Abstract
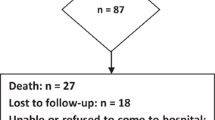
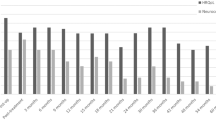
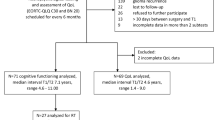
Ginkgo biloba has been reported to improve cognitive function in older adults and patients with Alzheimer’s disease and multi-infarct dementia. We conducted an open-label phase II study of this botanical product in symptomatic irradiated brain tumor survivors. Eligibility criteria included: life expectancy ≥30 weeks, partial or whole brain radiation ≥6 months before enrollment, no imaging evidence of tumor progression in previous 3 months, or stable or decreasing steroid dose, and no brain tumor treatment planned while on study. The Ginkgo biloba dose was 120 mg/day (40 mg t.i.d.) for 24 weeks followed by a 6-week washout period. Assessments performed at baseline, 12, 24 (end of treatment), and 30 weeks (end of washout) included KPS, Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Brain (FACT-Br), Profile of Mood States, Mini-Mental Status Exam, Trail Making Test Parts A (TMT-A) and B (TMT-B), Digit Span Test, Modified Rey Osterrieth Complex Figure (ROCF), California Verbal Learning Test Part II, and the F-A-S Test. Results: Of the 34 patients enrolled on study, 23 (68 %) completed 12 weeks of treatment and 19 (56 %) completed 24 weeks of treatment. There were significant improvements at 24 weeks in: executive function (TMT-B) (p = 0.007), attention/concentration (TMT-A) (p = 0.002), and non-verbal memory (ROCF—immediate/delayed recall) (p = 0.001/0.002), mood (p = 0.002), FACT-Br subscale (p = 0.001), and the FACT physical subscale (p = 0.003). Conclusions: Some improvement in quality of life and cognitive function were noted with Ginkgo biloba. However, treatment with Ginkgo biloba was associated with a high dropout rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loeffler JS, Patchell RA, Sawaya R (1999) Metastatic brain cancer. In: DeVita VT, JR, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA (eds) Cancer principles and practice of oncology, 5th edn. Lippencott, Raven, pp 2523–2535
Patchell RA (1997) Brain metastases. In: Black Peter McL, Loeffler JS (eds) Cancer of the nervous system. Blackwell, Cambridge, pp 653–663
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62(1):10–29
DeAngelis LM, Delattre J, Posner JB (1989) Radiation-induced dementia in patients cured of metastases. Neurology 39:789–796
Crossen JR, Garwood D, Glatstein E, Neuwelt E (1994) Neurobehavioral sequelae of cranial irradiation in adults: a review of radiation-induced encephalopathy. J Clin Oncol 12(3):627–642
Laukkanen E, Klonof H, Allan B et al (1988) The role of prophylactic brain irradiation in limited stage small-cell lung cancer: clinical, neuropsychological, and CT sequelae. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 14:1109–1117
Johnson BE, Becker B, Goff WB et al (1985) Neurologic, neuropsychologic, and computed cranial tomography scan abnormalities in 2- to 10-year survivors of small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 3:1659–1667
Kiebert GM, Curran D, Aaronson NK et al (1998) Quality of life after radiation therapy of cerebral low-grade gliomas of the adult: results of randomized phase III trial on dose response (EORTC trial 22844). EORTC radiotherapy co-operative group. Eur J Cancer 34(12):1902–1909
Archibald YM, Lunn D, Ruttan LA et al (1994) Cognitive functioning in long-term survivors of high-grade glioma. J Neurosurg 80:247–253
Meyers CA, Boake C (1993) Neurobehavioral disorders in brain tumor patients: rehabilitation strategies. Cancer Bull 45:362–364
Imperato JP, Paleologos NA, Vick NA (1990) Effects of treatment on long term survivors with malignant astrocytomas. Ann Neurol 28:818–822
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR et al (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:1037–1044
Weitzner MA, Meyers CA (1977) Cognitive functioning and quality of life in malignant glioma patients: a review of the literature. Psycho-Oncol 6(3):169–177
Corn BW, Yousem D, Scott CB et al (1994) White matter changes are correlated significantly with radiation dose: observations from randomized dose-escalation trial for malignant glioma (radiation therapy oncology group 83-02). Cancer 74:2828–2835
Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A et al (1987) MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. Am J Roentgenol 8:421–426
Rogers SL, Doody RS, Mohs RC et al (1998) Donepezil improves cognition and global function in Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Int Med 158:1021–1031
Le Bars PL, Katz MM, Berman N et al (1997) A placebo-controlled, double-blinded, randomized trial of an extract of Ginkgo biloba for dementia. JAMA 278:1327–1332
Jorm AF, Rodgers B, Christensen H (2004) Use of medications to enhance memory in a large community sample of 60–64 year olds. Int Psychogeriatr 16:209–217
