Abstract
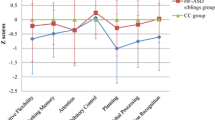
A comprehensive investigation of the neuropsychological strengths and weaknesses of children with autism may help to better describe their cognitive abilities and to design appropriate interventions. To this end we compared the NEPSY-II profiles of 22 children with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders (HFASD) with those of 44 healthy control (HC) children 2:1 matched by gender, age, race and education. Results showed that only Visuospatial Processing was relatively spared in HFASD, while deficits were observed in Attention and Executive Functions, Language, Learning and Memory, and Sensorimotor Processing. Theory of Mind difficulties were observed in verbal tasks but not in the understanding of emotional contexts, suggesting that appropriate contextual cues might help emotion understanding in HFASD children. These widespread neuropsychological impairments reflect alterations in multiple cognitive domains in HFASD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ameli, R., Courchesne, E., Lincoln, A., Kaufman, A. S., & Grillon, C. (1988). Visual memory processes in high-functioning individuals with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 18(4), 601–615.
Attwood, T. (2004). Cognitive behaviour therapy for children and adults with Asperger’s syndrome. Behaviour Change, 21(3), 147–162.
Baranek, G., Parham, L. D., & Bodfish, J. W. (2005). Sensory and motor features in autism: Assessment and intervention. In F. R. Volkmar, R. Paul, A. Klin, & D. Cohen (Eds.), Handbook of autism and pervasive developmental disorders, Volume 2: Assessment, intervention, and policy (3rd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Baron-Cohen, S. (2010). Empathizing, systemizing, and the extreme male brain theory of autism. Progress in Brain Research, 186, 167–175.
Bennetto, L., Pennington, B. F., & Rogers, S. J. (1996). Intact and impaired memory functions in autism. Child Development, 67, 1816–1835.
Bishop, D., Mayberry, M., Wong, D., Maley, A., Hill, W., & Hallmayer, J. (2004). Are phonological processing deficits part of the broad autism phenotype? American Journal of Medical Genetics, 128(1), 54–60.
Blair, R. J., Frith, U., Smith, N., Abell, F., & Cipolotti, L. (2002). Fractionation of visual memory: Agency detection and its impairment in autism. Neuropsychologia, 40(1), 108–118.
Bloemen, O. J., Deeley, Q., Sundram, F., Daly, E. M., Barker, G. J., Jones, D. K., et al. (2010). White matter integrity in Asperger syndrome: A preliminary diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging study in adults. Autism Research, 3, 203–213.
Boneh, A., Beauchamp, M., Humphrey, M., Watkins, J., Peters, H., & Yaplito-Lee, J. (2008). Newborn screening for glutaric aciduria type I in Victoria: Treatment and outcome. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 94, 287–291.
Botting, N., & Conti-Ramsden, G. (2003). Autism, primary pragmatic difficulties and specific language impairment: Can we distinguish them using psycholinguistic markers? Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 45, 515–524.
Boucher, J. (1981). Immediate free recall in early childhood autism: Another point of behavioral similarity with the amnesic syndrome. British Journal of Psychology, 72, 211–215.
Boucher, J., & Lewis, V. (1992). Unfamiliar face recognition in relatively able autistic children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 33(5), 843–859.
Boucher, J., & Warrington, E. K. (1976). Memory deficits in early infantile autism: Some similarities to the amnesic syndrome. British Journal of Psychology, 67, 73–87.
Bowler, D. M., Gaigg, S. B., & Gardiner, J. M. (2008). Subjective organisation in the free recall of adults with Asperger’s syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38, 103–114.
Bowler, D. M., Gaigg, S. B., & Gardiner, J. M. (2010). Multiple list learning in adults with autism spectrum disorder: Parallels with frontal lobe damage or further evidence of diminished relational processing? Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40, 179–187.
Bowler, D. M., Limoges, E., & Mottron, L. (2009). Different verbal learning strategies in autism spectrum disorder: Evidence from the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39, 910–915.
Burbach, J. P., & van der Zwaag, B. (2009). Contact in the genetics of autism and schizophrenia. Trends in Neurosciences, 32, 69–72.
Calderoni, S., Retico, A., Biagi, L., Tancredi, R., Muratori, F., & Tosetti, M. (2012). Female children with autism spectrum disorder: An insight from mass-univariate and pattern classification analyses. NeuroImage, 59, 1013–1022.
