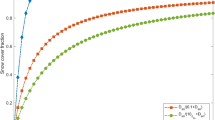
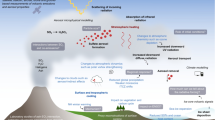
Abstract
Aerosols can affect the cloud-radiation feedback and the precipitation over the Indian monsoon region. In this paper, we propose that another pathway by which aerosols can modulate the multi-scale aspect of Indian monsoons is by altering the land–atmosphere interactions. The nonlinear feedbacks due to aerosol/diffuse radiation on coupled interactions over the Indian monsoon region are studied by: (1) reviewing recent field measurements and modeling studies, (2) analyzing the MODIS and AERONET aerosol optical depth datasets, and (3) diagnosing the results from sensitivity experiments using a mesoscale modeling system. The results of this study suggest that the large magnitude of aerosol loading and its impact on land–atmosphere interactions can significantly influence the mesoscale monsoonal characteristics in the Indo-Ganges Basin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boer GJ, Flato G, Ramsden D (2000) A transient climate change simulation with greenhouse gas and aerosol forcing: projected climate for the 21st century. Clim Dynam 16:427–450
Chang H (2004) Observations of the effects of aerosol loading on carbon and water cycles over various landscapes. MS thesis, NC State University (Available from: http://www. lib.ncsu.edu)
Chou C, Neelin JD, Lohmann U, Feichter J (2005) Local and remote impacts of aerosol climate forcing on tropical precipitation. J Climate 18:4621–4636
Chung CE, Ramanathan V, Kiehl JT (2002) Effects of the south Asian absorbing haze on the northeast monsoon and surface-air heat exchange. J Climate 15:2462–2476
Chung C, Ramanathan V (2006) Weakening of North Indian SST gradients and the monsoon rainfall in India and the Sahel. J Climate 19:2036–2045
Farquhar GD, Roderick ML (2003) Pinatubo, diffuse light, and the carbon cycle. Science 299:5615
Giorgi F, Francisco R (2000) Uncertainties in regional climate change predictions. A regional analysis of ensemble simulations with the HADCH2 GCM. Clim Dynam 16:169–182
Goudriaan J (1977) Crop micrometeorology and a simulation study. Center for Agricultural Publication and Documentation (PUDOC), Wageningen, The Netherlands
Gu L, Fuentes JD, Schugart HH, Staebler RM, Black TA (1999) Responses of net ecosystem exchanges of carbon dioxide to changes in cloudiness: results from two North American deciduous forests. J Geophys Res 104:31421–311434
Gu L, Baldocchi DD, Wofsy SC, Munger JW, Michalsky JJ, Urbanski SP, Boden TA (2003) Response of a deciduous forest to the Mount Pinatubo eruption: enhanced photosynthesis. Science 299:2035–2038
Hollinger DY, Kelliher FM, Byers JN, Hunt JE, McSeveny TM, Weir PL (1994) Carbon dioxide exchange between an undisturbed old-growth temperate forest and the atmosphere. Ecology 75:134–150
Kobayashi H, Matsunaga T, Hoyano A, Aoki M, Komori D, Boonyawat S (2004) Satellite estimation of photosynthetically active radiation in Southeast Asia: impacts of smoke and cloud cover. J Geophys Res 109 (D4) Article No. D04102
Krakauer NY, Randerson JT (2003) Do volcanic eruptions enhance or diminish net primary production? Evidence from tree rings. Global Biogeochem Cycles 17:1118 (doi: 10.1029/2003GB002076)
Lal M, Cubasch U, Voss R, Waszkewitz J (1995) Effect of transient increases in greenhouse gases and sulphate aerosols on monsoon climate. Curr Sci 69:752–763
Lal M, Nozawa T, Emori S, Harasawa H, Takahashi K, Kimoto M, Abe-Ouchi A, Nakajima T, Takemura T, Numaguti A (2001) Future climate change: Implications for Indian summer monsoon and its variability. Curr Sci 81:1196–1207
Lin JC, Matsui T, Pielke RA Sr, Kummerow C (2006) Effects of biomass burning-derived aerosols on precipitation and clouds in the Amazon Basin: a satellite-based empirical study. J Geophys Res 111:D19204 (doi: 10.1029/2005JD006884)
Menon S, Hansen J, Nazarenko L, Luo Y (2002) Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science 297:2250–2503
Mitchell JFB, Johns TC, Gregory JM, Tett SFB (1995) Climate response to increasing levels of greenhouse gases and sulphate aerosols. Nature 376:501–504
Niyogi D, Chang H et al. (2004) Direct observations of the effects of aerosol loading on net ecosystem CO2 exchanges over different landscapes. Geophys Res Lett 31:L20506 (doi: 10.1029/2004GL020915)
Peterson T, Golubev V, Groisman P (1995) Evaporation losing its strength. Nature 377:687–688
Pielke RA Sr (2002) Mesoscale meteorological modeling, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Pinker RT, Zhang B, Dutton EG (2005) Do satellites detect trends in surface solar radiation? Science 308:850–854
Pielke RA Sr, Adegoke JO, Chase TN, Marshall CH, Matsui T, Niyogi D (2006) A new paradigm for assessing the role of agriculture in the climate system and in climate change. Agric For Meteorol (doi: 10.1016/j.agformet.2006.06.012)
Pielke RA Sr et al (2002) The influence of land-use change and landscape dynamics on the climate system- relevance to climate change policy beyond the radiative effect of greenhouse gases. Philos Trans A360:1705–1719
Qian Y, Leung R, Ghan SJ, Giorgi F (2003) Regional climate effects of aerosols over China: modeling and observation. Tellus B 55:914–934
Ramanathan V et al (2005) Atmospheric brown clouds: impacts on South Asian climate and hydrological cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5326–5333
Ramanathan V, Crutzen PJ, Kiehl JT, Rosenfeld D (2001a) Aerosols, climate, and the hydrological cycle. Science 294:2119–2124
Ramanathan V et al. (2001b) Indian Ocean experiment: an integrated analysis of the climate forcing and effects of the great Indo-Asian haze. J Geophys Res 106:371–398
Reichenau T, Esser G (2003) Is interannual fluctuation of atmospheric CO2 dominated by combined effects of ENSO and volcanic aerosols? Global Biogeochem Cycles 17(4):1094 (doi: 10.1029/2002GB002025)
Robock A (2000) Volcanic eruptions and climate. Rev Geophys 38:191–219
Roderick M, Farquhar G (2002) The cause of decreased pan evaporation over the past 50 years. Science 298:1410–1411
Roderick M, Farquhar GD, Berry SL, Noble IR (1999) On the direct effect of clouds and atmospheric particles on the productivity and structure of vegetation. Oecologia 129:21–30
Yu H, Dickinson M, Chin YJ, et al. (2004) The direct radiative effect of aerosols as determined from a combination of MODIS retrievals and GOCART simulations. J Geophys Res 109:D03206 (doi:10.1029/2003JD003914)
Yu H, Liu SC, Dickinson RE (2002) Radiative effects of aerosols on the evolution of the atmospheric boundary layer. J Geophys Res 107:4142 (doi:10.1029/2001JD000754)
Wild M, Gilgen H, Roesch A, Ohmura A, Long CN, Dutton EG, Forgan B, Kallis A, Russak V, Tsvetkov A (2005) From dimming to brightening: decadal changes in solar radiation at Earth’s surface. Science 308:847–850
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niyogi, D., Chang, HI., Chen, F. et al. Potential impacts of aerosol–land–atmosphere interactions on the Indian monsoonal rainfall characteristics. Nat Hazards 42, 345–359 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-006-9085-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-006-9085-y