Abstract
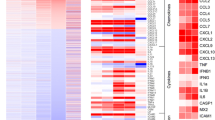
Previously, we have shown that peripheral challenge of mice with double stranded RNA (dsRNA), a viral mimic, evokes global upregulation of cerebral inflammatory genes and, particularly, genes encoding chemokines. Because chemokine networks are potent modulators of brain function, the present study was undertaken to comprehensively characterize the cerebral response of chemokine ligand and receptor genes to peripheral immune system stimulation. Briefly, C57BL/6 mice were intraperitoneally injected with 12 mg/kg of polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (PIC) and the expression of 39 mouse chemokine ligand and 20 receptor genes was monitored in the cerebellum by real time quantitative RT-PCR within 24 h. Almost half of the ligand genes featured either transient or sustained upregulation from several- to several thousand-fold. Five CXC type genes, i.e., Cxcl9, Cxcl11, Cxcl10, Cxcl2 and Cxcl1, were the most robustly upregulated, and were followed by six CC type genes, i.e., Ccl2, Ccl7, Ccl5, Ccl12, Ccl4 and Ccl11. Seven genes showed moderate upregulation, whereas the remaining genes were unresponsive. Six receptor genes, i.e., Cxcr2, Ccr7, Cxcr5, Ccr6, Ccr1 and Ccr5, featured a several-fold upregulation. Similar chemokine gene response was observed in the forebrain and brainstem. This upregulation of chemokine genes could be induced in naïve mice by transfer of blood plasma from PIC-challenged mice. Employing oligodeoxynucleotide-labeled PIC we further showed that intraperitoneally injected PIC was not transferred to the blood. In conclusion, peripheral PIC challenge elicits a broad upregulation of cerebral chemokine genes, and this upregulation is mediated by blood-borne agents.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler MW, Rogers TJ (2005) Are chemokines the third major system in the brain? J Leukoc Biol 78:1204–1209
Adler MW, Geller EB, Chen X, Rogers TJ (2005) Viewing chemokines as a third major system of communication in the brain. AAPS J 7:E865–E870
Allen SJ, Crown SE, Handel TM (2007) Chemokine: receptor structure, interactions, and antagonism. Annu Rev Immunol 25:787–820
Bacon K, Baggiolini M, Broxmeyer H, Horuk R, Lindley I, Mantovani A, Maysushima K, Murphy P, Nomiyama H, Oppenheim J, Rot A, Schall T, Tsang M, Thorpe R, Van DJ, Wadhwa M, Yoshie O, Zlotnik A, Zoon K (2002) Chemokine/chemokine receptor nomenclature. J Interferon Cytokine Res 22:1067–1068
Baggiolini M (1998) Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature 392:565–568
Bajetto A, Bonavia R, Barbero S, Florio T, Schettini G (2001) Chemokines and their receptors in the central nervous system. Front Neuroendocrinol 22:147–184
Bajetto A, Bonavia R, Barbero S, Schettini G (2002) Characterization of chemokines and their receptors in the central nervous system: physiopathological implications. J Neurochem 82:1311–1329
Banisadr G, Queraud-Lesaux F, Boutterin MC, Pelaprat D, Zalc B, Rostene W, Haour F, Parsadaniantz SM (2002) Distribution, cellular localization and functional role of CCR2 chemokine receptors in adult rat brain. J Neurochem 81:257–269
Banisadr G, Rostene W, Kitabgi P, Parsadaniantz SM (2005) Chemokines and brain functions. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 4:387–399
Barna BP, Pettay J, Barnett GH, Zhou P, Iwasaki K, Estes ML (1994) Regulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in adult human non-neoplastic astrocytes is sensitive to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or antibody to the 55-kDa TNF receptor. J Neuroimmunol 50:101–107
Belperio JA, Keane MP, Arenberg DA, Addison CL, Ehlert JE, Burdick MD, Strieter RM (2000) CXC chemokines in angiogenesis. J Leukoc Biol 68:1–8
Benelli R, Lorusso G, Albini A, Noonan DM (2006) Cytokines and chemokines as regulators of angiogenesis in health and disease. Curr Pharm Des 12:3101–3115
Berman JW, Guida MP, Warren J, Amat J, Brosnan CF (1996) Localization of monocyte chemoattractant peptide-1 expression in the central nervous system in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and trauma in the rat. J Immunol 156:3017–3023
Biber K, Dijkstra I, Trebst C, De Groot CJ, Ransohoff RM, Boddeke HW (2002) Functional expression of CXCR3 in cultured mouse and human astrocytes and microglia. Neuroscience 112:487–497