Carper, R. A., & Courchesne, E. (2005). Localized enlargement of the frontal cortex in early autism. Biological Psychiatry, 57, 126–133.
Carver, L. J., & Dawson, G. (2007). Development and neural bases of face recognition in autism. Molecular Psychiatry, 7(2), 18–20.
Cheung, C., Yu, K., Fung, G., Leung, M., Wong, C., Li, Q., et al. (2010). Autistic disorders and schizophrenia: related or remote? An anatomical likelihood estimation. PLoS One, 5(8), 122–133.
Courchesne, E., Karns, C., Davis, H. R., Ziccardi, R., Carper, R., Tigue, Z., et al. (2001). Unusual brain growth patterns in early life in patients with autistic disorder: An MRI study. Neurology, 57, 245–254.
Couture, S. M., Penn, D. L., Losh, M., Adolphs, R., Hurley, R., & Piven, J. (2010). Comparison of social cognitive functioning in schizophrenia and high functioning autism: More convergence than divergence. Psychological Medicine, 40(4), 569–579.
Craig, J. S., Hatton, C., Craig, F. B., & Bentall, R. P. (2004). Persecutory beliefs, attributions and Theory of Mind: Comparison of patients with paranoid delusions, Asperger’s syndrome and healthy controls. Schizophrenia Research, 69(1), 29–33.
Crespi, B., Stead, P., & Elliot, M. (2010). Evolution in health and medicine Sackler colloquium: Comparative genomics of autism and schizophrenia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(Suppl 1), 1736–1741.
Da Fonseca, D., Santos, A., Bastard-Rosset, D., Rondan, C., Poinso, F., & Deruelle, C. (2008). Can children with autistic spectrum disorders extract emotions out of contextual cues? Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 3, 50–56.
Davidson, A. J., McCann, M. E., Morton, N. S., & Myles, P. S. (2008). Anesthesia and outcome after neonatal surgery. Anesthesiology, 109, 941–944.
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., & van der Heide, L. (1991). Face recognition and lip reading in autism. European Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 3, 69–86.
Eagle, M. N., & Wakefield, J. M. (2007). Gestalt psychology and the mirror neuron discovery. Gestalt Theory, 29(1), 54–64.
Edgin, J. O., & Pennington, B. F. (2005). Spatial cognition in autism spectrum disorders: Superior, impaired, or just intact? Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 35, 729–745.
Fagerlund, B., Pagsberg, A. K., & Hemmingsen, R. P. (2006). Cognitive deficits and levels of IQ in adolescent onset schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. Schizophrenia Research, 85, 30–39.
Fein, D., Dunn, M., Allen, D. A., Aram, D. M., Hall, N., Morris, R., et al. (1996). Language and neuropsychological findings. In I. Rapin & L. Wing (Eds.), Preschool children with inadequate communication: Developmental language disorder, autism, low IQ. Clinics in Developmental Medicine, 139 (pp. 123–154). London: Mac Keith.
Frith, C. D. (1995). The cognitive neuropsychology of schizophrenia. Hove, UK: Psychology Press.
Frith, C. (2004). Is autism a disconnection disorder? Lancet Neurology, 3, 577.
Gallese, V. (2003). The manifold nature of interpersonal relations: the quest for a common mechanism. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biologica Sciences, 358, 517–528.
Gepner, B., de Gelder, B., & de Schonen, S. (1996). Face processing in autistics: Evidence for a generalized deficit? Child Neuropsychology, 2, 123–139.
Geurts, H. M., Verté, S., Oosterlaan, J., Roeyers, H., & Sergeant, J. A. (2004). How specific are executive functioning deficits in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and autism? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 45(4), 836–854.
Ghaziuddin, M., & Mountain-Kimchi, K. (2004). Defining the intellectual pro file of Asperger syndrome: Comparison with high-functioning autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 34, 279–284.
Goodenough, F. L. (1975). Measurement of intelligence by drawings. New York: New York Press.
Happé, F., Booth, R., Charlton, R., & Hughes, C. (2006). Executive function deficits in autism spectrum disorders and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Examining profiles across domains and ages. Brain and Cognition, 61(1), 25–39.
