Abstract
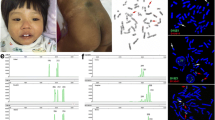
Cytogenetic abnormalities in the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome (PWS/AS) critical region have been described in individuals with autism. Maternal duplications and linkage disequilibrium in families with autism suggest the existence of a susceptibility locus at 15q11–q13. Here, we describe a 6-year-old girl diagnosed with autism, developmental delay, and delayed expressive and receptive language. The karyotype was designated de novo 47, XX, idic(15)(q13). Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and molecular analysis with 15q11–q13 markers revealed an additional copy of the region being of maternal origin. Duplication of the 15q11–q13 segment represents the most consistent known chromosomal abnormality reported in association with autism. This present case report reinforces the hypothesis that additional copies of this chromosome segment are causally related to autism.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolton, P. F., Dennis, N. R., Browne, C. E., Thomas, N. S., Veltman, M. W., Thompson, R. J., & Jacobs, P. (2001). The phenotypic manifestations of interstitial duplications of proximal 15q with special reference to the autistic spectrum disorders. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 105, 675–685.
Borgatti, R., Piccinelli, P., Passoni, D., Dalpra, L., Miozzo, M., Micheli, R., Gagliardi, C., & Balottin, U. (2001). Relationship between clinical and genetic features in “inverted duplicated chromosome 15” patients. Pediatric Neurology, 24, 111–116.
Buxbaum, J. D., Silverman, J. M., Smith, C. J., Greenberg, D. A., Kilifarski, M., Reichert, J., Cook, E. H. Jr., Fang, Y., Song, C. Y., & Vitale, R. (2002). Association between a GABRB3 polymorphism and autism. Molecular Psychiatry, 7, 311–316.
Caine, A., Mason, G., Daly, H. A., & Ricketts, S. M. (1993). An unusual tricentric X chromosome detected prenatally. Prenatal Diagnosis, 13, 1061–1065.
Cheng, S. D., Spinner, N. B., Zackai, E. H., & Knoll, J. H. (1994). Cytogenetic and molecular characterization of inverted duplicated chromosomes 15 from 11 patients. American Journal of Human Genetics, 55, 753–759.
Cook, E. H. Jr., Courchesne, R. Y., Cox, N. J., Lord, C., Gonen, D., Guter, S. J., Lincoln, A., Nix, K., Haas, R., Leventhal, B. L., & Courchesne, E. (1998). Linkage-disequilibrium mapping of autistic disorder, with 15q11–13 markers. American Journal of Human Genetics, 62, 1077–1083.
Cook, E. H. Jr., Lindgren, V., Leventhal, B. L., Courchesne, R., Lincoln, A., Shulman, C., Lord, C., & Courchesne, E. (1997). Autism or atypical autism in maternally but not paternally derived proximal 15q duplication. American Journal of Human Genetics, 60, 928–934.
Crolla, J. A., Harvey, J. F., Sitch, F. L., & Dennis, N. R. (1995). Supernumerary marker 15 chromosomes: a clinical, molecular and FISH approach to diagnosis and prognosis. Human Genetics, 95, 161–70.
Eggermann, K., Mau, U. A., Bujdoso, G., Koltai, E., Engels, H., Schubert, R., Eggermann, T., Raff, R., & Schwanitz, G. (2002). Supernumerary marker chromosomes derived from chromosome 15: analysis of 32 new cases. Clinical Genetics, 62, 89–93.
Fenton, G., D’Ardia, C., Valente, D., Del Vecchio, I., Fabrizi, A., & Bernabei, P. (2003). Vineland adaptive behavior profiles in children with autism and moderate to severe developmental delay. Autism, 7, 269–287.
Flejter, W. L., Bennett-Baker, P. E., Ghaziuddin, M., McDonald, M., Sheldon, S., & Gorski, J. L. (1996). Cytogenetic and molecular analysis of inv dup(15) chromosomes observed in two patients with autistic disorder and mental retardation. Am J Med Genet, 61, 182–187.
Folstein, S. E., & Rosen-Sheidley, B. (2001). Genetics of autism: Complex aetiology for a heterogeneous disorder. Nature Review Genetics, 2, 943–955.
Gillberg, C. (1998). Chromosomal disorders and autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 28, 415–425.
Gillberg, C., Steffenburg, S., Wahlstrom, J., Gillberg, I. C., Sjostedt, A., Martinsson, T., Liedgren, S., & Eeg-Olofsson, O. (1991). Autism associated with marker chromosome. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 30, 489–494.
Huang, B., & Bartley, J. (2003). Partial hexasomy of chromosome 15. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 121, 277–280.
Huang, B., Crolla, J. A., Christian, S. L., Wolf-Ledbetter, M. E., Macha, M. E., Papenhausen, P. N., & Ledbetter, D. H. (1997). Refined molecular characterization of the breakpoints in small inv dup(15) chromosomes. Human Genetics, 99, 11–17.
Lamb, J. A., Moore, J., Bailey, A., & Monaco, A. P. (2000). Autism: Recent molecular genetic advances. Human Molecular Genetics, 9, 861–868.
