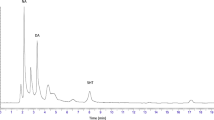
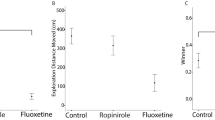
Abstract
We investigated the cumulative effects of cathinone on behavioural alterations in single-caged vervet monkeys. Fourteen adult vervets were divided into tests (12 animals) and controls (2 animals), and exposed to escalating doses of cathinone at alternate days of each week for 4 months in presence and absence of cage enrichment. One month of pre-treatment phase served to establish baseline values. Composite behavioural scores of aggression, anxiety, abnormal responses, withdrawal and appetite loss were done. A series of repeated measures analysis of variances were conducted to examine the extent to which cathinone administration was associated with patterns of changes in behavioural data. Results indicate a dose-dependent effect of cathinone on increases of aggression, anxiety, abnormal responses, withdrawal, and appetite loss. The findings demonstrate that at high doses and long-term exposure, cathinone causes behavioural alterations probably via changes in presynaptic striatal dopamine system.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Bekairi AM, Abulaban FS, Qureshi S, Shah AH (1991) The toxicity of Catha edulis (Khat). A review. Fitoterapia LXII:291–300
Banjaw MY, Miczek K, Schmidt WJ (2005) Repeated Catha edulis oral administration enhances the baseline aggressive behaviour in isolated rats. J Neural Transm 113:543–556
Bayne KA (1989) Nylon balls revisited. Lab Primate Newsl 28:5–6
Berman SM, Kuczenski R, McCracken JT, London ED (2009) Potential adverse effects of amphetamine treatment on brain and behaviour: a review. Mol Psychiatry 14:123–142
Blundell JE (1984) Serotonin and appetite. Neuropharmacology 23:1537–1551
Calcagnetti DJ, Schechter MD (1993) Place preference for the psychostimulant-cathinone is blocked by pretreatment with a dopamine release inhibitor. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 17:637–649
Castner SA, Goldman-Rakic PS (1999) Long-lasting psychotomimetic consequences of repeated low-dose amphetamine exposure in rhesus monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:10–28
Charney DS, Drystal JJ, Southwick SM, Nagy LM, Woods SW, Heninger GR (1990) Serotonin function in panic and generalized anxiety disorders. Psychiatr Ann 20:593–604
Clinical Practice Guideline (2001) Treatment of the school-aged child with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 108:1033–1044
Cox G, Rampes H (2003) Adverse effects of khat. A review. Adv Psychiatr Treat 9:456–463
Efron D, Jarman F, Barker M (1997) Side effects of methylphenidate and dexamphetamine in children with attention deficit disorder: a double-blind, cross-over trial. Pediatrics 100:662–666
Eisch AJ, Harburg GC (2006) Opiates, psychostimulants, and adult hippocampal neurogenesis: insights for addiction and Stem Cell Biology. Hippocampus 16:271–286
Eisenberg MS, Maher TJ, Silverman HI (1987) A comparison of the effects of phenylpropanolamine, d-amphetamine and d-norpseudoephedrine on open-field locomotion and food intake in the rat. Appetite 9:31–37
Fairbanks LA, Jorgensen MJ, Huff A, Blau K, Hung YY, Mann JJ (2004) Adolescent impulsivity predicts adult dominance attainment for male vervet monkeys. Am J Primatol 64:1–17
Foltin RW, Woolverton WL, Schuster CR (1983) Effects of psychomotor stimulants alone and in pairs, on milk drinking in the rat after intraperitoneal and intragastric administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 226:411–418
Goldman-Rakic PS, Lidow MS, Gallager DW (1990) Overlap of dopaminergic adrenergic and serotonergic receptors and complementarity of their subtypes in primate prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 10:2125–2138
Gordon TL, Meehan SM, Schechter MD (1993) Differential effects of Nicotine but not cathinone on motor activity of P and NP rats. Biochem Behav 44:657–659
Goudie AJ (1985) Comparative effects of cathinone and amphetamine on fixed interval operant responding: a rate-dependency analysis. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:355–365
Isbell LA, Cheney DL, Seyfarth RM (1991) Group fusions and minimum group sizes in vervet monkeys (Cercopithecus aethiops). AM J Primatol 25:57–65
Ishikawa T, Li Zhu B, Miyashi S, Ishizu H, Maeda H (2007) Increase in clusterin- containing follicles in the adenohypophysis of drug abusers. Int J Legal Med 121:395–402
James AS, Groman SM, Seu E, Jorgensen M, Fairbanks LA, Jentsch JD (2007) Dimensions of impulsivity are associated with poor spatial working memory performance in monkeys. J Neurosci 27:14358–14364
