Abstract
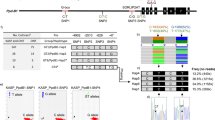
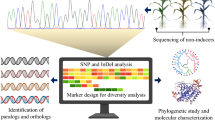
Simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers are considered very useful molecular markers for genetic and molecular breeding, specifically for non-model species. To develop a set of whole genome-wide distributed SSR marker for annual ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum L.), we obtained the first transcriptome dataset of annual ryegrass subjected to drought stress and identified a total of 11,254 EST-SSR. Fifty EST-SSR markers were selected to test the amplification and polymorphism rates in 23 accessions of Lolium and Festuca diploid species. The results showed that all of the 50 functionally relevant markers were polymorphic, with allele number and polymorphism content averaging 7.4 and 0.839, respectively, and fully transferable across 23 accessions of Lolium and Festuca species. Sequencing of PCR products showed that the nucleotide sequences of Lolium and Festuca species had a high level of conservation. Different types of tri-repeats as abundant SSR motifs were observed in repeat sequence regions. A number of EST-SSRs were mapped to genome sequences of Lolium perenne and chromosomes of Brachypodium distachyon. Among them, 973 and 1375 Lolium SSR markers were located on the five chromosomes of B. distachyon and L. perenne scaffolds, respectively. In addition, we confirmed that EST-SSRs as well as SRAP markers could clearly identify varieties of Lolium and Festuca species, and the two sets of molecular markers had a significant correlation (r = 0.74). This set of EST-SSR markers are valuable genetic tools for genetic diversity, evolutionary, and association mapping studies in Lolium, Festuca, and many other grass species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alisoltani A, Ebrahimi S, Azarian S, Hematyar M, Shiran B, Jahanbazi H, Fallahi H, Mousavi-Fard S, Rafiei F (2015) Parallel consideration of SSRs and differentially expressed genes under abiotic stress for targeted development of functional markers in almond and related Prunus species. Sci Hortic 198:462–472
Altermann E, Klaenhammer TR (2005) PathwayVoyager: pathway mapping using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database. BMC Genomics 6(1):60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-6-60
Asp T, Frei UK, Didion T, Nielsen KK, Lübberstedt T (2007) Frequency, type, and distribution of EST-SSRs from three genotypes of Lolium perenne, and their conservation across orthologous sequences of Festuca arundinacea, Brachypodium distachyon, and Oryza sativa. BMC Plant Biol 7(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-7-36
Ayres NM, Mcclung AM, Larkin PD, Hfj B, Jones CA, Park WD (1997) Microsatellites and a single-nucleotide polymorphism differentiate apparent amylose classes in an extended pedigree of US rice germ plasm. Theor Appl Genet 94(6):773–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050477
Bajgain P, Rouse MN, Anderson JA (2015) Comparing genotyping-by-sequencing and single nucleotide polymorphism chip genotyping for quantitative trait loci mapping in wheat. Crop Sci 56(1):232–248
Bhandawat A, Singh G, Raina AS, Kaur J, Sharma RK (2016) Development of genic SSR marker resource from RNA-Seq data in Dendrocalamus latiflorus. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 25(2):179–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-015-0323-9
Byrne S, Armstead I, Swain SC, Panitz F, Bendixen C, Hedegaard J, Nagy I, Farrell JD, Studer B, Caccamo M (2014) A draft sequence assembly of the perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) genome. In: International Plant and Animal Genome Conference Xxii
Cheng Y, Ma X, Zhou K, Humphreys MW, Zhang XQ (2016) Phylogenetic analysis of Festuca–Lolium complex using SRAP markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 63(1):7–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-015-0324-5
Diekmann K, Hodkinson TR, Wolfe KH, Bekerom RVD, Dix PJ, Barth S (2009) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of a major allogamous forage species, perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) DNA Res 16(3):165–176. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsp008
Fu N, Wang Q, Shen HL (2013) De novo assembly, gene annotation and marker development using Illumina paired-end transcriptome sequences in celery (Apium graveolens L.) PLoS One 8(2):e57686. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057686
Garg R, Patel RK, Tyagi AK, Jain M (2011) De novo assembly of chickpea transcriptome using short reads for gene discovery and marker identification. DNA Res 18(1):53–63. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsq028
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Sharma S, Singh R, Kumar N, Balyan HS (2003) Transferable EST-SSR markers for the study of polymorphism and genetic diversity in bread wheat. Mol Gen Genomics 270(4):315–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-003-0921-4
Hand ML, Spangenberg GC, Forster JW, Cogan NOI (2013) Plastome sequence determination and comparative analysis for members of the Lolium-Festuca grass species complex. G3: Genes Genomes Genet 3(4):607–616. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.112.005264
Kantety RV, La RM, Matthews DE, Sorrells ME (2002) Data mining for simple sequence repeats in expressed sequence tags from barley, maize, rice, sorghum and wheat. Plant Mol Biol 48(5):501–510. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014875206165