Biber K, Neumann H, Inoue K, Boddeke HW (2007) Neuronal ‘On’ and ‘Off’ signals control microglia. Trends Neurosci 30:596–602
Carter SL, Muller M, Manders PM, Campbell IL (2007) Induction of the genes for Cxcl9 and Cxcl10 is dependent on IFN-gamma but shows differential cellular expression in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and by astrocytes and microglia in vitro. Glia 55:1728–1739
Cartier L, Hartley O, Dubois-Dauphin M, Krause KH (2005) Chemokine receptors in the central nervous system: role in brain inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 48:16–42
Charo IF, Ransohoff RM (2006) The many roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in inflammation. N Engl J Med 354:610–621
Che X, Ye W, Panga L, Wu DC, Yang GY (2001) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expressed in neurons and astrocytes during focal ischemia in mice. Brain Res 902:171–177
Cho J, Nelson TE, Bajova H, Gruol DL (2009) Chronic CXCL10 alters neuronal properties in rat hippocampal culture. J Neuroimmunol 207:92–100
Cowell RM, Silverstein FS (2003) Developmental changes in the expression of chemokine receptor CCR1 in the rat cerebellum. J Comp Neurol 457:7–23
Cunningham C, Campion S, Teeling J, Felton L, Perry VH (2007) The sickness behaviour and CNS inflammatory mediator profile induced by systemic challenge of mice with synthetic double-stranded RNA (poly I:C). Brain Behav Immun 21:490–502
Dantzer R (2004) Cytokine-induced sickness behaviour: a neuroimmune response to activation of innate immunity. Eur J Pharmacol 500:399–411
Dantzer R (2006) Cytokine, sickness behavior, and depression. Neurol Clin 24:441–460
Dantzer R, O’Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW (2008) From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:46–56
Davatelis G, Wolpe SD, Sherry B, Dayer JM, Chicheportiche R, Cerami A (1989) Macrophage inflammatory protein-1: a prostaglandin-independent endogenous pyrogen. Science 243:1066–1068
Flugel A, Hager G, Horvat A, Spitzer C, Singer GM, Graeber MB, Kreutzberg GW, Schwaiger FW (2001) Neuronal MCP-1 expression in response to remote nerve injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:69–76
Flynn G, Maru S, Loughlin J, Romero IA, Male D (2003) Regulation of chemokine receptor expression in human microglia and astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol 136:84–93
Fortier ME, Kent S, Ashdown H, Poole S, Boksa P, Luheshi GN (2004) The viral mimic, polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid, induces fever in rats via an interleukin-1-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 287:R759–R766
Giovannelli A, Limatola C, Ragozzino D, Mileo AM, Ruggieri A, Ciotti MT, Mercanti D, Santoni A, Eusebi F (1998) CXC chemokines interleukin-8 (IL-8) and growth-related gene product alpha (GROalpha) modulate Purkinje neuron activity in mouse cerebellum. J Neuroimmunol 92:122–132
Glabinski AR, Ransohoff RM (1999) Chemokines and chemokine receptors in CNS pathology. J Neurovirol 5:3–12
Glabinski AR, Balasingam V, Tani M, Kunkel SL, Strieter RM, Yong VW, Ransohoff RM (1996) Chemokine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is expressed by astrocytes after mechanical injury to the brain. J Immunol 156:4363–4368
Gosselin RD, Varela C, Banisadr G, Mechighel P, Rostene W, Kitabgi P, Melik-Parsadaniantz S (2005) Constitutive expression of CCR2 chemokine receptor and inhibition by MCP-1/CCL2 of GABA-induced currents in spinal cord neurones. J Neurochem 95:1023–1034
Gourmala NG, Buttini M, Limonta S, Sauter A, Boddeke HW (1997) Differential and time-dependent expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 mRNA by astrocytes and macrophages in rat brain: effects of ischemia and peripheral lipopolysaccharide administration. J Neuroimmunol 74:35–44
Guha-Thakurta N, Majde JA (1997) Early induction of proinflammatory cytokine and type I interferon mRNAs following Newcastle disease virus, poly [rI:rC], or low-dose LPS challenge of the mouse. J Interferon Cytokine Res 17:197–204
Guyon A, Skrzydelski D, De Giry I, Rovere C, Conductier G, Trocello JM, Dauge V, Kitabgi P, Rostene W, Nahon JL, Melik PS (2009) Long term exposure to the chemokine CCL2 activates the nigrostriatal dopamine system: a novel mechanism for the control of dopamine release. Neuroscience 162:1072–1080
