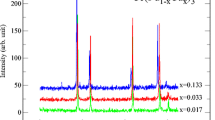
We report on X-ray powder diffraction, magnetic susceptibility, electrical resistivity, and specific heat measurements on samples of Ce1-xLaxPt3Si and CePt3Si1+δ in order to better understand this unusual heavy Fermion superconductor’s normal and superconducting state properties. By suppressing the antiferromagnetic transition, TN = 2.2 K, using La-doping on the Ce-site in CePt3Si, we find that in Ce1-xLaxPt3Si, x ≥ 0.8, ρ, χ, and C/T show non-Fermi liquid temperature dependences. C/T ~ Tα with α ~ 1 for the temperature range of 0.3–3 K while low-temperature (2–20 K) susceptibility data follow 1/χ−1/χ0 = aTη behavior with η = 0.36. In addition, χ and C/T exhibit single-ion behavior in this composition range (x ≥ 0.8), i.e. the measured values expressed per Ce-mole are independent of x. Via doping the Si-site with a small excess—2–4—of Si, we present specific heat data for the bulk superconducting transition at Tc ~ 0.8 K showing that this excess sharpens the transition, obviating the need for annealing. Measurements of the X-ray diffraction patterns, ρ, χ, and C/T of these CePt3Si1+δ samples, when compared to similar measurements on annealed CePt3Si samples, indicate that the microscopic mechanism for the strengthening and sharpening of ΔC(Tc) with Si-excess may be similar to that responsible in the annealed material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seaman C.L., Maple M.B., Lee B.W., Ghamaty S., Torikachvili M.S., Kang J.-S., Liu L.Z., Allen J.W., Cox D.L. (1991) Phys. Rev. Lett. 67:2882
Stewart G.R., Rev. Mod. Phys. 73, 797 (2001); see also G. R. Stewart, Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 743 (2006) for an update.
Bauer E., Hilscher G., Michor H., Paul Ch., Scheidt E.W., Gribanov A., Seropegin Yu., Noel H., Sigrit M., Rogl P. (2004) Phys. Rev. Lett. 92:027003
St. Laumann, Lackner R., Michor H., Hilscher G., Bauer E. (2006) Physica B 378-380:386
For a review, see E. Bauer, G. Hilscher, H. Michor, M. Sieberer, E. W. Scheidt, A. Gribanov, Yu. Seropegin, P. Rogl, A. Amato, W. Y. Song, J.-G. Park, D. T. Adroja, M. Nicklas, G. Sparn, M. Yogi, and Y. Kitaoka, Physica B 359-361, 360 (2005).
Frigeri P.A., Agterberg D.F., Koga A., Sigrist M. (2004) Phys. Rev. Lett. 92:097001
Saxena S.S., Monthoux P. (2004) Nature 427:799
Kim J.S., Mixson D.J, Burnette D.J., Jones T., Kummar P., Andraka B., Stewart G.R., Cracium V., Acree W., Yuan H.Q., Vandervelde D., Salamon M.B. (2005) Phys. Rev. B 71:212505
Stewart G.R. (1983) Rev. Sci. Instr. 54:1
Hewson A.C. (1997) The Kondo Problem to Heavy Fermions. Cambridge University Press Cambridge, England
A recent study of CePt3+δSi1-δ, for δ = 0.03, i.e. for sub-stoichiometric Si, found a definite decrease in T c measured inductively, see G. Motoyama, S. Yamamoto, H. Takezoe, Y. Oda, K. Ueda, and T. Kohara, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 75, 13706 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.S., Mixson, D.J., Burnette, D.J. et al. Normal and Superconducting State Properties of Doped CePt3Si. J Low Temp Phys 147, 135–146 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-007-9304-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-007-9304-2