Abstract
Purpose
Brain metastases can be radiographically cystic or solid. Cystic metastases are associated with a greater intracranial disease burden and poorer oncologic outcomes, but the impact of cystic versus solid appearance on local control after radiation remains unknown. We investigated whether cystic versus solid nature is predictive of local control after management with stereotactic or whole brain radiation (WBRT) and whether the radiation modality utilized is an effect modifier.
Methods
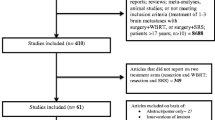
We identified 859 patients with 2211 newly-diagnosed brain metastases managed with upfront stereotactic radiation or WBRT without preceding resection/aspiration at Brigham and Women’s Hospital/Dana-Farber Cancer Institute between 2000 and 2015. Multivariable Cox regression with an interaction term and sandwich covariance matrix was used to quantify local failure.
Results
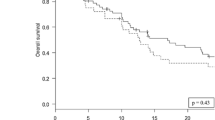
Cystic lesions were more likely to recur than solid ones when managed with stereotactic radiation (HR 2.33, 95% CI 1.32–4.10, p = 0.004) but not WBRT (HR 0.92, 95% CI 0.62–1.36, p = 0.67), p-interaction = 0.007. 1 year local control rates for cystic versus solid metastases treated with stereotactic radiation were 75% versus 88%, respectively; estimates with WBRT were 76% versus 76%, respectively. However, no significant differences were noted between the two cohorts in post-radiation outcomes including all-cause mortality and neurologic death (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
Among patients with brain metastases, stereotactic radiation yields improved local control and less morbidity than WBRT, and consequently for many patients the cystic versus solid designation does not impact treatment selection. However, our results suggest that in patients with a large number of cystic brain metastases, a lower threshold to consider WBRT, as opposed to stereotactic radiation, should be employed. If our results can be confirmed, further investigation into the underlying mechanism(s) would be warranted.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cagney DN, Martin AM, Catalano PJ, Redig AJ, Lin NU, Lee EQ, Wen PY, Dunn IF, Bi WL, Weiss SE, Haas-Kogan DA, Alexander BM, Aizer AA (2017) Incidence and prognosis of patients with brain metastases at diagnosis of systemic malignancy: a population-based study. Neuro-oncology https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nox077
Nayak L, Lee EQ, Wen PY (2012) Epidemiology of brain metastases. Curr Oncol Rep 14:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-011-0203-y
Muldoon LL, Soussain C, Jahnke K, Johanson C, Siegal T, Smith QR, Hall WA, Hynynen K, Senter PD, Peereboom DM, Neuwelt EA (2007) Chemotherapy delivery issues in central nervous system malignancy: a reality check. J Clin Oncol 25:2295–2305. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.09.9861
Brown PD, Jaeckle K, Ballman KV, Farace E, Cerhan JH, Anderson SK, Carrero XW, Barker FG 2nd, Deming R, Burri SH, Menard C, Chung C, Stieber VW, Pollock BE, Galanis E, Buckner JC, Asher AL (2016) Effect of radiosurgery alone versus radiosurgery with whole brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 316:401–409. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.9839
Fink KR, Fink JR (2013) Imaging of brain metastases. Surg Neurol Int 4:S209–S219. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.111298
Sun B, Huang Z, Wu S, Ding L, Shen G, Cha L, Wang J, Song S (2016) Cystic brain metastasis is associated with poor prognosis in patients with advanced breast cancer. Oncotarget 7:74006–74014. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12176
Higuchi F, Kawamoto S, Abe Y, Kim P, Ueki K (2012) Effectiveness of a 1-day aspiration plus Gamma Knife surgery procedure for metastatic brain tumor with a cystic component. J Neurosurg 117 Suppl:17–22. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.7.GKS121001
Wang H, Qi S, Dou C, Ju H, He Z, Ma Q (2016) Gamma Knife radiosurgery combined with stereotactic aspiration as an effective treatment method for large cystic brain metastases. Oncol Lett 12:343–347. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.4603
Kim M, Cheok S, Chung LK, Ung N, Thill K, Voth B, Kwon DH, Kim JH, Kim CJ, Tenn S, Lee P, Yang I (2015) Characteristics and treatments of large cystic brain metastasis: radiosurgery and stereotactic aspiration. Brain Tumor Res Treat 3:1–7. https://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2015.3.1.1
Lee SR, Oh JY, Kim SH (2016) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for cystic brain metastases. Br J Neurosurg 30:43–48. https://doi.org/10.3109/02688697.2015.1039489
Park WH, Jang IS, Kim CJ, Kwon DH (2009) Gamma knife radiosurgery after stereotactic aspiration for large cystic brain metastases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 46:360–364. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2009.46.4.360
