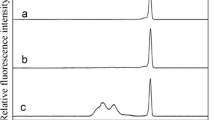
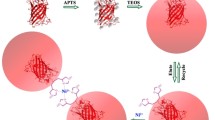
Abstract
How protein–protein interaction affects protein–nanoparticle self-assembly is the key to the understanding of biomolecular coating of nanoparticle in biological fluids. However, the relationship between protein shape and its interaction with nanoparticles is still under-exploited because of lack of a well-conceived binding system and a method to detect the subtle change in the protein–nanoparticle assemblies. Noticing this unresolved need, we cloned and expressed a His-tagged SpeA protein that adopts a bridge-shaped dimer structure, and utilized a high-resolution capillary electrophoresis method to monitor assembly formation between the protein and quantum dots (QDs, 5 nm in diameter). We observed that the bridge-shaped structure rendered a low SpeA:QD stoichiometry at saturation. Also, close monitoring of imidazole (Im) displacement of surface-bound protein revealed a unique two-step process. High-concentration Im could displace surface-bound SpeA protein and form a transient QD–protein intermediate, through a kinetically controlled displacement process. An affinity-driven equilibrium step then followed, resulting in re-assembling of the QD–protein complex in about 1 h. Through a temporarily formed intermediate, Im causes a rearrangement of His-tagged proteins on the surface. Thus, our work showcases that the synergistic interplay between QD–His-tag interaction and protein–protein interaction can result in unique properties of protein–nanoparticle assembly for the first time.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alivisatos AP (1996) Semiconductor clusters nanocrystals and quantum dots. Science 271:933–937
Bailey RE, Smith AM, Nie S (2004) Quantum dots in biology and medicine. Physica E 25:1–12
Blanco-Canosa JB, Medintz IL, Farrell D, Mattoussi H, Dawson PE (2010) Rapid covalent ligation of fluorescent peptides to water solubilized quantum dots. J Am Chem Soc 132:10027–10033
Bruchez M, Moronne M, Gin P, Weiss S, Alivisatos AP (1998) Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281:2013–2016
Cai W, Chen X (2008) Preparation of peptide-conjugated quantum dots for tumor vasculature-targeted imaging. Nat Protoc 3:89–96
Caragheorgheopol A, Chechik V (2008) Mechanistic aspects of ligand exchange in Au nanoparticles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 10:5029–5041
Carra H, Welcher BC, Schokman RD, David CS, Bavari S (2003) Mutational effects on protein folding stability and antigenicity: the case of streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A. Clin Immunol 108:60–68
Cedervall T, Lynch I, Lindman S, Berggård T, Thulin E, Nilsson H, Dawson KA, Linse S (2007) Understanding the nanoparticle–protein corona using methods to quantify exchange rates and affinities of proteins for nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:2050–2055
Chan WCW, Nie S (1998) Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 281:2016–2018
Chen Y, Thakar R, Snee PT (2008) Imparting nanoparticle function with size-controlled amphiphilic polymers. J Am Chem Soc 130:3744–3745
Clapp AR, Medintz IL, Mauro JM, Fisher BR, Bawendi MG, Mattoussi H (2004) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer between quantum dot donors and dye-labeled protein acceptors. J Am Chem Soc 126:301–310
Clapp AR, Goldman ER, Mattoussi H (2006) Capping of CdSe-ZnS quantum dots with DHLA and subsequent conjugation with proteins. Nat Protoc 1:1258–1266
Colvin VL (2003) The potential environmental impact of engineered nanomaterials. Nat Biotechnol 21:1166–1170
Dif A, Boulmedais F, Pinot M, Roullier V, Baudy-Floc’h M, Coquelle FM, Clarke S, Neveu P, Vignaux F, Le Borgne R, Dahan M, Gueroui Z, Marchi-Artzner V (2009) Small and stable peptidic PEGylated quantum dots to target polyhistidine-tagged proteins with controlled stoichiometry. J Am Chem Soc 131:14738–14746
Feng Y, Xing S, Xu J, Wang H, Lim JW, Chen H (2010) Probing the kinetics of ligand exchange on colloidal gold nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Dalton Trans 39:349–351
Gao X, Cui Y, Levenson RM, Chung LWK, Nie S (2004) In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 22:969–976
Hatakeyama M, Kishi H, Kita Y, Imai K, Nishio K, Karasawa S, Masaike Y, Satoshi S, Sandhu A, Tanimoto A, Gomi T, Kohda E, Abe M, Handa H (2011) A two-step ligand exchange reaction generates highly water-dispersed magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J Mater Chem 21:5959–5966
Hochuli E, Bannwarth W, Döbeli H, Gentz R, Stüber D (1988) Genetic approach to facilitate purification of recombinant proteins with a novel metal chelate adsorbent. Nat Biotechnol 6:1321–1325
Hong R, Fischer NO, Emrick T, Rotello VM (2005) Surface PEGylation and ligand exchange chemistry of FePt nanoparticles for biological applications. Chem Mat 17:4617–4621
Ishii D, Kinbara K, Ishida Y, Ishii N, Okochi M, Yohda M, Aida T (2003) Chaperonin-mediated stabilization and ATP-triggered release of semiconductor nanoparticles. Nature 423:628–632
Klein J (2007) Probing the interactions of proteins and nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:2029–2030
Li Y, Wang J, Zhang H, Yang J, Guan L, Chen H, Luo Q, Zhao Y (2010) High-sensitivity quantum dot-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer bioanalysis by capillary electrophoresis. Biosens Bioelectron 25:1283–1289
