Abstract
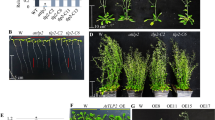
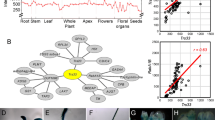
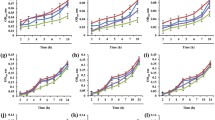
Tubby and Tubby-like proteins (TLPs) play essential roles in the development and function of mammal neuronal cells. In addition to the conserved carboxyl (C)-terminal Tubby domain, which is required for their plasma membrane (PM) tethering, plant TLPs also possess an amino (N)-terminal F-box domain to interact with specific Arabidopsis Skp1-like (ASK) proteins as functional SCF-type E3 ligases. Here, we report the molecular characterization of Arabidopsis TLPs (AtTLPs). β-Glucuronidase staining showed overlapped but distinct expression patterns of AtTLPs in Arabidopsis. Yeast two-hybrid assays further revealed that AtTLP1, AtTLP3, AtTLP6, AtTLP7, AtTLP9, AtTLP10 and AtTLP11 all interacted with specific ASKs, but AtTLP2, AtTLP5 and AtTLP8 did not. Subcellular localization observations in both Arabidopsis protoplasts and tobacco pollen tubes indicated that all GFP-AtTLP fusion proteins, except GFP-AtTLP8 which lacks the conserved phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate binding sites, were targeted to the PM. Detailed studies on AtTLP3 demonstrated that AtTLP3 is a PM-tethered PIP2 binding protein which functions redundantly with AtTLP9 in abscisic acid (ABA)- and osmotic stress-mediated seed germination. Our results suggest that AtTLPs possibly work in multiple physiological and developmental processes in Arabidopsis, and AtTLP3 is also involved in ABA signaling pathway like AtTLP9 during seed germination and early seedling growth.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao Y, Wang CT, Jiang CM, Pan J, Zhang GB, Liu H, Zhang HX (2014) The tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF)-like family protein SEVEN IN ABSENTIA 2 (SINA2) promotes drought tolerance in an ABA-dependent manner in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 202:174–187
Boggon TJ, Shan WS, Santagata S, Myers SC, Shapiro L (1999) Implication of tubby proteins as transcription factors by structure-based functional analysis. Science 286:2119–2125
Bu Q, Lv T, Shen H, Luong P, Wang J, Wang Z, Huang Z, Xiao L, Engineer C, Kim TH, Schroeder JI, Huq E (2014) Regulation of drought tolerance by the F-box protein MAX2 in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 164:424–439
Cai M, Qiu DY, Yuan T, Ding XH, Li HJ, Duan L, Xu CG, Li XH, Wang SP (2008) Identification of novel pathogen-responsive cis-elements and their binding proteins in the promoter of OsWRKY13, a gene regulating rice disease resistance. Plant Cell Environ 31:86–96
Calderón-Villalobos L, Nill C, Marrocco K, Kretsch T, Schwechheimer C (2007) The evolutionarily conserved Arabidopsis thaliana F-box protein AtFBP7 is required for efficient translation during temperature stress. Gene 392:106–116
Cheng Y, Zhou W, El Sheery NI, Peters C, Li M, Wang X, Huang J (2011) Characterization of the Arabidopsis glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase (GDPD) family reveals a role of the plastid-localized AtGDPD1 in maintaining cellular phosphate homeostasis under phosphate starvation. Plant J 66:781–795
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Dreher K, Callis J (2007) Ubiquitin, hormones and biotic stress in plants. Ann Bot 99:787–822
He J, Duan Y, Hua D, Fan G, Wang L, Liu Y, Chen Z, Han L, Qu LJ, Gong ZZ (2012) DEXH box RNA helicase-mediated mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in Arabidopsis mediates crosstalk between abscisic acid and auxin signaling. Plant Cell 24:1815–1833
Hua Z, Vierstra RD (2004) The cullin-RING ubiquitin-protein ligases. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62:299–334
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusion: betaglucurodinase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Kleinboelting N, Huep G, Kloetgen A, Viehoever P, Weisshaar B (2012) GABI-Kat SimpleSearch: new features of the Arabidopsis thaliana T-DNA mutant database. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D1211–D1215
Kleyn PW, Fan W, Kovats SG, Lee JJ, Pulido JC, Wu Y, Berkemeier LR, Misumi DJ, Holmgren L, Charlat O et al (1996) Identification and characterization of the mouse obesity gene tubby: a member of a novel gene family. Cell 85:281–290
Ko JH, Yang SH, Han KH (2006) Upregulation of an Arabidopsis RING-H2 gene, XERICO, confers drought tolerance through increased abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant J 47:343–355
Koops P, Pelser S, Ignatz M, Klose C, Marrocco-Selden K, Kretsch T (2011) EDL3 is an F-box protein involved in the regulation of abscisic acid signalling in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 62:5547–5560
Kou YJ, Qiu DY, Wang L, Li XH, Wang SP (2009) Molecular analyses of the rice tubby-like protein gene family and their response to bacterial infection. Plant Cell Rep 28:113–121