Franzin A, Vimercati A, Picozzi P, Serra C, Snider S, Gioia L, Ferrari da Passano C, Bolognesi A, Giovanelli M (2008) Stereotactic drainage and gamma knife radiosurgery of cystic brain metastasis. J Neurosurg 109:259–267. https://doi.org/10.3171/JNS/2008/109/8/0259
Oshima A, Kimura T, Akabane A, Kawai K (2017) Optimal implantation of ommaya reservoirs for cystic metastatic brain tumors preceding gamma knife radiosurgery. J Clin Neurosci 39:199–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2016.12.042
Yamanaka Y, Shuto T, Kato Y, Okada T, Inomori S, Fujino H, Nagano H (2006) Ommaya reservoir placement followed by Gamma Knife surgery for large cystic metastatic brain tumors. J Neurosurg 105 Suppl:79–81. https://doi.org/10.3171/sup.2006.105.7.79
Seymour ZA, Fogh SE, Westcott SK, Braunstein S, Larson DA, Barani IJ, Nakamura J, Sneed PK (2015) Interval from imaging to treatment delivery in the radiation surgery age: how long is too long? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 93:126–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.05.001
Horky LL, Hsiao EM, Weiss SE, Drappatz J, Gerbaudo VH (2011) Dual phase FDG-PET imaging of brain metastases provides superior assessment of recurrence versus post-treatment necrosis. J Neurooncol 103:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0365-8
Cagney DN, Martin AM, Catalano PJ, Reitman ZJ, Mezochow GA, Lee EQ, Wen PY, Weiss SE, Brown PD, Ahluwalia MS, Arvold ND, Tanguturi SK, Haas-Kogan DA, Alexander BM, Redig AJ, Aizer AA (2018) Impact of pemetrexed on intracranial disease control and radiation necrosis in patients with brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer receiving stereotactic radiation. Radiother Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2018.01.005
Martin AM, Cagney DN, Catalano PJ, Alexander BM, Redig AJ, Schoenfeld JD, Aizer AA (2018) Immunotherapy and symptomatic radiation necrosis in patients with brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiation. JAMA Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3993
Lin DY (1994) Cox regression analysis of multivariate failure time data: the marginal approach. Stat Med 13:2233–2247
Ebinu JO, Lwu S, Monsalves E, Arayee M, Chung C, Laperriere NJ, Kulkarni AV, Goetz P, Zadeh G (2013) Gamma knife radiosurgery for the treatment of cystic cerebral metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85:667–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.06.043
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG, Arbuckle RB, Swint JM, Shiu AS, Maor MH, Meyers CA (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:1037–1044. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-204
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villa S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortmann RD, Carrie C, Ben Hassel M, Kouri M, Valeinis E, van den Berge D, Collette S, Collette L, Mueller RP (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.30.1655
Soffietti R, Kocher M, Abacioglu UM, Villa S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortmann RD, Carrie C, Ben Hassel M, Kouri M, Valeinis E, van den Berge D, Mueller RP, Tridello G, Collette L, Bottomley A (2013) A European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase III trial of adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation in patients with one to three brain metastases from solid tumors after surgical resection or radiosurgery: quality-of-life results. J Clin Oncol 31: 65–72 https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.41.0639JCO.2011.41.0639
Brown PD, Ballman KV, Cerhan JH, Anderson SK, Carrero XW, Whitton AC, Greenspoon J, Parney IF, Laack NNI, Ashman JB, Bahary JP, Hadjipanayis CG, Urbanic JJ, Barker FG 2nd, Farace E, Khuntia D, Giannini C, Buckner JC, Galanis E, Roberge D (2017) Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC.3): a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:1049–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30441-2
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, Dinapoli R, Kline R, Loeffler J, Farnan N (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90 – 05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Martin AM, Cagney DN, Catalano PJ et al (2017) Immunotherapy and radiation necrosis in patients with brain metastases managed with stereotactic radiation. JAMA Oncology. In press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
This study was approved by the Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women’s Cancer Institute Institutional Review Board. Informed consent was waived.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brigell, R.H., Cagney, D.N., Martin, A.M. et al. Local control after brain-directed radiation in patients with cystic versus solid brain metastases. J Neurooncol 142, 355–363 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03106-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03106-1