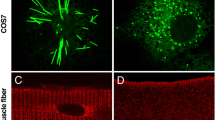
Abstract
The impact of calcium signaling on many cellular functions is reflected by the tight regulation of the intracellular Ca2+ concentration that is ensured by diverse pumps, channels, transporters and Ca2+ binding proteins. In this review, we present recently identified novel sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum proteins that may have a potential involvement in the regulation of Ca2+ homeostasis in striated muscles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson AA, Treves S, Biral D, Betto R, Sandona D, Ronjat M, Zorzato F, 2003 The novel skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum JP-45 protein. Molecular cloning, tissue distribution, developmental expression, and interaction with alpha 1.1 subunit of the voltage-gated calcium channel J Biol Chem 278: 39987–39992
Avila G, 2005 Intracellular Ca2+ dynamics in malignant hyperthermia and central core disease: established concepts, new cellular mechanisms involved Cell Calcium 37: 121–127
Beard NA, Laver DR, Dulhunty AF, 2004 Calsequestrin and the calcium release channel of skeletal and cardiac muscle Prog Biophys Mol Biol 85: 33–69
Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Lipp P, 1998 Calcium: a life and death signal Nature 395: 645–648
Bers DM, 2002 Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling Nature 415: 198–205
Bers DM, 2004 Macromolecular complexes regulating cardiac ryanodine receptor function J Mol Cell Cardiol 37: 417–429
Block BA, Imagawa T, Campbell KP, Franzini-Armstrong C, 1988 Structural evidence for direct interaction between the molecular components of the transverse tubule/sarcoplasmic reticulum junction in skeletal muscle J Cell Biol 107: 2587–2600
Buratti R, Prestipino G, Menegazzi P, Treves S, Zorzato F, 1995 Calcium dependent activation of skeletal muscle Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) by calmodulin Biochem Biophys Res Commun 213: 1082–1090
Coronado R, Morrissette J, Sukhareva M, Vaughan DM, 1994 Structure and function of ryanodine receptors Am J Physiol 266: C1485–14504
Costello B, Chadwick C, Saito A, Chu A, Maurer A, Fleischer S, 1986 Characterization of the junctional face membrane from terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum J Cell Biol 103: 741–753
Damiani E, Tobaldin G, Bortoloso E, Margreth A, 1997 Functional behaviour of the ryanodine receptor/Ca(2+)-release channel in vesiculated derivatives of the junctional membrane of terminal cisternae of rabbit fast muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Cell Calcium 22: 129–150
Delbono O, Renganathan M, Messi ML, 1997 Excitation-Ca2+ release-contraction coupling in single aged human skeletal muscle fiber Muscle Nerve Suppl. 5: S88–S99
Dinchuk JE, Henderson NL, Burn TC, Huber R, Ho SP, Link J, O’Neil KT, Focht RJ, Scully MS, Hollis JM, Hollis GF, Friedman PA, 2000 Aspartyl beta -hydroxylase (Asph) and an evolutionarily conserved isoform of Asph missing the catalytic domain share exons with junctin J Biol Chem 275: 39543–39554
Dulhunty AF, Haarmann CS, Green D, Laver DR, Board PG, Casarotto MG, 2002 Interactions between dihydropyridine receptors and ryanodine receptors in striated muscle Prog Biophys Mol Biol 79: 45–75
Ferreiro A, Monnier N, Romero NB, Leroy JP, Bonnemann C, Haenggeli CA, Straub V, Voss WD, Nivoche Y, Jungbluth H, Lemainque A, Voit T, Lunardi J, Fardeau M, Guicheney P, 2002 A recessive form of central core disease, transiently presenting as multi-minicore disease, is associated with a homozygous mutation in the ryanodine receptor type 1 gene Ann Neurol 51: 750–759
Flucher BE, 1992 Structural analysis of muscle development: transverse tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, and the triad Dev Biol 154: 245–260
Franzini-Armstrong C, Protasi F, 1997 Ryanodine receptors of striated muscles: a complex channel capable of multiple interactions Physiol Rev 77: 699–729
Gommans IM, Vlak MH, de Haan A, van Engelen BG, 2002 Calcium regulation and muscle disease J Muscle Res Cell Motil 23: 59–63
González E, Messi L, Zheng Z, Delbono O, 2003 Insulin-like growth factor-1 prevents age-related decrease in specific force and intracellular Ca2+ in single intact muscle fibres from transgenic mice J Physiol 552: 833–844
Gyorke S, Gyorke I, Lukyanenko V, Terentyev D, Viatchenko-Karpinski S, Wiesner TF, 2002 Regulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release by luminal calcium in cardiac muscle Front Biosci 7: d1454–1463
Hellstern S, Pegoraro S, Karim CB, Lustig A, Thomas DD, Moroder L, Engel J, 2001 Sarcolipin, the shorter homologue of phospholamban, forms oligomeric structures in detergent micelles and in liposomes J Biol Chem 276: 30845–30852
