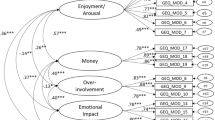
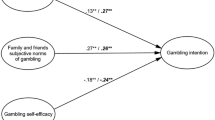
Abstract
Most high school adolescents have reported past year gambling, and males gamble more frequently and problematically than females. Ethnic minority adolescents appear to be gambling at a higher rate than Caucasian adolescents. There is evidence indicating that adolescent gambling outcome expectancies are correlated with gambling behavior, but limited evidence that this relation differs by gender. In the present study gender was evaluated as a moderator in the relation between gambling outcome expectancies and gambling behaviors in an African-American high school sample. Males gambled more frequently, gambled more problematically and held more positive gambling outcome expectancies than females. Gender was found to moderate the relations between gambling frequency and the expectations of material gain, affect, self-evaluation and parental approval. Gender also moderated the relations between gambling problems and expectations of affect and self-evaluation. These findings should inform future adolescent gambling prevention and intervention programs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Barnes, G. M., Welte, J. W., Hoffman, J. H., & Tidwell, M. C. (2009). Gambling, alcohol, and other substance use among youth in the United States. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 70, 134–142.
Blom, G. (1958). Statistical estimates and transformed beta variables. New York: Wiley.
Botvin, G. J., Baker, E., Dusenbury, L., Tortu, S., & Botvin, E. M. (1990). Preventing adolescent drug abuse through a multimodal cognitive-behavioral approach: Results of a 3-year study. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 58, 437–446. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.58.4.437.
Businelle, M. S., Kendzor, D. E., Rash, C. J., Patterson, S. M., & Copeland, A. L. (2009). The development and validation of the methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) beliefs questionnaire (MDMA-BQ) in college students. Addiction Research and Therapy, 17, 432–445. doi:10.1080/16066350801902442.
Derevensky, J. L., & Gupta, R. (2000). Prevalence estimates of adolescent gambling: A comparison of the SOGS-RA, DSM-IV-J, and the GA 20 questions. Journal of Gambling Behavior, 16, 227–251. doi:10.1023/A:1009485031719.
Dunn, M. E., Lau, H., & Cruz, I. Y. (2000). Changes in activation of alcohol expectancies in memory in relation to changes in alcohol use after participation in an expectancy challenge program. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 8, 566–575. doi:10.1037/1064-1297.8.4.566.
Faregh, N., & Derevensky, J. (2011). A comparative latent class analysis of endorsement profiles of DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for problem gambling among adolescents from a community and a treatment sample. Addiction Research & Theory, 19(4), 323–333. doi:10.3109/16066359.2011.552817.
Gillespie, M. A. M., Derevensky, J., & Gupta, R. (2007). The utility of outcome expectancies in the prediction of adolescent gambling behaviour. Journal of Gambling Issues, 19, 69–85. doi:10.4309/jgi.2007.19.4.
Gupta, R., & Derevensky, J. (1998). Adolescent gambling behaviour: A prevalence study and examination of the correlates associated with problem gambling. Journal of Gambling Studies, 14, 319–345. doi:10.1023/A:1023068925328.
Hardoon, K. K., Gupta, R., & Derevensky, J. L. (2004). Psychosocial variables associated with adolescent gambling. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 18, 170–179. doi:10.1037/0893-164X.18.2.170.
Holmbeck, G. N. (2002). Post-hoc probing of significant moderational and mediational effects in studies of pediatric populations. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 27, 87–96.
Jones, B. T., Corbin, W., & Fromme, K. (2001). A review of expectancy theory and alcohol consumption. Addiction, 96, 57–72. doi:10.1046/j.1360-0443.2001.961575.x.
Kroneman, L., Loeber, R., & Hipwell, A. E. (2004). Is neighborhood context differently related to externalizing problems and delinquency for girls compared with boys? Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 7, 109–122. doi:10.1023/B:CCFP.0000030288.01347.a2.
Lynch, W. J., Maciejewski, P. K., & Potenza, M. N. (2004). Psychiatric correlates of gambling in adolescents and young adults grouped by age at gambling onset. Archives of General Psychiatry, 61, 1116–1122. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.61.11.1116.