Liu DS, Phipps WS, Loh KH, Howarth M, Ting AY (2012) Quantum dot targeting with lipoic acid ligase and HaloTag for single-molecule imaging on living cells. ACS Nano 6:11080–11087
Lu Y, Wang J, Wang J, Wang L, Au SW, Xia J (2012) Genetically encodable design of ligand “bundling” on the surface of nanoparticles. Langmuir 28:13788–13792
Lundqvist M, Stigler J, Elia G, Lynch I, Cedervall T, Dawson KA (2008) Nanoparticle size and surface properties determine the protein corona with possible implications for biological impacts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:14265–14270
Lynch I, Dawson KA, Linse S (2006) Detecting cryptic epitopes created by nanoparticles. Sci STKE 327:pe14
Medintz IL, Clapp AR, Mattoussi H, Goldman ER, Fisher B, Mauro JM (2003) Self-assembled nanoscale biosensors based on quantum dot FRET donors. Nat Mater 2:630–638
Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER, Mattoussi H (2005) Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging labeling and sensing. Nat Mater 4:435–446
Michalet X, Pinaud FF, Bentolila LA, Tsay JM, Doose S, Li JJ, Sundaresan G, Wu AM, Gambhir SS, Weiss S (2005) Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 307:538–544
Milani S, Bombelli FB, Pitek AS, Dawson KA, Rädler J (2012) Reversible versus irreversible binding of transferrin to polystyrene nanoparticles: soft and hard corona. ACS Nano 6:2532–2541
Monopoli MP, Walczyk D, Campbell A, Elia G, Lynch I, Bombelli FB, Dawson KA (2011) Physical–chemical aspects of protein corona: relevance to in vitro and in vivo biological impacts of nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 133:2525–2534
Papageorgiou AC, Collins CM, Gutman DM, Kline JB, O’Brien SM, Tranter HS, Acharya KR (1999) Structural basis for the recognition of superantigen streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A (SpeA1) by MHC class II molecules and T-cell receptors. EMBO J 18:9–21
Prasuhn DE, Deschamps JR, Susumu K, Stewart MH, Boeneman K, Blanco-Canosa JB, Dawson PE, Medintz IL (2010) Polyvalent display and packing of peptides and proteins on semiconductor quantum dots: predicted versus experimental results. Small 6:555–564
Rodriguez PL, Harada T, Christian DA, Pantano DA, Tsai RK, Discher DE (2013) Minimal “self” peptides that inhibit phagocytic clearance and enhance delivery of nanoparticles. Science 339:971–975
Sapsford KE, Pons T, Medintz IL, Higashiya S, Brunel FM, Dawson PE, Mattoussi H (2007) Kinetics of metal-affinity driven self-assembly between proteins or peptides and CdSe–ZnS quantum dots. J Phys Chem C 111:11528–11538
Schieber C, Bestetti A, Lim JP, Ryan AD, Nguyen TL, Eldridge R, White AR, Gleeson PA, Donnelly PS, Williams SJ, Mulvaney P (2012) Conjugation of transferrin to azide-modified CdSe/ZnS core–shell quantum dots using cyclooctyne click chemistry. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 51:10523–10527
Shen H, Jawaid AM, Snee PT (2009) Poly(ethylene glycol) carbodiimide coupling reagents for the biological and chemical functionalization of water-soluble nanoparticles. ACS Nano 3:915–923
Slocik JM, Naik RR (2010) Probing peptide–nanomaterial interactions. Chem Soc Rev 39:3454–3463
Walczyk D, Bombelli FB, Monopoli MP, Lynch I, Dawson KA (2010) What the cell “sees” in bionanoscience. J Am Chem Soc 132:5761–5768
Wang J, Xia J (2011) Preferential binding of a novel polyhistidine peptide dendrimer ligand on quantum dots probed by capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem 83:6323–6329
Wang J, Xia J (2012) Capillary Electrophoretic studies on displacement and proteolytic cleavage of surface bound oligohistidine peptide on quantum dots. Anal Chim Acta 709:120–127
Wang J, Li Y, Zhang H, Wang H, Lin S, Chen J, Zhao Y, Luo Q (2010) Bioconjugation of concanavalin and CdTe quantum dots and the detection of glucose. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 364:82–86
Wang J, Jiang P, Han Z, Qiu L, Wang C, Zheng B, Xia J (2012a) Fast self-assembly kinetics of quantum dots and a dendrimeric peptide ligand. Langmuir 28:7962–7966
Wang J, Huang X, Zan F, Guo CG, Cao C, Ren J (2012b) Studies on bioconjugationo of quantum dots using capillary electrophoresis and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Electrophoresis 33:1987–1995
Wiogo HTR, Lim M, Bulmus V, Gutiérrez L, Woodward RC, Amal R (2012) Insight into serum protein interaction with functionalized nanoparticles in biological media. Langmuir 28:4346–4356
Wu X, Liu H, Liu J, Haley KN, Treadway JA, Larson JP, Ge N, Peale F, Bruchez MP (2002) Immunofluorescent labeling of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 21:41–46
Zhou M, Nakatani E, Gronenberg LS, Tokimoto T, Wirth MJ, Hruby VJ, Roberts A, Lynch RM, Ghosh I (2007) Peptide-labeled quantum dots for imaging GPCRs in whole cells and as single molecules. Bioconjugate Chem 18:323–332
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong (GRF grant CUHK 403711, 404812), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81201085, 31100530) and the Science & Technology Support Program of Changzhou (Society Development) (No. CE20125052). This work was also supported by “A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jianhao Wang and Pengju Jiang have contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Jiang, P., Gao, L. et al. Unique self-assembly properties of a bridge-shaped protein dimer with quantum dots. J Nanopart Res 15, 1914 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1914-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1914-9