Kwak JM, Mori IC, Pei ZM, Leonhardt N, Torres MA, Dangl JL, Bloom RE, Bodde S, Jones JD, Schroeder JI (2003) NADPH oxidase AtrbohD and AtrbohF genes function in ROS-dependent ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 22:2623–2633
Lai CP, Shaw JF (2012) Interaction analyses of Arabidopsis tubby-like proteins with ASK proteins. Bot Stud 53:447–458
Lai CP, Lee CL, Chen PH, Wu SH, Yang CC, Shaw JF (2004) Molecular analyses of the Arabidopsis TUBBY-like protein gene family. Plant Physiol 134:1586–1597
Lai CP, Chen PH, Huang JP, Tzeng YH, Chaw SM, Shaw JF (2012) Functional diversification of theTubby-like protein gene families (TULPs) during eukaryotic evolution. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 1:2–8
Luo DX, Bernard DG, Balk J, Hai H, Cui XF (2012) The DUF59 family gene AE7 acts in the cytosolic iron-sulfur cluster assembly pathway to maintain nuclear genome integrity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:4135–4148
Moon J, Parry G, Estelle M (2004) The ubiquitin–proteasome pathway and plant development. Plant Cell 16:3181–3195
Mukhopadhyay S, Jackson PK (2011) The tubby family proteins. Genome Biol 12:255
Noben-Trauth K, Naggert JK, North MA, Nishina PM (1996) A candidate gene for the mouse mutation tubby. Nature 380:534–538
Pandey GK, Cheong YH, Kim KN, Grant JJ, Li LG, Hung W, D’Angelo C, Weinl S, Kudla J, Luan S (2004) The calcium sensor calcineurin B-Like 9 modulates abscisic acid sensitivity and biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:1912–1924
Reitz MU, Bissue JK, Zocher K, Attard A, Huckelhoven R, Becker K, Imani J, Eichmann R, Schafer P (2012) The subcellular localization of tubby-like proteins and participation in stress signaling and root colonization by the mutualist Piriformospora indica. Plant Physiol 160:349–364
Reitz MU, Pai S, Imani J, Schafer P (2013) New insights into the subcellular localization of tubby-like proteins and their participation in the Arabidopsis–Piriformospora indica interaction. Plant Signal Behav 8:e25198
Santagata S, Boggon TJ, Baird CL, Gomez CA, Zhao J, Shan WS, Myszka DG, Shapiro L (2001) G-protein signaling through tubby proteins. Science 292:2041–2050
Schumann N, Navarro-Quezada A, Ullrich K, Kuhl C, Quint M (2011) Molecular evolution and selection patterns of plant F-box proteins with C-terminal kelch repeats. Plant Physiol 155:835–850
Stone SL, Callis J (2007) Ubiquitin ligases mediate growth and development by promoting protein death. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:624–632
Wang C, Bao Y, Wang QQ, Zhang HX (2013) Introduction of the rice CYP714D1 gene into Populus inhibits expression of its homologous genes and promotes growth, biomass production and xylem fibre length in transgenic trees. J Exp Bot 64:2847–2857
Yang ZF, Zhou Y, Wang XF, Gu SL, Yu JM, Liang GH, Yan CJ, Xu CW (2008) Genomewide comparative phylogenetic and molecular evolutionary analysis of tubby-like protein family in Arabidopsis, rice, and poplar. Genomics 92:246–253
Yoo SD, Cho YH, Sheen J (2007) Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nature Protoco 2:1565–1572
Zhang Y, Xu W, Li Z, Deng XW, Wu W, Xue Y (2008) F-box protein DOR functions as a novel inhibitory factor for abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure under drought stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 148:2121–2133
Acknowledgments
We thank the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center and the Nottingham Arabidopsis Stock Centre and GABI-Kat (Kleinboelting et al. 2012) for providing us the T-DNA insertion mutants; BiFC vectors were kindly provided by Dr. Guang Li (Shanghai Institute of Plant Physiology and Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China). Vectors containing the ASK cDNAs were kindly provided by Dr. Nadine Schumann and Dr. Marcel Quint (Independent Junior Research Group and Department of Stress and Developmental Biology, Leibniz Institute of Plant Biochemistry, Halle, Germany). This work has been supported by the following grants: the National Natural Science Foundation of China 31000288, 31171169, 31100212, 31371228, 31370670; the National Basic Research Program of China 2010CB126600; the National Mega Project of GMO Crops 2013ZX08001003-007, 2013ZX08004002-006; and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences XDA08030108.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, Y., Song, WM., Jin, YL. et al. Characterization of Arabidopsis Tubby-like proteins and redundant function of AtTLP3 and AtTLP9 in plant response to ABA and osmotic stress. Plant Mol Biol 86, 471–483 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-014-0241-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-014-0241-6