Hauck, M., Fein, D., Maltby, N., Waterhouse, L., & Feinstein, C. (1998). Memory for faces in children with autism. Child Neuropsychology, 4, 187–198.
Haviland, A., Nagin, S. D., & Rosenbaum, P. R. (2007). Combining propensity score matching and group-based trajectory analysis in an observational study. Psychological Methods, 12, 247–267.
Hazlett, H. C., Poe, M. D., Gerig, G., Smith, R. G., & Piven, J. (2006). Cortical gray and white brain tissue volume in adolescents and adults with autism. Biological Psychiatry, 59, 1–6.
Hazlett, H. C., Poe, M., Gerig, G., Smith, R. G., Provenzale, J., Ross, A., et al. (2005). Magnetic resonance imaging and head circumference study of brain size in autism: birth through age 2 years. Archives of General Psychiatry, 62, 1366–1376.
Hooper, S. R., Poon, K. K., Marcus, L., & Fine, C. (2006). Neuropsychological characteristics of school-age children with high-functioning autism: performance on the NEPSY. Child Neuropsychology, 12(4–5), 299–305.
Hughes, C., & Russell, J. (1993). Autistic children’s difficulty with mental disengagement from an object: Its implications for theories of autism. Developmental Psychology, 29(3), 498–510.
Hughes, C., Russell, J., & Robbins, T. W. (1994). Evidence for executive dysfunction in autism. Neuropsychologia, 32, 477–492.
Joseph, R. M., Keehn, B., Connolly, C., Wolfe, J. M., & Horowitz, T. S. (2009). Why is visual search superior in autism spectrum disorder? Developmental Science, 12, 1083–1096.
Joseph, R. M., McGrath, L. M., & Tager-Flusberg, H. (2005). Executive dysfunction and its relation to language ability in verbal school-age children with autism. Developmental Neuropsychology, 27(3), 361–378.
Just, M. A., Cherkassky, V. L., Keller, T. A., Kana, R. K., & Minshew, N. J. (2007). Functional and anatomical cortical under connectivity in autism: Evidence from an fMRI study of an executive function task and corpus callosum morphometry. Cerebral Cortex, 17, 951–961.
Just, M. A., Cherkassky, V. L., Keller, T. A., & Minshew, N. J. (2004). Cortical activation and synchronization during sentence comprehension in high-functioning autism: Evidence of under connectivity. Brain, 127, 1811–1821.
Kana, R. K., Libero, L. E., & Moore, M. S. (2011). Disrupted cortical connectivity theory as an explanatory model for autism spectrum disorders. Physics of Life Review, 8(4), 410–437.
King, B. H., & Lord, C. (2011). Is schizophrenia on the autism spectrum? Brain Research, 22(1380), 34–41.
Klin, A. K., Sparrow, S. S., de Bildt, A., Cicchetti, D. V., Cohen, D. J., & Volkmar, F. R. (1999). A normed study of face recognition in autism and related disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29(6), 499–508.
Klin, A., Volkmar, F. R., & Sparrow, S. S. (2000). Asperger syndrome. New York: The Guilford Press.
Korkman, M., Kirk, U., & Fellman, V. (1998). NEPSY: A developmental neuropsychological assessment. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation.
Korkman, M., Kirk, U., & Kemp, S. (2007). NEPSY-II: A developmental neuropsychological assessment. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation.
Koshino, H., Kana, R. K., Keller, T. A., Cherkassky, V. L., Minshew, N. J., & Just, M. A. (2008). fMRI investigation of working memory for faces in autism: Visual coding and underconnectivity with frontal areas. Cerebral Cortex, 18(2), 289–300.
Kravariti, E., Dixon, T., Frith, C., et al. (2005). Association of symptoms and executive function in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Schizophrenia Research, 74, 221–231.
Landa, R. (2000). Social language use in Asperger syndrome and high-functioning autism. In A. Klin, F. Volkmar, & S. Sparrow (Eds.), Asperger syndrome (pp. 125–158). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Liss, M., Fein, D., Allen, D., Dunn, M., Feinstein, C., Morris, R., et al. (2001). Executive functioning in high-functioning children with autism. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 42, 261–270.
Lopez, B. R., Lincoln, A. J., Ozonoff, S., & Lai, Z. (2005). Examining the relationship between executive functions and restricted, repetitive symptoms of Autistic Disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 35(4), 445–446.
