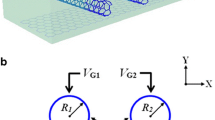
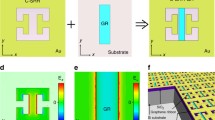
Abstract
Graphene plasmonics has been introduced as a novel platform to design various nano- and microstructures to function in a wide range of spectrum from optical to THz frequencies. Herein, we propose a tunable plasmonic metamaterial in the THz regime by using metallic (silver) concentric microscale split ring resonator arrays on a multilayer metasurface composed of silica and silicon layers. We obtained an absorption percentage of 47.9% including two strong Fano resonant dips in THz regime for the purely plasmonic metamaterial without graphene layer. Considering the data of an atomic graphene sheet (with the thickness of ~0.35 nm) in both analytical and experimental regimes obtained by prior works, we employed a graphene layer under concentric split ring resonator arrays and above the multilayer metasurface to enhance the absorption ratio in THz bandwidth. Our numerical and analytical results proved that the presence of a thin graphene layer enhances the absorption coefficient of MM to 64.35%, at the highest peak in absorption profile that corresponds to the Fano dip position. We also have shown that changing the intrinsic characteristics of graphene sheet leads to shifts in the position of Fano dips and variations in the absorption efficiency. The maximum percentage of absorption (~67%) was obtained for graphene-based MM with graphene layer with dissipative loss factor of 1477 Ω. Employing the antisymmetric feature of the split ring resonators, the proposed graphene-based metamaterial with strong polarization dependency is highly sensitive to the polarization angle of the incident THz beam.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadivand A, Pala N (2014) Plasmon response of a metal-semiconductor 4π-spiral as a negative-index metamaterial. J Nanopart Res 16:2764
Ahmadivand A, Pala N (2015) Tailoring negative-refractive index metamaterials composed of semiconductor-metal-semiconductor gold ring/disk cavity heptamers to support strong Fano resonances in the visible spectrum. J Opt Soc Am A 32:204–212
Ahmadivand A, Sinha R, Gerislioglu B, Karabiyik M, Pala N, Shur MS (2016) Transition from capacitive coupling to direct charge transfer in asymmetric terahertz plasmonic assemblies. Opt Lett 41:5333–5336
Al-Naib IAI, Jansen C, Born N, Koch M (2011) Polarization and angle independent terahertz metamaterials with high Q-factors. Appl Phys Lett 98:091107
Bahl I, Bhartia P (1988) Microwave solid state circuit design. Wiley, New York
Bao Q, Loh KP (2012) Graphene photonics, plasmonics, and broadband optoelectronic devices. ACS Nano 6:3677–3694
Campione S, Guclu C, Ragan R, Capolino F (2014) Enhanced magnetic and electric fields via Fano resonances in metasurfaces of circular clusters of plasmonic nanoparticles. ACS Photonics 1:254–260
Cao W, Singh R, Zhang C, Han J, Tonouchi M, Zhang W (2013) Plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials: active near field coupling between bright superconducting and dark metallic mode resonators. Appl Phys Lett 103:101106
Capolino F (2009) Theory and phenomena of metamaterials. CRC Press, Tailor & Francis, US
Chakraborty C, Beams R, Goodfellow KM, Wicks GW, Novotny L, Vamivakas AN (2014) Optical antenna enhanced graphene photodetector. Appl Phys Lett 105:241114
Cheng Q, Cui TJ, Jiang WX, Cai BG (2010) An omnidirectional electromagnetic absorber made of metamaterial. New J Phys 12:063006
Cui Y, Fung KH, Xu J, Ma H, Jin Y, He S, Fang NX (2012) Ultrabroadband light absorption by a sawtooth anisotropic metamaterial slab. Nano Lett 12:1443–1447
Dikin DA, Stankovich S, Zimney EJ, Piner RD, Dommett GHB, Evmenenko G, Nguyen ST, Ruoff RS (2007) Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide paper. Nature 448:457–460
Draine BT, Flatau PJ (1994) Discrete-dipole approximation for scattering calculations. J Opt Soc Am A 11:1491–1499
Drosdoff D, Phan AD, Woods LM (2014) Transverse electric mode for near-field radiative heat transfer in graphene-metamaterial systems. Adv Opt Mater 2:1038–1042
Efetov DK, Kim P (2010) Controlling electron-photon interactions in graphene at ultrahigh carrier densities. Phys Rev Lett 105:256805
