Abstract
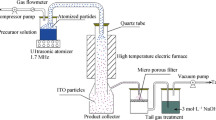
Nano-sized ZnO particles with a narrow size distribution and high crystallinity were prepared from aqueous solutions with high concentrations of Zn2+ containing salts and citric acid in a conventional spray pyrolysis setup. Structure, morphology and size of the produced material were compared to ZnO material produced by simple spray pyrolysis of zinc nitrates in the same experimental setup. Using transmission electron microscopy and electron tomography it has been shown that citric acid-assisted spray pyrolysed material is made up of micron sized secondary particles comprising a shell of lightly agglomerated, monocrystalline primary ZnO nanoparticles with sizes in the 20–30 nm range, separable by a simple ultrasonic treatment step.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bals S, Batenburg KJ, Verbeeck J, Sijbers J, Van Tendeloo G (2007) Quantitative three-dimensional reconstruction of catalyst particles for bamboo-like carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett 7:3669–3674
Batenburg KJ, Bals S, Sijbers J, Kübel C, Kaiser U, Conorado EA, Midgley PA, Hernandez J-C, Van Tendeloo G (2009) 3D imaging of nanomaterials by discrete tomography. Ultramicroscopy (in press), corrected proof. Available online 31 January 2009, ISSN 0304-3991. doi:10.1016/j.ultramic.2009.01.009
Dang ZM, Fan LZ, Zhao SJ, Nan CW (2003) Preparation of nanosized ZnO and dielectric properties of composites filled with nanosized ZnO. Mater Sci Eng B 99:386–389
Gilbert P (1972) Iterative methods for the three-dimensional reconstruction of an object from projections. J Theor Biol 36:105–117
Gregor J, Benson T (2008) Computational analysis and improvement of SIRT. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 27:918–924
Kang HS, Kang YC, Park HD, Shul YG (2003) Morphology of particle prepared by spray pyrolysis from organic precursor solution. Mater Lett 57:1288–1294
Kodas TT, Hampden-Smith MJ (1999) Aerosol processing of materials. Wiley, New York
Lee JH, Ko KH, Park BO (2003) Electrical and optical properties of ZnO transparent conducting films by the sol–gel method. J Cryst Growth 247:119–125
Lee KK, Kang YC, Jung KY, Kim JH (2005) Preparation of nano-sized BaTiO3 particle by citric-acid assisted spray pyrolysis. J Alloy Compd 395:280–285
Lenggoro IW, Itoh Y, Lida N, Okuyama K (2003) Control of size and morphology in NiO particles prepared by a low-pressure spray pyrolysis. Mater Res Bull 38:1819–1827
Look DC (2001) Recent advances in ZnO materials and devices. Mater Sci Eng B 80:383–387
Panatarani C, Lenggoro IW, Okuyama K (2003) Synthesis of single crystalline ZnO nanoparticles by salt-assisted spray pyrolysis. J Nanopart Res 5:47–53
Singh P, Kumar A, Deepak DK (2007) Growth and characterization of ZnO nanocrystalline thin films and nanopowder via low-cost ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. J Cryst Growth 306:303–310
Tian ZR, Voigt JA, Liu J, Mckenzie B, McDermott MJ, Rodriguez MA, Konishi H, Xu H (2003) Complex and oriented ZnO nanostructures. Nat Mat 2(12):821–826
Wang XD, Summers CJ, Wang ZL (2004) Large-scale hexagonal-patterned growth of aligned ZnO nanorods for nano-optoelectronics and nanosensor arrays. Nano Lett 4:423–426
Xia B, Lenggoro IW, Okuyama K (2001) Novel route to nanoparticle synthesis by salt-assisted aerosol decomposition. Adv Mater 13:1579–1582
Yang Y, Chen H, Zhao B, Bao X (2004) Size control of ZnO nanoparticles via thermal decomposition of zinc acetate coated on organic additives. J Cryst Growth 263:447–453
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge support from the European Union under the Framework 6 program under a contract from an Integrated Infrastructure Initiative (Reference 026019 ESTEEM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11051_2009_9630_MOESM1_ESM.mpg
A 3D discrete tomography reconstructed movie showing a secondary spherical structure built up of primary ZnO nanoparticles produced by CA-assisted spray pyrolysis. (MPG 6543 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turner, S., Tavernier, S.M.F., Huyberechts, G. et al. Assisted spray pyrolysis production and characterisation of ZnO nanoparticles with narrow size distribution. J Nanopart Res 12, 615–622 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-009-9630-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-009-9630-1