Lord, C. (2011). Epidemiology: How common is autism? Nature, 8(474), 166–168.
Luria, A. R. (1962). Higher cortical functions in man. Moscow: Moscow University Press.
Mahone, E. M., Powell, S. K., Loftis, C. W., Goldberg, M. C., Denckla, M. D., & Mostofsky, S. H. (2006). Motor persistence and inhibition in autism and ADHD. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 12, 622–631.
Marini, A., Lorusso, M. L., D’Angelo, G., Civati, F., Turconi, A. C., Fabbro, F., et al. (2007). Evaluation of narrative abilities in patients suffering from Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Brain and Language, 102(1), 1–12.
Mason, R. A., Williams, D. L., Kana, R. K., Minshew, N., & Just, M. A. (2008). Theory-of-Mind disruption and recruitment of the right hemisphere during narrative comprehension in autism. Neuropsychologia, 46, 269–280.
Miniscalco, C., Hagberg, B., Kadesjö, B., Westerlund, M., & Gillberg, C. (2007). Narrative skills, cognitive profiles and neuropsychiatric disorders in 7–8-year-old children with late developing language. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 42(6), 665–681.
Minshew, N. J., & Goldstein, G. (2001). The pattern of intact and impaired memory functions in autism. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 42, 1095–1101.
Minshew, N. J., Goldstein, G., Muenz, L. R., & Payton, J. B. (1992). Neuropsychological functioning in nonmentally retarded autistic individuals. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 14, 749–761.
Minshew, N. J., Goldstein, G., & Siegel, D. (1995). Speech and language in high-functioning autistic individuals. Neuropsychology, 9, 255–261.
Minshew, N. J., Goldstein, G., & Siegel, D. J. (1997). Neuropsychologic functioning in autism: Profile of a complex information processing disorder. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 3, 303–316.
Müller, R. A. (2007). The study of autism as a distributed disorder. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Review, 13(1), 85–95.
Mundy, P., & Sigman, M. (2006). Joint attention, social competence and developmental psychopathology. In D. Cicchetti & D. Cohen (Eds.), Developmental psychopathology, second edition, volume one: Theory and methods. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Oliveras-Rentas, R. E., Kenworhty, L., Roberson, R. B., Martin, A., & Wallace, G. L. (2012). WISC-IV profile in high functioning autism spectrum disorders: Impaired speed is associated with increased autism communication symptoms and decreased adaptive communication abilities. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(5), 655–664.
Ozonoff, S. (1995). Reliability and validity of the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test in studies of autism. Neuropsychology, 9, 491–500.
Ozonoff, S. (1997). Components of executive function in autism and other disorders. In J. Russell (Ed.), Autism as an executive disorder (pp. 179–211). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Ozonoff, S., Cook, I., Coon, H., Dawson, G., Joseph, R. M., Klin, A., et al. (2004). Performance on Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery subtests sensitive to frontal lobe function in people with autistic disorder: Evidence from the Collaborative Programs of Excellence in Autism network. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 34(2), 139–150.
Ozonoff, S., & Jensen, J. (1999). Brief report: Specific executive function profiles in three neurodevelopmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29, 171–177.
Ozonoff, S., & McEvoy, R. E. (1994). A longitudinal study of executive function and Theory of Mind development in autism. Developmental Psychopathology, 6, 415–431.
Ozonoff, S., Pennington, B. F., & Rogers, S. J. (1991). Executive function deficits in high-functioning autistic individuals: Relationship to Theory of Mind. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 32, 1081–1105.
Ozonoff, S., & Strayer, D. L. (1997). Inhibitory function in nonretarded children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 27, 59–77.
Pennington, B. F., & Ozonoff, S. (1996). Executive functions and developmental psychopathology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 37, 51–87.
Pinkham, A. E., Hopfinger, J. B., Pelphrey, K. A., Piven, J., & Penn, D. L. (2008). Neural bases for impaired social cognition in schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorders. Schizophrenia Research, 99, 164–175.
Planche, P., & Lemonnier, E. (2011). Does the islet of ability on visuospatial tasks in children with high-functioning autism really indicate a deficit in global processing? Encephale, 37(1), 10–17.
Raven, J. C. (1954). Standard progressive matrices. Firenze: Giunti OS.