Martins, S., Storr, C. L., Ialongo, N. S., & Chilcoat, H. D. (2008). Gender differences in mental health characteristics and gambling among African-American adolescent gamblers. The American Journal on Addictions, 17, 126–134. doi:10.1080/10550490701861227.
Nower, L., Gupta, R., Blaszczynski, A., & Derevensky, J. (2004). Suicidal ideation and depression among youth gamblers: A preliminary examination of three studies. International Gambling Studies, 4, 69–80. doi:10.1080/1445979042000224412.
Rahman, A. S., Pilver, C. E., Desai, R. A., et al. (2012). The relationship between age of gambling onset and adolescent problematic gambling severity. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 46, 675–683. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2012.02.007.
Schaffner, L. (1999). Violence and female delinquency: Gender transgressions and gender invisibility. Berkeley Women’s Law Journal, 14, 40–65.
Sharkansky, E. J. & Finn, P. R. (1998). Effects of outcome expectancies and disinhibition on ad lib alcohol consumption. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 56, 198–206.
Stein, K. D., Goldman, M. S., & Del Boca, F. K. (1997). Happy hour: The relative effects of alcohol expectancies and positive mood on drinking behavior. San Francisco: Annual Meeting of the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Stinchfield, R. (2000). Gambling and correlates of gambling among Minnesota public school students. Journal of Gambling Studies, 16, 153–173. doi:10.1023/A:1009428913972.
Vachon, J., Vitaro, F., Wanner, B., & Tremblay, R. E. (2004). Adolescent gambling: Relationships with parent gambling and parenting practices. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 18, 398–401.
Wahl, S. K., Turner, L. R., Mermelstein, R. J., & Flay, B. R. (2005). Adolescents’ smoking expectancies: Psychometric properties and prediction of behavior change. Niccotine and Tobacco Research, 7, 613–623. doi:10.1080/14622200500185579.
Welte, J. W., Barnes, G. M., Tidwell, M. O., & Hoffman, J. H. (2009). The association between problem gambling and conduct disorder in a U.S. national survey of adolescents and young adults. Journal of Adolescent Health, 45, 396–401. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2009.02.002.
Welte, J. W., Wieczorek, W. F., Barnes, G. M., Tidwell, M. C., & Hoffman, J. H. (2004). The relationship of ecological and geographic factors to gambling behavior and pathology. Journal of Gambling Studies, 20, 405–423. doi:10.1007/s10899-004-4582-y.
Wickwire, E. M., Whelan, J. P., & Meyers, A. W. (2010). Outcome expectancies and gambling behavior among urban adolescents. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 24, 75–88. doi:10.1037/a0017505.
Wickwire, E. M., Whelan, J. P., Meyers, A. W., & Murray, D. M. (2007). Environmental correlates of gambling behavior in urban adolescents. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 35, 179–190. doi:10.1007/s10802-006-9065-4.
Winters, K. C., Stinchfield, R., & Fulkerson, J. (1993). Patterns and characteristics of adolescent gambling. Journal of Gambling Studies, 9, 371–386. doi:10.1007/BF01014628.
Winters, K. C., Stinchfield, R. D., & Kim, L. G. (1995). Monitoring adolescent gambling in Minnesota. Journal of Gambling Studies, 11, 165–183. doi:10.1007/BF02107113.
Young, R. M., Connor, J. P., & Feeney, G. F. (2011). Alcohol expectancy changes over a 12-week cognitive-behavioral therapy program are predictive of treatment success. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 40, 18–25. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2010.08.003.
Zahn, M. A., Hawkins, S. R., Chiancone, J., & Whitworth, A. (2008). The girls study group: Charting the way to delinquency prevention for girls. Retrieved from https://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/ojjdp/223434.pdf
Zitzow, D. (2003). American Indian gambling. In H. J. Shaffer, M. N. Hall, J. Vander Bilt, & E. George (Eds.), Futures at stake: Youth, gambling, and society (pp. 39–48). Reno, NV: University of Nevada Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simmons, J.L., Whelan, J.P., Meyers, A.W. et al. Gambling Outcome Expectancies and Gambling Behavior Among African-American Adolescents: Gender as a Moderating Variable. J Gambl Stud 32, 205–215 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-015-9521-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-015-9521-6