Leana-Cox, J., Jenkins, L., Palmer, C. G., Plattner, R., Sheppard, L., Flejter, W. L., Zackowski, J., Tsien, F., & Schwartz, S. (1994). Molecular cytogenetic analysis of inv dup(15) chromosomes, using probes specific for the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome region: clinical implications. American Journal of Human Genetics, 54, 748–756.
Lichter, P., Cremer, T., Borden, J., Manuelidis, L., & Ward, D. C. (1988). Delineation of individual human chromosomes in metaphase and interphase cells by in situ suppression hybridization using recombinant DNA libraries. Human Genetics, 80, 224–234.
Lord, C., Pickles, A., McLennan, J., Rutter, M., Bregman, J., Folstein, S., Fombonne, E., Leboyer, M., & Minshew, N. (1997). Diagnosing autism: Analyses of data from the Autism Diagnostic Interview. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 27, 501–517.
Lord, C., Risi, S., Lambrecht, L., Cook, E. H. Jr., Leventhal, B. L., DiLavore, P. C., Pickles, A., & Rutter, M. (2000). The autism diagnostic observation schedule-generic: A standard measure of social and communication deficits associated with the spectrum of autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30, 205–223.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., & Le Couteur, A. (1994). Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised: A revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 24, 659–685.
Maggouta, F., Roberts, S. E., Dennis, N. R., Veltman, M. W., & Crolla, J. A. (2003). A supernumerary marker chromosome 15 tetrasomic for the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome critical region in a patient with a severe phenotype. Journal of Medical Genetics, 40, e84.
Mann, S. M., Wang, N. J., Liu, D. H., Wang, L., Schultz, R. A., Dorrani, N., Sigman, M., & Schanen, N. C. (2004). Supernumerary tricentric derivative chromosome 15 in two boys with intractable epilepsy: Another mechanism for partial hexasomy. Human Genetics, 115, 104–111.
Menold, M. M., Shao, Y., Wolpert, C. M., Donnelly, S. L., Raiford, K. L., Martin, E. R., Ravan, S. A., Abramson, R. K., Wright, H. H., Delong, G. R., Cuccaro, M. L., Pericak-Vance, M. A., & Gilbert, J. R. (2001). Association analysis of chromosome 15 gabaa receptor subunit genes in autistic disorder. Journa of Neurogenetics, 15, 245–259.
Mignon, C., Malzac, P., Moncla, A., Depetris, D., Roeckel, N., Croquette, M. F., & Mattei, M. G. (1996). Clinical heterogeneity in 16 patients with inv dup 15 chromosome: Cytogenetic and molecular studies, search for an imprinting effect. European Journal of Human Genetics, 4, 88–100.
Muhle, R., Trentacoste, S. V., & Rapin, I. (2004). The genetics of autism. Pediatrics, 113, e472–e486.
Nazarenko, S., Sazhenova, E., Baumer, A., & Schinzel, A. (2004). Segmental maternal heterodisomy of the proximal part of chromosome 15 in an infant with Prader-Willi syndrome. European Journal Human Genetics, 12, 411–414.
Nicholls, R. D., Saitoh, S., & Horsthemke, B. (1998). Imprinting in Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. Trends in Genetics, 14, 194–200.
Nurmi, E. L., Bradford, Y., Chen, Y., Hall, J., Arnone, B., Gardiner, M. B., Hutcheson, H. B., Gilbert, J. R., Pericak-Vance, M. A., Copeland-Yates, S. A., Michaelis, R. C., Wassink, T. H., Santangelo, S. L., Sheffield, V. C., Piven, J., Folstein, S. E., Haines, J. L., & Sutcliffe, J. S. (2001). Linkage disequilibrium at the Angelman syndrome gene UBE3A in autism families. Genomics, 77, 105–113.
Olsen, R. W., & Tobin, A. J. (1990). Molecular biology of GABAA receptors. Faseb Journal, 4, 1469–1480.
Pinkel, D., Landegent, J., Collins, C., Fuscoe, J., Segraves, R., Lucas, J., & Gray, J. (1988). Fluorescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome-specific libraries: Detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 85, 9138–9142.
Qumsiyeh, M. B., Rafi, S. K., Sarri, C., Grigoriadou, M., Gyftodimou, J., Pandelia, E., Laskari, H., & Petersen, M. B. (2003). Double supernumerary isodicentric chromosomes derived from 15 resulting in partial hexasomy. Americal Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 116, 356–359.
Rineer, S., Finucane, B., & Simon, E. W. (1998). Autistic symptoms among children and young adults with isodicentric chromosome 15. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 81, 428–433.
Roberts, S., Maggouta, F., Thompson, R., Price, S., & Thomas, S. (2002a). A patient with a supernumerary marker chromosome (15), Angelman syndrome, and uniparental disomy resulting from paternal meiosis II non-disjunction. Journal of Medical Genetics, 39, E9.
Roberts, S. E., Dennis, N. R., Browne, C. E., Willatt, L., Woods, G., Cross, I., Jacobs, P. A., & Thomas, S. (2002b). Characterisation of interstitial duplications and triplications of chromosome 15q11-q13. Human Genetics, 110, 227–234.