Rhinewine, J. P., Lencz, T., Thaden, E. P., et al. (2005). Neurocognitive profile in adolescents with early-onset schizophrenia: Clinical correlates. Biological Psychiatry, 58, 705–712.
Riches, N. G., Loucas, T., Baird, G., Charman, T., & Simonoff, E. (2011). Non-word repetition in adolescents with specific language impairment and autism plus language impairments: A qualitative analysis. Journal of Communication Disorders, 44(1), 23–36.
Robinson, S., Goddard, L., Dritschel, B., Wisley, M., & Howlin, P. (2009). Executive functions in children with autism spectrum disorders. Brain and Cognition, 71(3), 362–368.
Rumsey, J. M., & Hamburger, S. D. (1990). Neuropsychological divergence of high-level autism and severe dyslexia. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 20(2), 155–168.
Russel, J. (1997). How executive disorders can bring aboutan adeguate “Theory of Mind”. In J. Russel (Ed.), Autism as an executive disorder (pp. 256–304). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Russell, J., Jarrold, C., & Hood, B. (1999). Two intact executive capacities in children with autism: Implications for the core executive dysfunctions in the disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29, 103–112.
Samson, F., Mottron, L., Soulières, I., & Zeffiro, T. A. (2012). Enhanced visual functioning in autism: An ALE meta-analysis. Human Brain Mapping, 33, 1553–1581.
Scheeren A.M., Koot H.M., & Begeer S. (2012). Social interaction style of children and adolescent with high functioning spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, Feb 1. (Epub ahead of print).
Schmidt, G. L., Kopelioff, L., Winterrowd, E., Pennington, B. F., Hepburn, S. L., & Rojas, D. C. (2008). Impairments in phonological processing and non-verbal intellectual function in parents of children with autism. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 30, 557–567.
Sergeant, J. A., Geurts, H., & Oosterlaan, P. (2002). How specific is a deficit of executive functioning for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder? Behavioural Brain Research, 130, 3–28.
Shukla, D. K., Keehn, B., Lincoln, A. J., & Müller, R. A. (2010). White matter compromise of callosal and subcortical fiber tracts in children with autism spectrum disorder: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 49(12), 1269–1278.
Tager-Flusberg, H. (2004). Strategies for conducting research on language in autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 34, 75–80.
Tsatsanis, K. D. (2005). Neuropsychological characteristics in autism and related conditions. In F. Volkmar, R. Paul, A. KIin, & D. Cohen (Eds.), Handbook of autism and pervasive developmental disorders: Diagnosis, development, neurobiology, and behavior (3rd ed.). Wiley: New York.
Urgesi, C., Campanella, F., & Fabbro, F. (2011). NEPSY-II, Contributo alla Taratura Italiana. Firenze: Giunti OS.
Verté, S., Geurts, H. M., Roeyers, H., Oosterlaan, J., & Sergeant, J. A. (2005). Executive functioning in children with autism and Tourette syndrome. Development and Psychopatholy, 17(2), 415–445.
Volker, M. A., Lopata, C., Smerbeck, A. M., Knoll, V. A., Thomeer, M. L., Toomey, J. A., et al. (2010). BASC-2 PRS Profile for students with high functioning autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40, 188–199.
Whitehouse, A. J. O., Barry, J. G., & Bishop, D. V. M. (2008). Further defining the language impairment of autism: Is there a specific language impairment subtype? Journal of Communication Disorders, 41, 319–346.
Williams, D. L., Goldstein, G., & Minshew, N. J. (2005). Impaired memory for faces and social scenes in autism: Clinical implications of the memory disorder. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 20, 1–15.
Williams, D. L., Goldstein, G., & Minshew, N. J. (2006). The profile of memory function in children with autism. Neuropsychology, 20(1), 21–29.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Italian Ministry of Health under Strategic Program ‘Inquiry into Disruption of Intersubjective Equipment in Autism Spectrum Disorder in Childhood (IDIA)’ (Principal Investigator F.M.) and partially by grant from the IRCCS “E. Medea” (Ricerca Corrente, Ministry of Health to C.U.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narzisi, A., Muratori, F., Calderoni, S. et al. Neuropsychological Profile in High Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorders. J Autism Dev Disord 43, 1895–1909 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-012-1736-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-012-1736-0