DeKosky ST, Williamson JD, Fitzpatrick AL et al (2008) Ginkgo biloba for prevention of dementia: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 300(19):2253–2262
Snitz BE, O’Meara ES, Carlson MC et al (2009) Ginkgo biloba for preventing cognitive decline in older adults: a randomized trial. JAMA 302:2663–2670
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini Mental State”: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Reitan R (1958) Validity of the Trail Making Test as an indicator of organic brain damage. Percept Mot Skills 8:271–276
Wechsler D (1981) Wechsler adult intelligence scale-revised. Psychological Corporation, New York
Fastenau PS, Denburg NL, Hufford BJ (1999) Adult norms for the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test and for supplemental recognition and matching trials from the Extended Complex Figure Test. Clin Neuropsychol 13:30–47
Benton AL, Hamsher K (1983) Multilingual aphasia examination. AJA Associates, Iowa City
Delis DC, Kramer JH, Kaplan E et al (2000) California Verbal Learning Test-II. Psychological Corporation, New York
Weitzner MA, Meyers CA, Gelke CK et al (1995) The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy (FACT) scale: development of a brain subscale and revalidation of the general version (FACT-G) in patients with primary brain tumors. Cancer 75:1151–1161
McNair DM, Lorr M, Droppleman LF (1992) Profile of mood states manual. Educational and Industrial Testing Service, San Diego
Bak JS, Green RL (1980) Changes in neuropsychological functioning in an aging population. J Consult Clin Psychol 48:395–399
Dupont WD, Plummer WD Jr (1990) Power and sample size calculations: a review and computer program. Control Clin Trials 11:116–128
Kleijnen J, Knipschild P (1992) Ginkgo biloba. Lancet 340:1136–1474
Cott J (1995) Natural product formulations available in Europe for psychotropic indications. Psychopharmacol Bull 31:745–751
Ni Y, Zhao B, Hou J, Xin W (1996) Preventative effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on apoptosis in rats cerebellar neuronal cells induced by hydroxyl radicals. Neurosci Lett 214:115–118
Oyama Y, Chikahisa L, Ueha T et al (1996) Ginkgo biloba extract protects brain neurons against oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide. Brain Res 712:349–352
Klein J, Chatterjee SS, Löffelholz K (1997) Phospholipid breakdown and choline release under hypoxic conditions: inhibition by bilobalide, a constituent of Ginkgo biloba. Brain Res 755:347–350
Emerit I, Arutyunyan R, Oganesian N et al (1995) Radiation-induced clastogenic factors: anti-clastogenic effect of Ginkgo biloba extract. Free Radical Biol Med 18:985–991
Dumont E, Petit E, Tarrade T et al (1992) UV-C irradiation-induced peroxidative degradation of microsomal fatty acids in proteins: protection by an extract of Ginkgo biloba. Free Radical Biol Med 13:197–203
Regine WF, Schmitt FA, Scott CB et al (2004) Feasibility of neurocognitive outcome evaluations in patients with brain metastases in a multi-institutional cooperative group setting: results of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group trial BR-0018. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:1346–1352
Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC et al (2005) Radiosurgery with or without whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases: the patients’ perspective regarding complications. Am J Clin Oncol 28:173–179
Duffner PK (2004) Long-term effects of radiation therapy on cognitive and endocrine function in children with leukemia and brain tumors. Neurologist 10:293–310
Levin VA, Yung WK, Bruner J et al (2002) Phase II study of accelerated fractionation radiation therapy with carboplatin followed by PCV chemotherapy for the treatment of anaplastic gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:58–66
Weitzner MA, Meyers CA, Valentine AD (1995) Methylphenidate in the treatment of neurobehavioral slowing associated with cancer and cancer treatment. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 7:347–350
Meyers CA, Weitzner MA, Valentine AD et al (1998) Methylphenidate therapy improves cognition, mood, and function of brain tumor patients. J Clin Oncol 16:2522–2527
McCaffrey RJ, Westervelt HJ (1995) Issues associated with repeated neuropsychological assessments. Neuropsychol Rev 5:203–221
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by NIH/NCI/DCP Grant 2 U10 CA 81851-09-13. There are no financial disclosures from any authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attia, A., Rapp, S.R., Case, L.D. et al. Phase II study of Ginkgo biloba in irradiated brain tumor patients: effect on cognitive function, quality of life, and mood. J Neurooncol 109, 357–363 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0901-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0901-9