:82–87
Strong WM, Dalal RC, Weston EJ, Cooper JE, Lehane KJ, King AJ, Chicken CJ (1996) Sustaining productivity of a vertisol at warra, Queensland, with fertilisers, no-tillage or legumes. 2. Long-term fertiliser nitrogen needs to enhance wheat yields and grain protein. Aust J Exp Agric 36:665–674
Thomsen IK, Sorensen P (2006) Tillage induced N mineralisation and N uptake in winter wheat on a coarse sandy loam. Soil Tillage Res 89:58–69
Vu DT, Tang C, Armstrong RD (2009) Tillage system affects phosphorus form and depth distribution in three contrasting Victorian soils. Aust J Soils Res 47:33–45
Vu DT, Armstrong RD, Sale WG, Tang C (2010) Phosphorus availability for three crop species as a function of soil type and fertiliser history. Plant Soil 337:497–510
Zapata F (1990) Isotope techniques in soil fertility and plant nutrition studies. In: Hardarson G (ed) Use of nuclear techniques in studies of soil-plant relationships. FAO/ International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, pp 61–128
Zarcinas BA, McLaughlin MJ, Smart MK (1996) The effect of acid digestion technique on the performance of nebulisation systems used in inductively coupled plasma spectrometry. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 27(5–8):1331–1354
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the expert technical assistance of Caroline Johnston (CSIRO) with the preparation of the 33P component and subsequent chemical analysis, Dr B Kuskopf (University of Melbourne) for 15 N analysis and Roger Perris, Claire McMahon and Mel Munn (Department of Economic Development, Jobs, Transport and Resources) for assistance with collecting the intact cores and running the glasshouse experiment. The research was co-funded by the Grains Research & Development Corporation (Project DAV00095).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philip John White.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Armstrong, R.D., Dunsford, K., McLaughlin, M.J. et al. Phosphorus and nitrogen fertiliser use efficiency of wheat seedlings grown in soils from contrasting tillage systems.. Plant Soil 396, 297–309 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2586-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2586-2