Fan Y, Zhang F, Zhao Q, Wei Z, Li H (2014) Tunable terahertz coherent perfect absorption in a monolayer graphene. Opt Lett 39:6269–6972
Fan Y, Shen NH, Koschny T, Soukoulis CM (2015) Tunable terahertz meta-surface with graphene cut-wires. ACS Photonics 2:151–156
Fang Z, Liu Z, Wang Y, Ajayan PM, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2012) Graphene-antenna sandwich photodetector. Nano Lett 12:3808–3813
Gao W, Shu J, Qiu C, Xu Q (2012) Excitation of plasmonic waves in graphene by guided-mode resonance. ACS Nano 6:7806–7813
Grigorenko AN, Polini M, Novoselov KS (2012) Graphene plasmonics. Nat Photonics 6:749–758
He Q, Wu S, Yin Z, Zhang H (2012) Graphene-based electronic sensors. Chem Sci 3:1764–1772
Huang Z, Koschny T, Soukoulis CM (2012) Theory of pump-probe experiments of metallic metamaterials coupled to a gain medium. Phys Rev Lett 108:187402
Jackson JD (1998) Classical electrodynamics. Wiley, New York
Jiang T, Zhao J, Feng Y (2009) Stopping light by an air waveguide with anisotropic metamaterial cladding. Opt Express 17:170–177
Jo S, Ki DK, Jeong D, Lee HJ, Kettemann S (2011) Spin relaxation properties in graphene due to its linear dispersion. Phys Rev B 84:075453
Ju L, Geng B, Horng J, Girit C, Martin M, Hao Z, Bechtel HA, Liang X, Zettl A, Shen YR, Wang F (2011) Graphene plasmonics for tunable terahertz metamaterials. Nat Nanotechnol 6:630–634
Koppens FHL, Chang DE, Javier Garcia de Abajo F (2011) Graphene plasmonics: a platform for strong light-matter interactions. Nano Lett 11:3370–3377
Lee SH, Choi M, Kim TT, Lee S, Liu M, Yin X, Choi HK, Lee SS, Choi CG, Choi SY, Zhang X, Min B (2012) Switching terahertz waves with gate-controlled active graphene metamaterials. Nat Mater 11:936–941
Li ZQ, Henriksen EA, Jiang Z, Hao Z, Martin MC, Kim P, Stormer HL, Basov DN (2008) Dirac charge dynamics in graphene by infrared spectroscopy. Nat Phys 4:532–535
Lide DR (2003) Handbook of chemistry and physics. CRC Press, Tailor & Francis, US
Liu M, Yin X, Ulin-Avila E, Geng B, Zentgraf T, Ju L, Wang F, Zhang X (2011) A graphene-based broadband optical modulator. Nature 474:64–67
Liu B, Sun Z, Zhang X, Liu J (2013) Mechanisms of DNA sensing on graphene oxide. Anal Chem 85:7987–7993
Low T, Avouris P (2014) Graphene plasmonics for terahertz to mid-infrared applications. ACS Nano 8:1086–1101
Marqués R, Medina F, Rafii-El-Idrissi R (2002) Role of bianisotropy in negative permeability and left-handed metamaterials. Phys Rev B 65:144440
Marqués R, Mesa F, Martel J, Medina F (2003) Comparative analysis of edge- and broadside-coupled split ring resonators for metamaterial design-theory and experiments. IEEE T Antenn Propag 51:2572–2581
Mattiucci N, D’Aguanno G, Alu A, Argyropoulos C, Foreman JV, Bloemer MJ (2012) Taming the thermal emissivity of metals: a metamaterial approach. Appl Phys Lett 100:201109
Mecklenburg M, Schuchardt A, Mishra YK, Kaps S, Adelung R, Lotnyk A, Kienle L, Schulte K (2012) Aerographite: ultra lightweight, flexible nanowall, carbon microtubes material with outstanding mechanical performance. Adv Mater 24:3486–3490
Miao X, Tongay S, Petterson MK, Berke K, Rinzler AG, Appleton BR, Hebard AF (2012) High efficiency graphene solar cells by chemical doping. Nano Lett 23:2745–2750
Neto AC, Guniea F, Peres NMR, Novoselov KS, Geim AK (2009) The electronic properties of graphene. Rev Mod Phys 80:109
Ni X, Emani NK, Kildishev AV, Boltasseva A, Shalaev VM (2012) Broadband light bending with plasmonic nanoantennas. Science 335:427
Palik ED (1997) Handbook of optical constants of solids. Academic Press, San Diego
Papasimakis N, Thongrattanasiri S, Zheludev NI, de Abajo FJG (2013) The magnetic response of graphene split-ring metamaterials. Light Sci Appl 2:e78
Ren X, Sha WEI, Choy WCH (2013) Tuning optical response of metallic dipole nanoantenna using graphene. Opt Express 21:31824–31829
Saenz E, Ikonen PMT, Gonzalo R, Tretyakov SA (2007) On the definition of effective permittivity and permeability for thin composite layers. J Appl Phys 101:114910
Shalaev VM (2007) Optical negative-index metamaterial. Nat Photonics 141-48(2007)