Hanisch UK (2002) Microglia as a source and target of cytokines. Glia 40:140–155
Harkness KA, Sussman JD, Davies-Jones GA, Greenwood J, Woodroofe MN (2003) Cytokine regulation of MCP-1 expression in brain and retinal microvascular endothelial cells. J Neuroimmunol 142:1–9
Hayashi M, Luo Y, Laning J, Strieter RM, Dorf ME (1995) Production and function of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and other beta-chemokines in murine glial cells. J Neuroimmunol 60:143–150
Hopkins SJ (2007) Central nervous system recognition of peripheral inflammation: a neural, hormonal collaboration. Acta Biomed 78(Suppl 1):231–247
Horuk R, Martin AW, Wang Z, Schweitzer L, Gerassimides A, Guo H, Lu Z, Hesselgesser J, Perez HD, Kim J, Parker J, Hadley TJ, Peiper SC (1997) Expression of chemokine receptors by subsets of neurons in the central nervous system. J Immunol 158:2882–2890
Hurwitz AA, Lyman WD, Berman JW (1995) Tumor necrosis factor alpha and transforming growth factor beta upregulate astrocyte expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. J Neuroimmunol 57:193–198
Jacobs BL, Langland JO (1996) When two strands are better than one: the mediators and modulators of the cellular responses to double-stranded RNA. Virology 219:339–349
Katafuchi T, Kondo T, Take S, Yoshimura M (2005) Enhanced expression of brain interferon-alpha and serotonin transporter in immunologically induced fatigue in rats. Eur J Neurosci 22:2817–2826
Katafuchi T, Kondo T, Take S, Yoshimura M (2006) Brain cytokines and the 5-HT system during poly I:C-induced fatigue. Ann NY Acad Sci 1088:230–237
Klein RS, Lin E, Zhang B, Luster AD, Tollett J, Samuel MA, Engle M, Diamond MS (2005) Neuronal CXCL10 directs CD8+ T-cell recruitment and control of West Nile virus encephalitis. J Virol 79:11457–11466
Konat GW, Borysiewicz E (2009) Cerebellar expression of inflammatory genes triggered by peripheral challenge with dsRNA. J Neurochem 108(suppl 1):133
Konat GW, Borysiewicz E, Fil D, James I (2009) Peripheral challenge with double-stranded RNA elicits global up-regulation of cytokine gene expression in the brain. J Neurosci Res 87:1381–1388
Krasowska-Zoladek A, Banaszewska M, Kraszpulski M, Konat GW (2007) Kinetics of inflammatory response of astrocytes induced by TLR 3 and TLR4 ligation. J Neurosci Res 85:205–212
Kuijpers M, van Gassen KL, de Graan PN, Gruol D (2010) Chronic exposure to the chemokine CCL3 enhances neuronal network activity in rat hippocampal cultures. J Neuroimmunol
Kunkel SL (1999) Through the looking glass: the diverse in vivo activities of chemokines. J Clin Invest 104:1333–1334
Laing KJ, Secombes CJ (2004) Chemokines. Dev Comp Immunol 28:443–460
Lane TE, Asensio VC, Yu N, Paoletti AD, Campbell IL, Buchmeier MJ (1998) Dynamic regulation of alpha- and beta-chemokine expression in the central nervous system during mouse hepatitis virus-induced demyelinating disease. J Immunol 160:970–978
Lax P, Limatola C, Fucile S, Trettel F, Di BS, Renzi M, Ragozzino D, Eusebi F (2002) Chemokine receptor CXCR2 regulates the functional properties of AMPA-type glutamate receptor GluR1 in HEK cells. J Neuroimmunol 129:66–73
Lenczowski MJ, Van Dam AM, Poole S, Larrick JW, Tilders FJ (1997) Role of circulating endotoxin and interleukin-6 in the ACTH and corticosterone response to intraperitoneal LPS. Am J Physiol 273:R1870–R1877
Lindner M, Trebst C, Heine S, Skripuletz T, Koutsoudaki PN, Stangel M (2008) The chemokine receptor CXCR2 is differentially regulated on glial cells in vivo but is not required for successful remyelination after cuprizone-induced demyelination. Glia 56:1104–1113
Machado RR, Soares DM, Proudfoot AE, Souza GE (2007) CCR1 and CCR5 chemokine receptors are involved in fever induced by LPS (E. coli) and RANTES in rats. Brain Res 1161:21–31
McManus CM, Brosnan CF, Berman JW (1998) Cytokine induction of MIP-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta in human fetal microglia. J Immunol 160:1449–1455
McManus CM, Liu JS, Hahn MT, Hua LL, Brosnan CF, Berman JW, Lee SC (2000) Differential induction of chemokines in human microglia by type I and II interferons. Glia 29:273–280
Melik-Parsadaniantz S, Rostene W (2008) Chemokines and neuromodulation. J Neuroimmunol 198:62–68