Hong CS, Kwak YG, Ji JH, Chae SW, Kim do H, 2001 Molecular cloning and characterization of mouse cardiac junctate isoforms Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289: 882–887
Imagawa T, Smith JS, Coronado R, Campbell KP, 1987 Purified ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum is the Ca2+-permeable pore of the calcium release channel J Biol Chem 262: 16636–16643
Ito K, Komazaki S, Sasamoto K, Yoshida M, Nishi M, Kitamura K, Takeshima H, 2001 Deficiency of triad junction and contraction in mutant skeletal muscle lacking junctophilin type 1 J Cell Biol 154: 1059–1067
Jayaraman T, Brillantes AM, Timerman AP, Fleischer S, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Marks AR, 1992 FK506 binding protein associated with the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) J Biol Chem 267: 9474–9477
Jones LR, Zhang L, Sanborn K, Jorgensen AO, Kelley J, 1995 Purification, primary structure, and immunological characterization of the 26-kDa calsequestrin binding protein (junctin) from cardiac junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum J Biol Chem 270: 30787–30796
Jurkat-Rott K, Lerche H, Lehmann-Horn F, 2002 Skeletal muscle channelopathies J Neurol 249: 1493–1502
Kawasaki T, Kasai M, 1994 Regulation of calcium channel in sarcoplasmic reticulum by calsequestrin Biochem Biophys Res Commun 199: 1120–1127
Kim KC, Caswell AH, Talvenheimo JA, Brandt NR, 1990 Isolation of a terminal cisterna protein which may link the dihydropyridine receptor to the junctional foot protein in skeletal muscle Biochemistry 29: 9281–9289
Lai FA, Erickson HP, Rousseau E, Liu QY, MeissnerG, 1988 Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle Nature 331: 315–319
Loke J, MacLennan DH, 1998 Malignant hyperthermia and central core disease: disorders of Ca2+ release channels Am J Med 104: 470–486
Lyfenko AD, Goonasekera SA, Dirksen RT, 2004 Dynamic alterations in myoplasmic Ca2+ in malignant hyperthermia and central core disease Biochem Biophys Res Commun 322: 1256–1266
MacKrill JJ, 1999 Protein-protein interactions in intracellular Ca2+-release channel function Biochem J, 337: 345–361
MacLennan DH, Wong PT, 1971 Isolation of a calcium-sequestering protein from sarcoplasmic reticulum Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 68: 1231–1235
MacLennan DH, 2000 Ca2+ signalling and muscle disease Eur J Biochem 267: 5291–5297
MacLennan DH, Asahi M, Tupling AR, 2003 The regulation of SERCA-type pumps by phospholamban and sarcolipin Ann NY Acad Sci 986: 472–480
Maier LS, Bers DM, 2002 Calcium, calmodulin, and calcium-calmodulin kinase II: heartbeat to heartbeat and beyond J Mol Cell Cardiol 34: 919–939
Marsili V, Mancinelli L, Menchetti G, Fulle S, Baldoni F, Fano G, 1992 S-100ab increases Ca2+ release in purified sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles of frog skeletal muscle J Muscle Res Cell Motil 13: 511–515
Marty I, Robert M, Villaz M, De Jongh K, Lai Y, Catterall WA, Ronjat M, 1994 Biochemical evidence for a complex involving dihydropyridine receptor and ryanodine receptor in triad junctions of skeletal muscle Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 2270–2274
Marx SO, Ondrias K, Marks AR, 1998 Coupled gating between individual skeletal muscle Ca2+ release channels (ryanodine receptors) Science 281: 818–821
Marx SO, Gaburjakova J, Gaburjakova M, Henrikson C, Ondrias K, Marks AR, 2001 Coupled gating between cardiac calcium release channels (ryanodine receptors) Circ Res 88: 1151–1158
Meissner G, 1994 Ryanodine receptor/Ca2+ release channels and their regulation by endogenous effectors Annu Rev Physiol 56: 485–508
Meldolesi J, Pozzan T, 1998 The endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ store: a view from the lumen Trends Biochem Sci. 23: 10–14
Melzer W, Herrmann-Frank A, Luttgau HC, 1995 The role of Ca2+ ions in excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal muscle fibres Biochim Biophys Acta 1241: 59–116
Meyers MB, Pickel VM, Sheu SS, Sharma VK, Scotto KW, Fishman GI, 1995 Association of sorcin with the cardiac ryanodine receptor J Biol Chem 270: 26411–26418
Milner RE, Famulski KS, Michalak M, 1992 Calcium binding proteins in the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum of muscle and nonmuscle cells Mol Cell Biochem 112: 1–13
Missiaen L, Robberecht W, van den Bosch L, Callewaert G, Parys JB, Wuytack F, Raeymaekers L, Nilius B, Eggermont J, De Smedt H, 2000 Abnormal intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and disease Cell Calcium 28: 1–21
Murray BE, Ohlendieck K, 1997 Cross-linking analysis of the ryanodine receptor and alpha1-dihydropyridine receptor in rabbit skeletal muscle triads Biochem J, 324: 689–696
Odermatt A, Taschner PE, Scherer SW, Beatty B, Khanna VK, Cornblath DR, Chaudhry V, Yee WC, Schrank B, Karpati G, Breuning MH, Knoers N, MacLennan DH, 1997 Characterization of the gene encoding human sarcolipin (SLN), a proteolipid associated with SERCA1: absence of structural mutations in five patients with Brody disease Genomics 45: 541–553
