Abstract
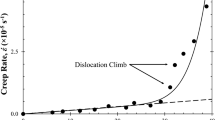
Creep properties of three Sn–Zn solder alloys (Sn–9Zn, Sn–20Zn, and Sn–25Zn, wt%) were studied using the impression creep technique. Microstructural characteristics were examined using a scanning electron microscope. The alloys exhibited stress exponents of about 5.0. The activation energy for creep was calculated to be ~50–75 kJ/mol with a mean value of 66.3 kJ/mol. The likely creep mechanism was identified to be the low temperature viscous glide of dislocations.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union (2003) Directive 2002/95/EC on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances (RoHS) in electrical and electronic equipment. J Eur Union 46(L 37):24–38
Plumbridge WJ, Gagg CR, Peters S (2001) The creep of lead-free solders at elevated temperatures. J Electron Mater 30:1178–1183
Sidhu RS, Deng X, Chawla N (2008) Microstructure characterization and creep behavior of Pb-free Sn-rich solder alloys: part II. Creep behavior of bulk solder and solder/copper joints. Metall Mater Trans 39A:349–362
Guo F, Choi S, Subramanian KN, Bieler TR, Lucas JP, Achari A, Paruchuri M (2003) Evaluation of creep behavior of near-eutectic Sn–Ag solders containing small amount of alloy additions. Mater Sci Eng A351:190–199
Dutta I (2013) A constitutive model for creep of lead free solders undergoing strain-enhanced microstructural coarsening: a first report. J Electron Mater 32:201–207
Mavoori H, Chin T, Vaynman S, Moran B, Keer L, Fine M (1997) Creep, stress relaxation, and plastic deformation in Sn–Ag and Sn–Zn eutectic solders. J Electron Mater 26:783–790
Rani SD, Murthy GS (2004) Impression creep behavior of tin based lead free solders. Mater Sci Technol 20:403–408
Kitajima M, Shono T (2005) Development of Sn–Zn–Al lead-free solder alloys. Fujitsu Sci Tech J 41:225–235
Kim YS, Kim KS, Hwang CW, Suganuma K (2003) Effect of composition and cooling rate on microstructure and tensile properties of Sn–Zn–Bi alloys. J Alloys Compd 352:237–242
Mahmudi R, Geranmayeh AR, Noori H, Shahabi M (2008) Impression creep of hypoeutectic Sn–Zn lead-free solder alloys. Mater Sci Eng A491:110–116
Sakr MS, Mohamed AZ, El-Daly AA, Abdel-Daiem AM, Bassyouni AH (1990) Microstructure dependence of steady state creep in Sn–Zn alloys. Egypt J Solids 13:34–41
Suganuma K, Kim SJ, Kim KS (2009) High temperature lead-free solders: properties and possibilities. JOM 61:64–71
Sastry DH, Murthy GS (1986) Impression creep behavior of metals at high temperatures. Trans Ind Inst Met 39:369–379
Baker H, Okamoto H (1992) ASM handbook: alloy phase diagrams, vol 3. ASM International, Materials Park
Vnuk F, Sahoo M, Baragar D, Smith RW (1980) Mechanical properties of Sn–Zn eutectic alloys. J Mater Sci 15:2573–2583. doi:10.1007/BF00550762
Yu EC, Li JCM (1977) Impression creep of LiF single crystals. Philos Mag 36:811–825
Hussien S, Jung YH, Murty KL (1985) An evaluation of mechanical anisotropy of Zircaloy using impression testing. Scripta Met 19:1045–1048
Godavarti PS, Murty KL (1987) Creep anisotropy of zinc using impression tests. J Mater Sci Lett 6(1987):456–458
Bird JE, Mukherjee AK, Dorn JE (1969) Correlations between high temperature creep behavior and structure. In: Brandon DG, Rosen A (eds) Quantitative relation between properties and microstructure. Israel University Press, Jerusalem, pp 255–342
Subrahmanyam B (1972) Elastic moduli of some eutectic alloys. Trans Jpn Inst Met 13:89–92
Mathew MD, Yang H, Movva S, Murty KL (2005) Creep deformation characteristics of tin and tin based electronic solder alloys. Metall Mater Trans A36:99–105
Charit I, Murty KL (2008) Creep behavior of Nb-modified zirconium alloys. J Nucl Mater 374:354–363
Boas W, Fensham PJ (1949) Rate of self-diffusion in tin crystals. Nature 164:1127–1128
Sherby OD, Burke PM (1967) Mechanical behavior of crystalline solids at elevated temperature. Prog Mater Sci 1:325–390
Meakin JD, Klokholm E (1960) Self-diffusion in tin single crystals. Trans AIME 218:463–466
Devries KL, Baker GS, Gibbs P (1963) Effect of pressure on creep in tin. J Appl Phys 34:2258
Wiseman CD, Sherby OD, Dorn JE (1957) Creep of single crystals and polycrystals of aluminum, lead and tin. Trans AIME 9:57–59
Bonar LG, Craig GB (1958) Activation energy for creep in tin. Can J Phys 36:1445–1449
Yang F, Li JCM (2007) Deformation behavior of tin and some tin alloys. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 18:191–210
Shrestha T, Basirat M, Charit I, Potirniche G, Rink K, Sahaym U (2012) Creep deformation mechanisms in modified 9Cr–1Mo steel. J Nucl Mater 423:110–119
Huang FH, Huntington HB (1974) Diffusion in Sb124, Cd109, Sn113 and Zn65. Phys Rev B 9:1479–1488
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shrestha, T., Gollapudi, S., Charit, I. et al. Creep deformation behavior of Sn–Zn solder alloys. J Mater Sci 49, 2127–2135 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7905-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7905-5