Mellado M, Rodriguez-Frade JM, Vila-Coro AJ, Fernandez S, Martin de Ana A, Jones DR, Toran JL, Martinez A (2001) Chemokine receptor homo- or heterodimerization activates distinct signaling pathways. EMBO J 20:2497–2507
Meucci O, Fatatis A, Simen AA, Bushell TJ, Gray PW, Miller RJ (1998) Chemokines regulate hippocampal neuronal signaling and gp120 neurotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14500–14505
Miller RJ, Rostene W, Apartis E, Banisadr G, Biber K, Milligan ED, White FA, Zhang J (2008) Chemokine action in the nervous system. J Neurosci 28:11792–11795
Minano FJ, Myers RD (1991) Anorexia and adipsia: dissociation from fever after MIP-1 injection in ventromedial hypothalamus and preoptic area of rats. Brain Res Bull 27:273–278
Minano FJ, Sancibrian M, Myers RD (1991) Fever induced by macrophage inflammatory protein-1 (MIP-1) in rats: hypothalamic sites of action. Brain Res Bull 27:701–706
Minano FJ, Fernandez-Alonso A, Myers RD, Sancibrian M (1996) Hypothalamic interaction between macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (MIP-1 alpha) and MIP-1 beta in rats: a new level for fever control? J Physiol 491(Pt 1):209–217
Mines M, Ding Y, Fan GH (2007) The many roles of chemokine receptors in neurodegenerative disorders: emerging new therapeutical strategies. Curr Med Chem 14:2456–2470
Molina-Holgado E, Molina-Holgado F (2010) Mending the broken brain: neuroimmune interactions in neurogenesis. J Neurochem
Muller M, Carter S, Hofer MJ, Campbell IL (2010) Review: the chemokine receptor CXCR3 and its ligands CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11 in neuroimmunity–a tale of conflict and conundrum. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 36:368–387
Myers RD, Paez X, Roscoe AK, Sherry B, Cerami A (1993) Fever and feeding: differential actions of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 (MIP-1), MIP-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta on rat hypothalamus. Neurochem Res 18:667–673
Nelson TE, Gruol DL (2004) The chemokine CXCL10 modulates excitatory activity and intracellular calcium signaling in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neuroimmunol 156:74–87
Oh JW, Schwiebert LM, Benveniste EN (1999) Cytokine regulation of CC and CXC chemokine expression by human astrocytes. J Neurovirol 5:82–94
Oh SB, Tran PB, Gillard SE, Hurley RW, Hammond DL, Miller RJ (2001) Chemokines and glycoprotein120 produce pain hypersensitivity by directly exciting primary nociceptive neurons. J Neurosci 21:5027–5035
Omari KM, John G, Lango R, Raine CS (2006) Role for CXCR2 and CXCL1 on glia in multiple sclerosis. Glia 53:24–31
Pease JE, Williams TJ (2006) The attraction of chemokines as a target for specific anti-inflammatory therapy. Br J Pharmacol 147(Suppl 1):S212–S221
Plata-Salaman CR, Borkoski JP (1994) Chemokines/intercrines and central regulation of feeding. Am J Physiol 266:R1711–R1715
Pruett SB, Fan R, Zheng Q (2003) Acute ethanol administration profoundly alters poly I:C-induced cytokine expression in mice by a mechanism that is not dependent on corticosterone. Life Sci 72:1825–1839
Puma C, Danik M, Quirion R, Ramon F, Williams S (2001) The chemokine interleukin-8 acutely reduces Ca(2+) currents in identified cholinergic septal neurons expressing CXCR1 and CXCR2 receptor mRNAs. J Neurochem 78:960–971
Quan N, Banks WA (2007) Brain-immune communication pathways. Brain Behav Immun 21:727–735
Ragozzino D, Giovannelli A, Mileo AM, Limatola C, Santoni A, Eusebi F (1998) Modulation of the neurotransmitter release in rat cerebellar neurons by GRO beta. NeuroReport 9:3601–3606
Ransohoff RM, Hamilton TA, Tani M, Stoler MH, Shick HE, Major JA, Estes ML, Thomas DM, Tuohy VK (1993) Astrocyte expression of mRNA encoding cytokines IP-10 and JE/MCP-1 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. FASEB J 7:592–600
Rittner HL, Brack A (2006) Chemokines and pain. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 7:643–646
Romanovsky AA, Ivanov AI, Lenczowski MJ, Kulchitsky VA, Van Dam AM, Poole S, Homer LD, Tilders FJ (2000) Lipopolysaccharide transport from the peritoneal cavity to the blood: is it controlled by the vagus nerve? Auton. Neurosci 85:133–140