Parekh AB, 2003 Mitochondrial regulation of intracellular Ca2+ signaling: more than just simple Ca2+ buffers News Physiol Sci 18: 252–256
Pasquali C, Fialka I, Huber LA, 1999 Subcellular fractionation, electromigration analysis and mapping of organelles J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 722: 89–102
Pozzan T, Rizzuto R, Volpe P, Meldolesi J, 1994 Molecular and cellular physiology of intracellular calcium stores Physiol Rev 74: 595–636
Protasi F, Franzini-Armstrong C, Allen PD, 1998 Role of ryanodine receptors in the assembly of calcium release units in skeletal muscle J Cell Biol 140: 831–842
Protasi F, 2002 Structural interaction between RYRs and DHPRs in calcium release units of cardiac and skeletal muscle cells Front Biosci 7: d650–658
Renganathan M, Messi ML, Delbono O, 1997 Dihydropyridine receptor-ryanodine receptor uncoupling in aged skeletal muscle J Membr Biol 157: 247–253
Renganathan M, Messi ML, Delbono O, 1998 Overexpression of IGF-1 exclusively in skeletal muscle prevents age-related decline in the number of dihydropyridine receptors J Biol Chem 273: 28845–28851
Rios E, Ma JJ, Gonzalez A, 1991 The mechanical hypothesis of excitation-contraction (EC) coupling in skeletal muscle J Muscle Res Cell Motil 12: 127–135
Rios E, Pizarro G, Stefani E, 1992 Charge movement and the nature of signal transduction in skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling Annu Rev Physiol 54: 109–133
Rizzuto R, Pozzan T, 2003 When calcium goes wrong: genetic alterations of a ubiquitous signaling route Nat Genet 34: 135–141
Saito A, Seiler S, Chu A, Fleischer S, 1984 Preparation and morphology of sarcoplasmic reticulum terminal cisternae from rabbit skeletal muscle J Cell Biol 99: 875–885
Simmerman HK, Jones LR, 1998 Phospholamban: protein structure, mechanism of action, and role in cardiac function Physiol Rev 78: 921–947
Takekura H, Kasuga N, Kitada K, Yoshioka T, 1996 Morphological changes in the triads and sarcoplasmic reticulum of rat slow and fast muscle fibres following denervation and immobilization J Muscle Res Cell Motil 17: 391–400
Takeshima H, Komazaki S, Nishi M, Iino M, Kangawa K, 2000 Junctophilins: a novel family of junctional membrane complex proteins Mol Cell 6: 11–22
Treves S, Scutari E, Robert M, Groh S, Ottolia M, Prestipino G, Ronjat M, Zorzato F, 1997 Interaction of S100A1 with the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of skeletal muscle Biochemistry 36: 11496–11503
Treves S, Feriotto G, Moccagatta L, Gambari R, Zorzato F, 2000 Molecular cloning, expression, functional characterization, chromosomal localization, and gene structure of junctate, a novel integral calcium binding protein of sarcoendoplasmic reticulum membrane J Biol Chem 275: 39555–39568
Treves S, Franzini-Armstrong C, Moccagatta L, Arnoult C, Grasso C, Schrum A, Ducreux S, Zhu MX, Mikoshiba K, Girard T, Smida-Rezgui S, Ronjat M, Zorzato F, 2004 Junctate is a key element in calcium entry induced by activation of InsP3 receptors and/or calcium store depletion J Cell Biol 166: 537–548
Valdivia HH, 1998 Modulation of intracellular Ca2+ levels in the heart by sorcin and FKBP12, two accessory proteins of ryanodine receptors Trends Pharmacol Sci 19: 479–482
Wehrens XH, Lehnart SE, Marks AR, 2005 Intracellular calcium release and cardiac disease Annu Rev Physiol 67: 69–98
Yano M, el-Hayek R, and Ikemoto N (2005) Conformational changes in the junctional foot protein/Ca2+ release channel mediate depolarization-induced Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 270: 3017–3021
Zimmer DB, Cornwall EH, Landar A, Song W, 1995 The S100 protein family: history, function, and expression Brain Res Bull 37: 417–429
Zorzato F, Anderson AA, Ohlendieck K, Froemming G, Guerrini R, Treves S, 2000 Identification of a novel 45 kDa protein (JP-45) from rabbit sarcoplasmic-reticulum junctional-face membrane Biochem J 351: 537–543
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the European Union HPRN-CT-2002–00331, from the Schweizereische die Erforschung der Muskelkrankheiten, from the Association Française contre les Myopathies, from F.I.R.B RBAU01ERMX and from the Swiss National Science Foundation SNF 3200-067820.02. This work was also supported by Department of Anaesthesia, University Hospital Basel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DIVET, A., PAESANTE, S., BLEUNVEN, C. et al. Novel sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum proteins and calcium homeostasis in striated muscles. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 26, 7–12 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-005-9001-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-005-9001-1