Abstract
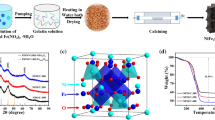
Metal oxide nanoparticle embedded porous carbon composite materials have various uses, including as catalyst supports and adsorbents, because of their good stability and unique porosity. Despite their importance, the synthetic strategies of metal-oxide nanoparticle-embedded porous carbon composites to control their properties have not been widely studied. Here, we present a facile synthesis method for γ-Fe2O3-embedded porous carbon materials via the pyrolysis of Fe-based metal–organic framework (MOF, MIL-100). We found that simple treatment to the starting material (MIL-100) allows control γ-Fe2O3 particle size, chemical composition, porosity, and H2 sorption property of the resulting composite materials. This work presents a synthesis of a series of porous carbon composites from a single MOF by treating further carbon source. This synthetic strategy may provide a clue for synthesis of a variety of composite materials using MOFs for battery electrode and catalyst applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Further experiment using different MOF is presented in electronic supplementary information. Although the porosity was not exactly controlled, we found that the surface area increased as increasing carbon contents. However, we also found that the nature of metal oxide NPs may affect to the porosity of the resulting composite materials.
References
Y. Yürüm, A. Taralp, T.N. Veziroglu, Storage of hydrogen in nanostructured carbon materials. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 34, 3784–3798 (2009)
P. Serp, J.L. Figueiredo, Carbon Materials for Catalysis (Wiley, New York, 2009)
Y. Yang, K. Chiang, N. Burke, Porous carbon-supported catalysts for energy and environmental applications: a short review. Catal. Today 178, 197–205 (2011)
N. Daems, X. Sheng, I.F.J. Vankelecom, P.P. Pescarmona, Metal—free doped carbon materials as electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 4085–4110 (2014)
J. Tang, J. Liu, N.L. Torad, T. Kimura, Y. Yamaguchi, Tailored design of functional nanoporous carbon materials toward fuel cell applications. Nano Today 9, 305–323 (2014)
A.D. Roberts, X. Li, H. Zhang, Porous carbon spheres and monoliths: morphology control, pore size tuning and their applications as Li-ion battery anode materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 4341–4356 (2014)
N. Yan, X. Zhou, Y. Li, F. Wang, H. Zhong, H. Wang, Q. Chen, Fe2O3 nanoparticles wrapped in multi-walled carbon nanotubes with enhanced lithium storage capability. Scientific Report 3, 3392 (2013)
B. Liu, H. Shioyama, T. Akita, Q. Xu, Metal-organic framework as a template for porous carbon synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 5390–5391 (2008)
H.L. Jiang, B. Liu, Y.Q. Lan, K. Kuratani, T. Akita, H. Shioyama, F. Zong, Q. Xu, From metal-organic framework to nanoporous carbon: toward a very high surface area and hydrogen uptake. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 11854–11857 (2011)
S.J. Yang, T. Kim, J.H. Im, Y.S. Kim, K. Lee, H. Jung, C.R. Park, MOF-derived hierarchically porous carbon with exceptional porosity and hydrogen storage capacity. Chem. Mater. 24, 464–470 (2012)
S. Lim, K. Suh, Y. Kim, M. Yoon, H. Park, D.N. Dybtsev, K. Kim, Porous carbon materials with a controllable surface area synthesized from metal–organic framework. Chem. Commun. 48, 7447–7449 (2012)
J. Hu, H. Wang, Q. Gao, H. Guo, Porous carbons prepared by using metal-organic framework as the precursor for supercapacitor. Carbon 48, 3599–3606 (2010)
S.J. Yang, S. Nam, T. Kim, J.H. Im, H. Jung, J.H. Kang, S. Wi, B. Park, C.R. Park, Preparation and exceptional lithium anodic performance of porous carbon-coated ZnO quantum dots derived from a metal–organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 7394–7397 (2013)
G. Zhang, S. Hou, H. Zhang, W. Zeng, F. Yan, C. Chao Li, H. Duan (2015) High-performance and ultra-stable lithium-ion batteries based on MOF-derived ZnO @ZnO quantum dots/C core-shell nanorod arrays on a caebon cloth anode. Adv. Mater. doi:10.1002/adma.201405222
