Abstract
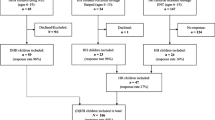
This paper describes the relationship between retrospective communication difficulties and current depressive symptomatology. A total of 143 deaf/hard-of-hearing late adolescents and adults (64 % White; 55 % female) completed questionnaires related to parent communication, language history and current psychological functioning. Logistic regression models were used to estimate the likelihood of having depression that is associated with understanding parents’ communication after controlling for gender, hearing level, and language history. Significant odds ratio indicated that the difficulties in understanding basic communication with parents increased the odds of depression symptomatology. The odds ratio indicates that when holding all other variables constant, the odds of reporting depression were at least 8 times higher for those who reported being able to understand some to none of what the same-sex parent said. For the different-gender parent, only the mother’s communication with the male individual was associated with depression. Although our study findings suggest that DHH men and women with history of communication difficulties at home are at risk for depression in adulthood, they do not provide information on the causal mechanisms linking communication difficulties early in life and depression later in life. Greater attention should be given to promoting healthy communication between DHH girls and their mothers as well as DHH boys and their fathers, which might reduce the impact on later emergence of depression in the DHH individual.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck, A. T., Steer, R. A., Ball, R., & Ranieri, W. (1996). Comparison of Beck depression inventories -IA and -II in psychiatric outpatients. Journal of Personality Assessment, 67, 588–597.
Dougherty, L. R., Klein, D. N., & Davila, J. A. (2004). Growth curve analysis of the course of dysthymic disorder: the effects of chronic stress and moderation by adverse parent-child relationships and family history. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 72, 1012–1021.
Eckhardt, E., Goldstein, Creamer, et al.(2013) A culturally and linguistically specific deaf depression screener: Results of prototype development. In 141st APHA Annual Meeting (November 2–November 6, 2013). APHA
Emond, A., Ridd, M., Sutherland, H., Allsop, L., Alexander, A., & Kyle, J. (2015). The current health of the signing deaf community in the UK compared with the general population: a cross-sectional study. BMJ open, 5(1), e006668.
Fellinger, J., Holzinger, D., Sattel, H., Laucht, M., & Goldberg, D. (2009). Correlates of mental health disorders among children with hearing impairments. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, 51, 635–641. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.03218.
Fellinger, J., Holzinger, D., & Pollard, R. (2012). Mental health of deaf people. The Lancet, 379(9820), 1037–1044.
Hartman, C. A., Van Sonderen, E. L. P., Den Boer, J. A., Minderaa, R. B., Ormel, J., & Landman Peeters, K. M. C. (2008). Risk of emotional disorder in offspring of depressed parents: gender differences in the effect of a second emotionally affected parent. Depression and Anxiety, 25(8), 653–660.
Kushalnagar, P., Topolski, T. D., Schick, B., et al. (2011). Mode of communication, perceived level of understanding, and perceived quality of life in youth who are deaf or hard of hearing. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education, 16, 512–523.
Kvam, M. H., Loeb, M., & Tambs, K. (2007). Mental health in deaf adults: symptoms of anxiety and depression among hearing and deaf individuals. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education, 12, 1–7.
Landman-Peeters, K. M. C., Hartman, C. A., van der Pompe, G., den Boer, J. A., Minderaa, R. B., & Ormel, J. (2005). Gender differences in the relation between social support, problems in parent-offspring communication, and depression and anxiety. Social Science & Medicine, 60(11), 2549–2559.
Leigh, I. W., & Anthony, S. (1999). Parent bonding in clinically depressed deaf and hard-of-hearing adults. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education, 4, 28–36.
Leigh, I. W., & Anthony-Tolbert, S. (2001). Reliability of the BDI-II with deaf persons. Rehabilitation Psychology, 46, 195.
Lewis, G., Collishaw, S., Thapar, A., et al. (2014). Parent–child hostility and child and adolescent depression symptoms: the direction of effects, role of genetic factors and gender. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 23, 317–327.
McLaughlin, K. A., Kubzansky, L. D., Dunn, E. C., et al. (2010). Childhood social environment, emotional reactivity to stress, and mood and anxiety disorders across the life course. Depression and Anxiety, 12, 1087–1094.
Moitra, T., & Mukherjee, I. (2012). Parent--adolescent communication and delinquency: a comparative study in Kolkata, India. Europe’s Journal of Psychology, 8(1), 74–94.
Sheeber, L. B., Davis, B., Leve, C., et al. (2007). Adolescents’ relationships with their mothers and fathers: associations with depressive disorder and subdiagnostic symptomatology. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 116, 144.
Skalicky, A., Kushalnagar, P., Topolski, TD, et al., (2010). Thematic analysis on DHH-related issues impacting quality of life outcomes. Poster presented at the International Society on Quality of Life Research conference; London.
Slavich, G. M., & Irwin, M. R. (2014). From stress to inflammation and major depressive disorder: A social signal transduction theory of depression. Psychological bulletin, 140, 774.
Watzlawick, P., Beavin, J. H., & Jackson, D. D. (1967). Pragmatics of human communication. New York: Norton.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) of the National Institutes of Health [1R01DC014463-01 A1 to P.K. and 3R01DC014463-01A1S1 diversity supplement to support S.B.]. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
Author K declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author B declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author S declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author L declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kushalnagar, P., Bruce, S., Sutton, T. et al. Retrospective Basic Parent-Child Communication Difficulties and Risk of Depression in Deaf Adults. J Dev Phys Disabil 29, 25–34 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10882-016-9501-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10882-016-9501-5