Abstract
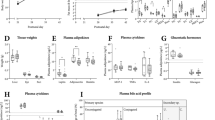
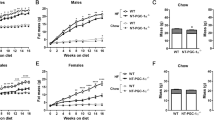
It was shown previously that the intestinal fatty acid binding protein (I-FABP) is not essential for the absorption of dietary fat. One notable feature of I-FABP deficiency was the enhancement of body weight gain in male mice but not in female mice. To explore a possible cause for this gender dimorphic effect, we examined the changes in expression of genes that encode liver fatty acid binding protein (L-FABP) and ileal lipid binding protein in the small intestine resulting from I-FABP deficiency. The results indicate that both L-FABP and ilbp levels are modestly increased in the small intestine of chow-fed mice lacking I-FABP. There was no discernible alteration of overall morphology or histology in the small intestine but changes in liver histology were evident in I-FABP deficient male mice. Glucose tolerance was also investigated in aged mice. I-FABP deficiency had no effect on glucose tolerance in male mice but it appeared to be improved in female mice. Thus, male and female mice clearly respond differently to the loss of I-FABP from the small intestine but the observed changes in the abundance of L-FABP and ilbp protein do not readily account for this phenomenon. (Mol Cell Boichem xxx: 1–8, 2005)
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FABP:
-
fatty acid binding protein
- FXR:
-
farnesold x receptor
- L-FABP:
-
liver FABP
- I-FABP:
-
intestinal FABP
- ilbp:
-
ileal lipid binding protein
References
Agellon LB, Toth MJ and Thomson AB: Intracellular lipid binding proteins of the small intestine. Mol Cell Biochem 239: 79–82, 2002
Richieri GV, Ogata RT, Zimmerman AW, Veerkamp JH and Kleinfeld AM: Fatty acid binding proteins from different tissues show distinct patterns of fatty acid interactions. Biochemistry 39: 7179–7204, 2000
Labonté ED, Li Q, Kay CM and Agellon LB: The relative ligand binding preference of the murine ileal lipid binding protein. Prot Exp Purif 28: 25–33, 2002
Martin GG, Danneberg H, Kumar LS, Atshaves BP, Erol E, Bader M, Schroeder F and Binas B: Decreased liver fatty acid binding capacity and altered liver lipid distribution in mice lacking the liver fatty acid-binding protein gene. J Biol Chem 278: 21429–21438, 2003
Newberry EP, Xie Y, Kennedy S, Han X, Buhman KK, Luo J, Gross RW and Davidson NO: Decreased hepatic triglyceride accumulation and altered fatty acid uptake in mice with deletion of the liver fatty acid-binding protein gene. J Biol Chem 278: 51664–51672, 2003
Erol E, Kumar LS, Cline GW, Shulman GI, Kelly DP and Binas B: Liver fatty acid binding protein is required for high rates of hepatic fatty acid oxidation but not for the action of PPARα in fasting mice. FASEB J 18: 347–349, 2004
Parks DJ, Blanchard SG, Bledsoe RK, Chandra G, Consler TG, Kliewer SA, Stimmel JB, Willson TM, Zavacki AM, Moore DD and Lehman JM: Bile acids: Natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science 284: 1365–1368, 1999
Wang H, Chen J, Hollister K, Sowers LC and Forman BM: Endogenous bile acids are ligands for the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR. Mol Cell 3: 543–553, 1999
Sinal CJ, Tohkin M, Miyata M, Ward JM, Lambert G and Gonzales FJ: Targeted disruption of the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR impairs bile acid and lipid homeostasis. Cell 102: 731–744, 2000
Kok T, Hulzebos CV, Wolters H, Havinga R, Agellon LB, Stellaard F, Shan B, Schwarz M and Kuipers F: Enterohepatic circulation of bile salts in farnesoid X receptor-deficient mice: efficient intestinal bile salt absorption in the absence of ileal bile acid-binding protein. J Biol Chem 278: 41930–41937, 2003
Vassileva G, Huwyler L, Poirier K, Agellon LB and Toth MJ: The intestinal fatty acid binding protein is not essential for dietary fat absorption in mice. Faseb J 14: 2040–2046, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agellon, L.B., Li, L., Luong, L. et al. Adaptations to the loss of intestinal fatty acid binding protein in mice. Mol Cell Biochem 284, 159–166 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-9042-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-9042-1