Abstract
Mutations in the tyrosine aminotransferase gene have been identified to cause tyrosinemia type II which is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Studies have demonstrated that an excessive production of ROS can lead to reactions with macromolecules, such as DNA, lipids, and proteins. Considering that the l-tyrosine may promote oxidative stress, the main objective of this study was to investigate the in vivo effects of l-tyrosine on DNA damage determined by the alkaline comet assay, in brain and blood of rats. In our acute protocol, Wistar rats (30 days old) were killed 1 h after a single intraperitoneal l-tyrosine injection (500 mg/kg) or saline. For chronic administration, the animals received two subcutaneous injections of l-tyrosine (500 mg/kg, 12-h intervals) or saline administered for 24 days starting at postnatal day (PD) 7 (last injection at PD 31), 12 h after the last injection, the animals were killed by decapitation. We observed that acute administration of l-tyrosine increased DNA damage frequency and damage index in cerebral cortex and blood when compared to control group. Moreover, we observed that chronic administration of l-tyrosine increased DNA damage frequency and damage index in hippocampus, striatum, cerebral cortex and blood when compared to control group. In conclusion, the present work demonstrated that DNA damage can be encountered in brain from animal models of hypertyrosinemia, DNA alterations may represent a further means to explain neurological dysfunction in this inherited metabolic disorder and to reinforce the role of oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of tyrosinemia type II.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buist NRM, Kennaway NG, Fellmann JH (1985). In: Bickel H, Wachtel U (eds) Inherited diseases of amino acid metabolism. Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 203–235
Goldsmith LA, Kang V, Bienfang DC, Jimbow K, Gerald P, Baden HP (1973) Tyrosinemia with plantar and palmar keratosis and keratitis. J Pediatr 83:798–805
Mitchell GA, Grompe M, Lambert M, Tanguay RM (2001) Hypertyrosinemia. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle Valle D (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1977–1982
Fois A, Borgogni P, Cioni M, Molinelli M, Frezzotti R, Bardelli AM, Lasorella G, Barberi L, Durand P, DoRocco M, Romano C, Parini R, Cirbetta C, Giovanninim G, Riva E, Balato N, Sartorio R, Mollica F, Zammarchi E, Battini ML (1986) Presentation of the data of the Italian registry for oculocutaneous tyrosinemia. J Inherit Metab Dis 9:S262–S263
Charfeddine C, Monastiri K, Mokni M, Laadjimi A, Kaabachi N, Perin O, Nilges M, Kassar S, Keirallah M, Guediche MN, Kamoun MR, Tebib N, Ben Dridi MF, Boubaker S, Ben Osman A, Abdelhak S (2006) Clinical and mutational investigations of tyrosinemia type II in northern Tunisia: identification and structural characterization of two novel TAT mutations. Mol Genet Metab 88:184–191
Huhn R, Stoermer H, Klingele B, Bausch E, Fois A, Farnetani M, Di Rocco M, Boue J, Kirk JM, Coleman R, Scherer G (1998) Novel and recurrent tyrosine aminotransferase gene mutations in tyrosinemia type II. Hum Genet 102:305–313
Meissner T, Betz RC, Pasternack SM, Eigelshoven S, Ruzicka T, Kruse R, Laitenberger G, Mayatepek E (2008) Richnere Hanhart syndrome detected by expanded newborn screening. Pediatr Dermatol 25:378–380
Natt E, Kao FT, Rettenmeier R, Scherer G (1986) Assignment of the human tyrosine aminotransferase gene to chromosome 16. Hum Genet 72:225–228
Greengard O, Andersson SM, Raiha NCR, Ohisalo JJ (1970) In biochemical actions of hormones. J Dev Physiol 2:17–27
Chakrapani A, Holme E (2006) Disorders of tyrosine metabolism. In: Fernandes J, Saudubray JM, Van den Berghe G, Walter JM (eds) Inborn metabolic diseases: diagnosis and treatment, 4th edn. Springer, Würzburg, pp 233–243
Maydan G, Andresen BS, Madsen PP, Zeigler M, Raas-Rothschild A, Zlotogorski A, Gutman A, Korman SH (2006) TAT gene mutation analysis in three Palestinian kindreds with oculocutaneous tyrosinaemia type II; characterization of a silent exonic transversion that causes complete missplicing by exon 11 skipping. J Inherit Metab Dis 29:620–626
Liu Z, Martin LJ (2001) Motor neurons rapidly accumulate DNA single-strand breaks after in vitro exposure to nitric oxide and peroxynitrite and in vivo axotomy. J Comp Neurol 432:35–60
Martin LJ, Liu Z (2002) DNA damage profiling in motor neurons: a single-cell analysis by comet assay. Neurochem Res 27:1093–1104
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayaski H, Miyamol Y, Rojas E, Ryu JC, Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and an in vivo genetic toxicological testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221
Sgaravatti AM, Vargas BA, Zandoná BR, Deckmann KB, Rockenback FJ, Moraes TB, Monserrat JM, Sgarbi MB, Pederzolli CD, Wyse ATS, Wannmacher CMD, Wajner M, Dutra-Filho CS (2008) Tyrosine promotes oxidative stress in cerebral cortex of young rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 26:553–559
Sgaravatti AM, Magnusson AS, de Oliveira AS, Rosa AP, Mescka CP, Zanin FR, Pederzolli CD, Wyse AT, Wannmacher CM, Wajner M, Dutra-Filho CS (2009) Tyrosine administration decreases glutathione and stimulates lipid and protein oxidation in rat cerebral cortex. Metab Brain Dis 24:415–425