Klein PE, Klein RR, Vrebalov J, Mullet JE (2003) Sequence-based alignment of sorghum chromosome 3 and rice chromosome 1 reveals extensive conservation of gene order and one major chromosomal rearrangement. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 34(5):605–621. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01751.x
Li DJ, Deng Z, Qin B, Liu X, Men ZH (2012) De novo assembly and characterization of bark transcriptome using Illumina sequencing and development of EST-SSR markers in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.) BMC Genomics 13(1):192. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-192
Mccouch SR, Temnykh S, Lukashova A, Coburn J, Declerck G, Cartinhour S, Harrington S, Thomson M, Septiningsih E, Semon M (2001) Microsatellite markers in rice: abundance, diversity, and applications. Rice Genet IV:117–135
Pan L, Zhang X, Wang J, Ma X, Zhou M, Huang LK, Nie G, Wang P, Yang Z, Li J (2016) Transcriptional profiles of drought-related genes in modulating metabolic processes and antioxidant defenses in Lolium multiflorum. Front Plant Sci 7(170). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00519
Saha MC, Mian MA, Eujayl I, Zwonitzer JC, Wang L, May GD (2004) Tall fescue EST-SSR markers with transferability across several grass species. Theor Appl Genet 109(4):783–791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1681-1
Salem M, Vallejo RL, Leeds TD, Palti Y, Liu S, Sabbagh A, Yao J (2012) RNA-Seq identifies SNP markers for growth traits in rainbow trout. PLoS One 7(5):e36264. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036264
Thiel T, Michalek W, Varshney RK, Graner A (2003) Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Theor Appl Genet 106(3):411–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1031-0
Wang FZ, Wang QB, Kwon SY, Kwak SS, WA S (2005) Enhanced drought tolerance of transgenic rice plants expressing a pea manganese superoxide dismutase. J Plant Physiol 162(4):465–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2004.09.009
Wang S, Wang X, He Q, Liu X, Xu W, Li L, Gao J, Wang F (2012) Transcriptome analysis of the roots at early and late seedling stages using Illumina paired-end sequencing and development of EST-SSR markers in radish. Plant Cell Rep 31(8):1437–1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1259-3
Wang Z, Yu G, Shi B, Wang X, Qiang H, Gao H (2014) Development and characterization of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers based on RNA-sequencing of Medicago sativa and in silico mapping onto the M. truncatula genome. PLoS One 9(3):e92029. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092029
Wit F (1958) Tetraploid Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) Euphytica 7(1):47–58
Wong MM, Cannon CH, Wickneswari R (2012) Development of high-throughput SNP-based genotyping in Acacia auriculiformis x A. mangium hybrids using short-read transcriptome data. BMC Genomics 13(1):726. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-726
Xia EH, Yao QY, Zhang HB, Jiang JJ, Zhang LP, Gao LZ (2016) CandiSSR: an efficient pipeline used for identifying candidate polymorphic SSRs based on multiple assembled sequences. Front Plant Sci 6(796):1171
Yang SS, Tu ZJ, Cheung F, Xu WW, Lamb JFS, Jung HJG, Vance CP, Gronwald JW (2011) Using RNA-Seq for gene identification, polymorphism detection and transcript profiling in two alfalfa genotypes with divergent cell wall composition in stems. BMC Genomics 12(1):19
Yu Y, Yuan D, Liang S, Li X, Wang X, Lin Z, Zhang X (2011) Genome structure of cotton revealed by a genome-wide SSR genetic map constructed from a BC1 population between gossypium hirsutum and G. barbadense. BMC Genomics 12(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-15
Zhang H, Wei L, Miao H, Zhang T, Wang C (2012a) Development and validation of genic-SSR markers in sesame by RNA-seq. BMC Genomics 13(1):316. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-316
Zhang J, Shan L, Duan J, Jin W, Chen S, Cheng Z, Qiang Z, Liang X, Li Y (2012b) De novo assembly and characterisation of the transcriptome during seed development, and generation of genic-SSR markers in peanut ( Arachis hypogaea L.) BMC Genomics 13(1):90. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-90
Authors and contributors
LP collected data and wrote the manuscript. XZ and XM designed the project. JW participated in technical editing of the manuscript. TH, ZY, and LT analyzed the data. All authors have read the manuscript.
Funding
This research work was funded by the earmarked fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (No. CARS-35-05), the National Basic Research Program (973 program) in China (No. 2014CB138705), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 31372363).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Fig S1
The distribution of repeated nucleotide types of SSR motifs in L. multiflorum (A-B) and the number of unigenes that are distributed on an annotated species (C). (PNG 423 kb)
Fig S2
Principal coordinate analysis of EST-SSR markers variation among 23 accessions of Lolium and Festuca species. (PNG 360 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, L., Huang, T., Yang, Z. et al. EST-SSR marker characterization based on RNA-sequencing of Lolium multiflorum and cross transferability to related species. Mol Breeding 38, 80 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-018-0775-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-018-0775-4