Rossi D, Zlotnik A (2000) The biology of chemokines and their receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 18:217–242
Rostene W, Guyon A, Kular L, Godefroy D, Barbieri F, Bajetto A, Banisadr G, Callewaere C, Conductier G, Rovere C, Melik-Parsadaniantz S, Florio T (2010) Chemokines and chemokine receptors: New actors in neuroendocrine regulations. Front Neuroendocrinol
Rot A, von Andrian UH (2004) Chemokines in innate and adaptive host defense: basic chemokinese grammar for immune cells. Annu Rev Immunol 22:891–928
Rottman JB, Ganley KP, Williams K, Wu L, Mackay CR, Ringler DJ (1997) Cellular localization of the chemokine receptor CCR5. Correlation to cellular targets of HIV-1 infection. Am J Pathol 151:1341–1351
Saas P, Walker PR, Quiquerez AL, Chalmers DE, Arrighi JF, Lienard A, Boucraut J, Dietrich PY (2002) A self-defence mechanism of astrocytes against Fas-mediated death involving interleukin-8 and CXCR2. NeuroReport 13:1921–1924
Sorensen TL, Tani M, Jensen J, Pierce V, Lucchinetti C, Folcik VA, Qin S, Rottman J, Sellebjerg F, Strieter RM, Frederiksen JL, Ransohoff RM (1999) Expression of specific chemokines and chemokine receptors in the central nervous system of multiple sclerosis patients. J Clin Invest 103:807–815
Tavares E, Minano FJ (2004) Differential sensitivities of pyrogenic chemokine fevers to CC chemokine receptor 5 antibodies. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 18:163–169
Tran PB, Miller RJ (2003) Chemokine receptors: signposts to brain development and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:444–455
Tran PB, Banisadr G, Ren D, Chenn A, Miller RJ (2007) Chemokine receptor expression by neural progenitor cells in neurogenic regions of mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 500:1007–1033
Traynor TR, Majde JA, Bohnet SG, Krueger JM (2004) Intratracheal double-stranded RNA plus interferon-gamma: a model for analysis of the acute phase response to respiratory viral infections. Life Sci 74:2563–2576
Valles A, Grijpink-Ongering L, de Bree FM, Tuinstra T, Ronken E (2006) Differential regulation of the CXCR2 chemokine network in rat brain trauma: implications for neuroimmune interactions and neuronal survival. Neurobiol Dis 22:312–322
van Heteren JT, Rozenberg F, Aronica E, Troost D, Lebon P, Kuijpers TW (2008) Astrocytes produce interferon-alpha and CXCL10, but not IL-6 or CXCL8, in Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome. Glia 56:568–578
Vlkolinsky R, Siggins GR, Campbell IL, Krucker T (2004) Acute exposure to CXC chemokine ligand 10, but not its chronic astroglial production, alters synaptic plasticity in mouse hippocampal slices. J Neuroimmunol 150:37–47
Wang J, Campbell IL (2005) Innate STAT1-dependent genomic response of neurons to the antiviral cytokine alpha interferon. J Virol 79:8295–8302
Weber F, Wagner V, Rasmussen SB, Hartmann R, Paludan SR (2006) Double-stranded RNA is produced by positive-strand RNA viruses and DNA viruses but not in detectable amounts by negative-strand RNA viruses. J Virol 80:5059–5064
Xia MQ, Bacskai BJ, Knowles RB, Qin SX, Hyman BT (2000) Expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR3 on neurons and the elevated expression of its ligand IP-10 in reactive astrocytes: in vitro ERK1/2 activation and role in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroimmunol 108:227–235
Zach O, Bauer HC, Richter K, Webersinke G, Tontsch S, Bauer H (1997) Expression of a chemotactic cytokine (MCP-1) in cerebral capillary endothelial cells in vitro. Endothelium 5:143–153
Zhou ZH, Han Y, Wei T, Aras S, Chaturvedi P, Tyler S, Rani MR, Ransohoff RM (2001) Regulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 transcription by interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in human astrocytoma cells: postinduction refractory state of the gene, governed by its upstream elements. FASEB J 15:383–392
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by a Research Funding Development Grant from WVU SoM.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fil, D., Borysiewicz, E. & Konat, G.W. A broad upregulation of cerebral chemokine genes by peripherally-generated inflammatory mediators. Metab Brain Dis 26, 49–59 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-010-9231-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-010-9231-9