Macêdo LG, Carvalho-Silva M, Ferreira GK, Vieira JS, Olegário N, Gonçalves RC, Vuolo FS, Ferreira GC, Schuck PF, Dal-Pizzol F, Streck EL (2013) Effect of acute administration of l-tyrosine on oxidative stress parameters in brain of young rats. Neurochem Res 38:2625–2630
Morre MC, Hefti F, Wurtman RJ (1980) Regional tyrosine levels in rat brain after tyrosine administration. J Neural Transm 49:45–50
Bongiovanni R, Yamamoto BK, Simpson C, Jaskiw GE (1980) Pharmacokinetics of systemically administered tyrosine: a comparison of serum, brain tissue and in vivo microdialysate levels in the rat. J Neurochem 87(1980):310–317
Singh N, McCoy M, Tice R, Schneider E (1988) A simple technique for quantification of low levels of DNA damage in individuals cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Collins AR (2004) The comet assay for DNA damage and repair: principles, applications, and limitations. Mol Biotechnol 26:249–261
Lindahl T (1993) Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA. Nature 362:709–715
Rao KS (1993) Genomic damage and its repair in young and aging brain. Mol Neurobiol 7:23–48
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (2001) Oxidative stress: adaptation, damage, repair and death. In: Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (eds) Free radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 246–350
Cooke MS, Olinski R, Evans MD (2006) Does measurement of oxidative damage to DNA have clinical significance? Clin Chim Acta 365:30–49
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantization of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Speit G, Hartmann A (1995) The contribution of excision repair to the DNA effects seen in the alkaline single cell gel test (comet assay). Mutagenesis 10:555–559
Salguero G, Akin E, Templin C, Kotlarz D, Doerries C, Landmesser U, Grote K, Schieffer B (2008) Renovascular hypertension by two-kidney one-clip enhances endothelial progenitor cell mobilization in a p47phox-dependent manner. J Hypertens 26:257–268
Sachse A, Wolf G (2007) Angiotensin II-induced reactive oxygen species and the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2439–2446
Wolf G (2005) Role of reactive oxygen species in angiotensin II mediated renal growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. Antioxid Redox Signal 7:1337–1345
Gill PS, Wilcox CS (2006) NADPH oxidases in the kidney. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1597–1607
Touyz RM (2004) Reactive oxygen species and angiotensin II signaling in vascular cells: implications in cardiovascular disease. Braz J Med Biol Res 37:1263–1273
Zhong N, Xu J (2008) Synergistic activation of the human MnSOD promoter by DJ-1 and PGC-1α: regulation by SUMOylation and oxidation. Hum Mol Genet 17:3357–3367
Madsen-Bouterse SA, Zhong Q, Mohammad G, Ho YS, Kowluru RA (2010) Oxidative damage of mitochondrial DNA in diabetes and its protection by manganese superoxide dismutase. Free Radic Res 44:313–321
Schmid U, Stopper H, Schweda F, Queisser N, Schupp N (2008) Angiotensin II induces DNA damage in the kidney. Cancer Res 68:9239–9246
Martin LJ, Pan Y, Price AC, Sterling W, Compeland NG, Jenkins NA, Price DL, Lee MK (2006) Parkinson’s disease α-synuclein transgenic mice develop neuronal mitochondrial degeneration and cell death. J Neurosci 26:41–50
Martin LJ, Liu Z, Chen K, Price AC, Pan Y, Swaby JA, Golden WC (2007) Motor neuron degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mutant superoxide dismutase-1 transgenic mice: mechanisms of mitochondriopathy and cell death. J Comp Neurol 500:20–46
Ferreira GK, Scaini G, Carvalho-Silva M, Gomes LM, Borges LS, Vieira JS, Constantino LS, Ferreira GC, Schuck PF, Streck EL (2013) Effect of l-tyrosine in vitro and in vivo on energy metabolism parameters in brain and liver of young rats. Neurotox Res 23:327–335
Gruno M, Peet N, Tein A, Salupere R, Sirotkina M, Valle J, Peetsalu A, Seppet EK (2008) Atrophic gastritis: deficient complex I of the respiratory chain in the mitochondria of corpus mucosal cells. J Gastroenterol 43:780–788
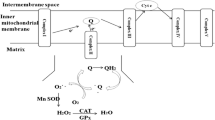
Adam-Vizi V (2005) Production of reactive oxygen species in brain mitochondria: contribution by electron transport chain and non-electron transport chain sources. Antioxid Redox Signal 7:1140–1149
Stoerner JW, Butler IJ, Morriss FH Jr, Howell RR Jr, Seifert WE Jr, Caprioli RM, Adcock EW, Denson SE (1980) CSF neurotransmitter studies: an infant with ascorbic acid-responsive tyrosinemia. Am J Dis Child 134:492–494
Jana S, Sinha M, Chanda D, Roy T, Banerjee K, Munshi S, Patro BS, Chakrabarti S (2011) Mitochondrial dysfunction mediated by quinone oxidation products of dopamine: implications in dopamine cytotoxicity and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812:663–673
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Grants from Programa de Pós-graduação em Ciências da Saúde—Universidade do Extremo Sul Catarinense (UNESC) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Prá, S.D.T., Ferreira, G.K., Carvalho-Silva, M. et al. l-Tyrosine Induces DNA Damage in Brain and Blood of Rats. Neurochem Res 39, 202–207 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1207-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1207-9