Roberts, S. E., Maggouta, F., Thomas, N. S., Jacobs, P. A., & Crolla, J. A. (2003). Molecular and fluorescence in situ hybridization characterization of the breakpoints in 46 large supernumerary marker 15 chromosomes reveals an unexpected level of complexity. American Journal of Human Genetics, 73, 1061–1072.
Robinson, W. P., Binkert, F., Gine, R., Vazquez, C., Muller, W., Rosenkranz, W., & Schinzel, A. (1993a). Clinical and molecular analysis of five inv dup(15) patients. European Journal of Human Genetics, 1, 37–50.
Robinson, W. P., Wagstaff, J., Bernasconi, F., Baccichetti, C., Artifoni, L., Franzoni, E., Suslak, L., Shih, L. Y., Aviv, H., & Schinzel, A. A. (1993b). Uniparental disomy explains the occurrence of the Angelman or Prader-Willi syndrome in patients with an additional small inv dup(15) chromosome. Journal of Medical Genetics, 30, 756–760.
Schinzel, A. A., Brecevic, L., Bernasconi, F., Binkert, F., Berthet, F., Wuilloud, A., & Robinson, W. P. (1994). Intrachromosomal triplication of 15q11–q13. Journal of Medical Genetics, 31, 798–803.
Schroer, R. J., Phelan, M. C., Michaelis, R. C., Crawford, E. C., Skinner, S. A., Cuccaro, M., Simensen, R. J., Bishop, J., Skinner, C., Fender, D., & Stevenson, R. E. (1998). Autism and maternally derived aberrations of chromosome 15q. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 76, 327–336.
Shao, Y., Cuccaro, M. L., Hauser, E. R., Raiford, K. L., Menold, M. M., Wolpert, C. M., Ravan, S. A., Elston, L., Decena, K., Donnelly, S. L., Abramson, R. K., Wright, H. H., DeLong, G. R., Gilbert, J. R., & Pericak-Vance, M. A. (2003). Fine mapping of autistic disorder to chromosome 15q11–q13 by use of phenotypic subtypes. American Journal of Human Genetics, 72, 539–548.
Simic, M., & Turk, J. (2004). Autistic spectrum disorder associated with partial duplication of chromosome 15; three case reports. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 13, 389–393.
Thomas, N. S., Roberts, S. E., & Browne, C. E. (2003). Estimate of the prevalence of chromosome 15q11–q13 duplications. Americal Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 120, 596–598.
Vogels, A., Matthijs, G., Legius, E., Devriendt, K., & Fryns, J. P. (2003). Chromosome 15 maternal uniparental disomy and psychosis in Prader-Willi syndrome. Journal of Medical Genetics, 40, 72–73.
Wandstrat, A. E., & Schwartz, S. (2000). Isolation and molecular analysis of inv dup(15) and construction of a physical map of a common breakpoint in order to elucidate their mechanism of formation. Chromosoma, 109, 498–505.
Wang, N. J., Liu, D., Parokonny, A. S., & Schanen, N. C. (2004). High-resolution molecular characterization of 15q11–q13 rearrangements by array comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH) with detection of gene dosage. American Journal of Human Genetics, 75, 267–281.
Webb, T. (1994). Inv dup(15) supernumerary marker chromosomes. Journal of Medical Genetics, 31, 585–594.
Weidmer-Mikhail, E., Sheldon, S., & Ghaziuddin, M. (1998). Chromosomes in autism and related pervasive developmental disorders: a cytogenetic study. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 42(Pt 1), 8–12.
Werner, M., Ben-Neriah, Z., Silverstein, S., Lerer, I., Dagan, Y., & Abeliovich, D. (2004). A patient with Prader-Willi syndrome and a supernumerary marker chromosome r(15)(q11.1–13p11.1)pat and maternal heterodisomy. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 129, 176–179.
Wolpert, C., Pericak-Vance, M. A., Abramson, R. K., Wright, H. H., & Cuccaro, M. L. (2000a). Autistic symptoms among children and young adults with isodicentric chromosome 15. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 96, 128–129.
Wolpert, C. M., Menold, M. M., Bass, M. P., Qumsiyeh, M. B., Donnelly, S. L., Ravan, S. A., Vance, J. M., Gilbert, J. R., Abramson, R. K., Wright, H. H., Cuccaro, M. L., & Pericak-Vance, M. A. (2000b). Three probands with autistic disorder and isodicentric chromosome 15. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 96, 365–372.
Xu, J., Zwaigenbaum, L., Szatmari, P., & Scherer, S. W. (2004). Molecular cytogenetics of autism. Current Genomics, 5, 347–364.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Genome Canada and the Hospital for Sick Children Foundation. We would like to thank Martin Li, Simone Russell, Mary Ann George, and Lili Senman for their help. SWS in an Investigator of the Canadian Institute of Health Research and an International Scholar of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwasnicka-Crawford, D.A., Roberts, W. & Scherer, S.W. Characterization of an Autism-Associated Segmental Maternal Heterodisomy of the Chromosome 15q11–13 Region. J Autism Dev Disord 37, 694–702 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-006-0225-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-006-0225-8