F. Zou, X. Hu, Z. Li, L. Qie, C. Hu, R. Zeng, Y. Jiang, Y. Huang, MOF-derived porous ZnO/ZnFe2O4/C octahedra with hollow interiors for high-rate lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 26, 6622–6628 (2014)
J. Tang, R.R. Salunkhe, J. Liu, N.L. Torad, M. Imura, S. Furukawa, Y. Yamaguchi, Thermal conversion of core-shell metal-organic frameworks: a new method for selectively functionalized nanoporous hybrid carbon. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 1572–1580 (2015)
F. Wei, J. Jiang, G. Yu, Y. Sui, A novel cobalt–carbon composite for the electrochemical supercapacitor electrode material. Mater. Lett. 146, 20–22 (2015)
A. Kong, C. Mao, Q. Lin, X. Wei, X. Bu, P. Feng, From cage-in-cage MOF to N-doped and Co-nanoparticle-embedded carbon for oxygen reduction reaction. Dalton Trans. 44, 6748–6754 (2015). doi:10.1039/c4dt03726j
K.E. deKrafft, C. Wang, W. Lin, Metal-organic framework templated synthesis of Fe2O3/TiO2 nanocomposite for hydrogen production. Adv. Mater. 24, 2014–2018 (2012)
X. Xu, R. Cao, S. Jeong, J. Cho, Spindle-like mesoporous α-Fe2O3 anode material prepared from MOF template for high-rate lithium batteries. Nano Lett. 12, 4988–4991 (2012)
A. Banerjee, R. Gokhale, S. Bhatnagar, J. Jog, M. Bhardwaj, B. Lefez, B. Hannoyer, S. Ogale, MOF derived porous carbon–Fe3O4 nanocomposite as a high performance, recyclable environmental superadsorbent. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 19694–19699 (2012)
G. Férey, C. Serre, C. Mellot-Draznieks, F. Millange, S. Surblé, J. Dutour, I. Margiolaki, A hybrid solid with giant pores prepared by a combination of targeted chemistry, simulation, and powder diffraction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 6296–6301 (2004)
P. Tarazona, U. Marini Bettolo Marconi, R. Evans, Phase equilibria of fluid interfaces and confined fluids: non-local versus local density functionals. Mol. Phys. 60, 573–595 (1987)
C. Lastoskie, K.E. Gubbins, N. Quirke, Pore size distribution analysis of microporous carbons: a density functional theory approach. J. Phys. Chem. 97, 4786–4796 (1993)
S.H. Yeon, P. Reddington, Y. Gogotsi, J.E. Fischer, C. Vakifahmetoglu, P. Colombo, Carbide-derived-carbons with hierarchical porosity form a preceramic polymer. Carbon 48, 201–210 (2010)
G.S. Paul, J.H. Kim, M.-S. Kim, K. Do, J. Ko, J.-S. Yu, Different hierarchical nanostructured carbons as counter electrodes for CdS quantum dot solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 375–381 (2012)
B. Fang, J.H. Kim, M.-S. Kim, A. Bonakdarpour, A. Lam, D.P. Wilkinson, J.-S. Yu, Fabrication of hollow core carbon spheres with hierarchical nanoarchitecture for ultrahigh electrical charge storage. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 19031–19038 (2012)
D.N. Dybtsev, H. Chun, S.H. Yoon, D. Kim, K. Kim, Microporous manganese formate: a simple metal-organic porous material with high framework stability and highly selective gas sorption properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 32–33 (2004)
H. Kim, D.G. Samsonenko, M. Yoon, J.W. Yoon, Y.K. Hwang, J.-S. Chang, K. Kim, Temperature-triggered gate opening for gas adsorption in microporous manganese formate. Chem. Commun. 44, 4697–4699 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Foundation for the Advancement of Science and Creativity (KOFAC) and funded by the Korean Government (MOE). This work was also supported by the Principle Research Program of the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute. We thank Mr. S. Kim and Y. Song for assistance for the XRD measurement and data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, E., Yoon, M. Facile synthesis of γ-Fe2O3@porous carbon materials using an Fe-based metal–organic framework: structure and porosity study. J Porous Mater 22, 1495–1502 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-015-0030-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-015-0030-x