Jansson T, Kristiansson B, Qirbi A (1988) Effect of khat on maternal food intake, maternal weight gain and fetal growth in the late-pregnant guinea pig. J Ethnopharmacol 23:11–17
Kalix P (1983) Mechanism of action of (−) cathinone, a new alkaloid from khat leaves. Alcohol Alcohol 18:301–303
Kalix P (1984) Effect of the alkaloid (−)-cathinone on the release of radioactivity from rat striatal tissue prelabelled with 3H-serotonin. Neuropsychobiology 12:127–129
Kalix P (1996) Catha edulis, a plant that has amphetamine effects. Pharm World Sci 18:69–73
Kalix P, Braenden O (1985) Pharmacological aspects of the chewing of khat leaves. Pharmacol Rev 37:149–164
Kimani ST, Nyongesa AW (2008) Effects of single daily khat (Catha edulis) extract on spatial learning and memory in CBA mice. Behav Brain Res 195:192–197
Lee MM (1995) The identification of cathinone in khat (Catha edulis): a time study. J Forensic Sci 40:116–121
Marais L, Daniels W, Brand L, Viljoen F, Hugo C, Stein DJ (2006) Psychopharmacology of maternal separation anxiety in vervet monkeys. Metab Brain Dis 21:201–210
Martin P, Bateson P (1993) Measuring behaviour: an introductory Guide. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Melega WP, Jorgensen MJ, Lacan G, Way BM, Pham J, Morton G, Cho AK, Fairbanks LA (2008) Long-term methamphetamine administration in the vervet monkey models aspects of a human exposure: brain neurotoxicity and behavioural profiles. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1441–1452
Mohammed A, Engidawork E (2011) Reproductive parameters are differentially altered following subchronic administration of Catha edulis Forsk (Khat) extract and cathinone in male rats. J Ethnopharmacol 134:977–983
Murray CD, Le Roux CW, Emmanuel AV, Halket JM, Pryborowska AM, Kamm MA, Murray-Lyon IM (2008) The effect of khat (Catha edulis) as an appetite suppressant is independent of ghrelin and PYY secretion. Appetite 51:747–750
Neary NM, Goldstone AP, Bloom SR (2004) Appetite regulation: from the gut to the hypothalamus. Clin Endocrinol 60:153–160
Pehek EA, Schechter MD, Yamamoto BK (1990) Effects of cathinone and amphetamine on the neurochemistry of dopamine in vivo. Neuropharmacology 29:1171–1176
Rapkin AJ, Pollack DB, Raleigh MJ, Stone B, McGuire MT (1995) Menstrual cycle and social behaviour in vervet monkeys. Psychoneuroendocrinology 20:289–297
Schuster C, Johanson R (1979) Behavioural studies of cathinone in monkeys and rats. In: Problems of Drug Dependence. NIDA Res Monogr 27:324–325
Spoont MR (1992) The modulatory role of serotonin in neural information processing: implications for human psychopathology. Psychol Bull 112:330–350
Sulser F (1989) New perspectives on the molecular pharmacology of affective disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci 238:231–239
Tecott LH, Sun LM, Akana SF, Strack AM, Lowestein DH, Dallman MF, Julius D (1995) Eating disorder and epilepsy in mice lacking 5-HT2c serotonin receptors. Nature 374:542–546
Toennes SM, Kauert GF (2002) Excretion and detection of cathinone, cathine and phenylpropanolamine in urine after khat chewing. Clin Chem 48:1715–1719
Toennes SW, Harder S, Schramm M, Neiss C, Kauert GF (2003) Pharmacokinetics of cathinone, cathine and norephedrine after the chewing of khat leaves. Br J Clin Pharmacol 56:125–130
Yanagita T (1979) Studies on cathinone: cardiovascular and behavioral effects in rats and self-administration experiments in monkeys. NIDA Res Monogr 2:326–327
Zelger J, Carlini E (1980) Anorexigenic effects of two amines obtained from Catha edulis Forsk (khat) in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 12:701–705
Zelger J, Schorno H, Carlin E (1980) Behavioural effects of cathinone: an amphetamine obtained from Catha edulis: comparisons with amphetamine, norpseudoephedrine, apomorphine and nomifensine. Bull Narc 32:67–81
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Gershon Deya, James Ndung’u, Margaret Kagina, Robert Tsuma and Stanley Marete for their technical assistance. This work was supported by the Khat Research Program (KRP) and the Office of International Programs at the University of Minnesota and Dean’s Committee Grant of the University of Nairobi.
Conflict of interest
There was no conflict of interest to declare
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nyongesa, A.W., Oduma, J.A., Nakajima, M. et al. Acute and sub-chronic effects of purified cathinone from khat (Catha edulis) on behavioural profiles in vervet monkeys (Chlorocebus aethiops). Metab Brain Dis 29, 441–449 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9441-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9441-z