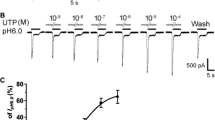
We examined effects of purotoxin 1 (PT1), a component of the venom of Geolycosa spiders, on a few voltageand ligand-operated ion channels present in the plasma membrane of sensory neurons from the rat dorsal root ganglia (DRGs). Purotoxin 1 in a 100 nM concentration evoked no changes in ion currents through voltage-operated sodium, potassium, and calcium channels in the membranes of isolated sensory neurons. This agent was also found to be ineffective with respect to capsaicin-sensitive receptor-channel complexes (TRPV1). Testing of the effects of PT1 on purinergic receptor-channel complexes P2X3, P2X2, and P2X2/3 showed that this toxin is a highly selective blocker of exclusively P2X3 receptors. The selectivity of action of PT1 demonstrated in our experiments shows that it is a unique agent, which opens up new prospects in the studies of structural/functional peculiarities of receptor-channel complexes P2X3 as a peripheral link of the nociception system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. J. Craik, N. L. Daly, and C. Waine, “The cystine knot motif in toxins and implications for drug design,” Toxicon, 39, 43–60 (2001).
R. S. Norton and P. K. Pallaghy, “The cystine knot structure of ion channel toxins and related polypeptides,” Toxicon, 36, 1573–1583 (1998).
N. W. Isaacs, “Cystine knots,” Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 5, 391–395 (1995).
A. A. Vassilevski, S. A. Kozlov, and E. V. Grishin, “Molecular diversity of spider venom,” Biochemistry, 74, 1505–1534 (2009).
E. V. Grishin, G. A. Savchenko, A. A. Vassilevski, et al., “Novel peptide from spider venom inhibits P2X3 receptors and inflammatory pain,” Ann. Neurol., 67, 680–683 (2010).
O. P. Hamill, A. Marty, E. Neher, et al., “Improved patchclamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches,” Pflügers Arch., 391, 85–100 (1981).
Y. Pankratov, U. V. Lalo, A. N. Dashkin, et al., “Heterogeneity of the functional expression of P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors in the primary nociceptive neurons of rat,” Neurochem. Res., 26, 993–1000 (2001).
R. J. Docherty, J. C. Yeats, and A. S. Piper, “Capsazepine block of voltage-activated calcium channels in adult rat dorsal root ganglion neurones in culture,” Br. J. Pharmacol., 121, 1461–1467 (1997).
V. Spelta, L. H. Jiang, A. Surprenant, et al., “Kinetics of antagonist actions at rat P2X2/3 heteromeric receptors,” Br. J. Pharmacol., 135, 1524–1530 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Neirofiziologiya/Neurophysiology, Vol. 42, No. 6, pp. 466–470, November-December, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savchenko, G.A., Volkova, T.M., Vasilevskii, A.A. et al. Purinergic Membrane Receptors as Targets for the Effect of Purotoxin 1, a Component of Venom of Spiders from the Geolycosa Genus. Neurophysiology 42, 387–391 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-011-9173-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-011-9173-9