Shen NH, Tassin P, Koschny T, Soukoulis CM (2014a) Comparison of gold- and graphene-based resonant nanostructures for terahertz metamaterials and an ultrathin graphene-based modulator. Phys Rev B 90:115437
Shen NH, Tassin P, Koschny T, Soukoulis CM (2014b) Comparison of gold-and graphene based resonant nanostructures for terahertz metamaterials and an ultrathin graphene-based modulator. Phys Rev B 90:115437
Singh R, Al-Naib IAI, Koch M, Zhang W (2011) Sharp Fano resonances in THz metamaterials. Opt Express 19:6312–6319
Singh R, Cao W, Al-Naib I, Cong L, Withayachumnankul W, Zhang W (2014) Ultrasensitive terahertz sensing with high-Q Fano resonances in metasurfaces. Appl Phys Lett 105:171101
Smith DR, Pendry JB, Wiltshire MCK (2004) Metamaterials and negative refractive index. Science 305:788–792
Sun D, Aivazian G, Jones AM, Ross JS, Yao W, Cobden D, Xu X (2012) Ultrafast hot-carrier-dominated photocurrent in graphene. Nat Nanotechnol 7:114–118
Tamayama Y, Nakanishi T, Kitano M (2012) Visible group delay in a metamaterial with field-gradient-induced transparency. Phys Rev B 85:073102
Tassin P, Koschny T, Kafesaki M, Soukoulis CM (2012) A comparison of graphene, superconductors, and metals as conductors for metamaterial and plasmonics. Nat Photonics 6:259–264
Vakil A, Engheta N (2011) Transformation optics using graphene. Science 332:1291–1294
Wang X, Cheng Z, Xu K, Tsang HK, Xu JB (2013) High-responsivity graphene/silicon-heterostructure waveguide photodetectors. Nat Photonics 7:888–891
Wu MC, Deokar AR, Liao JH, Shih PY, Ling YC (2013) Graphene-based photothermal agent for rapid and effective killing of bacteria. ACS Nano 7:1281–1290
Wunsch B, Stauber T, Sols F, Guinea F (2006) Dynamical polarization of graphene at finite doping. New J Phys 8:318
Xiang G, Guo H, Zhang X, Sum TC, Huan CHA (2010) The physic of ultrafast saturable absorption in graphene. Opt Express 18:4564–4573
Xiang Q, Yu J, Jaroniec M (2012) Graphene-based semiconductor photocatalyst. Chem Soc Rev 41:782–796
Yan H, Xia F, Zhu W, Freitag M, Dimitrakopoulos C, Bol AA, Tulevski G, Avouris P (2011) Infrared spectroscopy of wafer-scale graphene. ACS Nano 5:9854–9860
Yang SH, Jarrahi M (2015) Frequency-tunable continuous-wave terahertz sources based on GaAs photomixers. Appl Phys Lett 107:131111
Yang K, Feng L, Shi X, Liu Z (2013) Nano-graphene in biomedicine: Theranostic applications. Chem Soc Rev 42:530–547
Yao Y, Kats MA, Genevet P, Yu N, Kong J, Capasso F (2013) Broad electrical tuning of graphene-loaded plasmonic nanoantennas. Nano Lett 13:1257–1264
Yao Y, Kats MA, Shankar R, Song Y, Kong J, Loncar M, Capasso F (2014) Wide wavelength tuning of optical antennas on graphene with nanosecond response time. Nano Lett 14:214–219
Zarrabi FB, Mohaghegh M, Bazgir M, Azezoomand AS (2016) Graphene-gold nano-ring antenna for dual-resonance optical application. Opt Mater 51:98–103
Zhang S, Park YS, Li J, Lu X, Zhang W, Zhang X (2009) Negative refractive index in chiral metamaterials. Phys Rev B 102:023901
Zhang N, Zhang Y, Xu YJ (2012) Recent progress on graphene photocatalysts: current status and future perspectives. Nanoscale 4:5792–5813
Zhao X, Zhang Z, Wang L, Xi K, Cao Q, Wang D, Yang Y, Du Y (2013) Excellent microwave absorption property of graphene-coated Fe nanocomposites. Sci Rep 3:3421
Acknowledgments
Raju Sinha gratefully acknowledges the financial support provided through dissertational year fellowship by the University Graduate School (UGS) at Florida International University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by NSF CAREER program with the award number 0955013, and by Army Research Laboratory (ARL) Multiscale Multidisciplinary Modeling of Electronic Materials (MSME) Collaborative Research Alliance (CRA) (Grant No. W911NF-12-2-0023, Program Manager: Dr. Meredith L. Reed).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadivand, A., Sinha, R., Karabiyik, M. et al. Tunable THz wave absorption by graphene-assisted plasmonic metasurfaces based on metallic split ring resonators. J Nanopart Res 19, 3 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3696-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3696-3