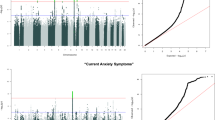
State and trait anxiety define different aspects of anxiety, and may represent environmentally and genetically mediated components of this phenotype. Furthermore their relationship, where trait anxiety is expressed through levels of state anxiety under threatening circumstances, may represent a process of interplay between a genetic vulnerability factor and an environmental stressor. To test these hypotheses, we explored genetic and environmental influences on measures of state and trait anxiety in a sample of 1058 twins (521 males and 537 females) aged 8–16. The results were consistent with these hypotheses. State anxiety is largely influenced by environmental factors in males and females whereas trait anxiety shows moderate genetic effects and substantial non-shared environment effects. Their association was accounted for by non-shared environmental effects, with modest genetic and shared environmental inputs. The implications of these results for vulnerability mechanisms involving stress reactivity on anxiety are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Brown, G. W., & Harris, T. O. (1989). Life events and illness. London: Unwin Hyman.
Carlson, E., & Sroufe, L. A. (1995). The contribution of attachment theory to developmental psychopathology. In D. Cicchetti & D. Cohen (Eds.), Developmental processes and psychopathology: Volume 1. Theoretical perspectives and methodological approaches (pp. 581–617). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Caspi, A., Sugden, K., Moffitt, T. E., Taylor, A., Craig, I. W., Harrington, H., McClay, J., Mill, J., Martin, J., Braithwaite, A., & Poulton, R. (2003). Influence of life stress on depression: Moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science, 301, 386–389.
Caspi, A., Taylor, A., Moffitt, T. E., & Plomin, R. (2000). Neighbourhood deprivation affects children's mental health: Environmental risks identified in a genetic design. Psychological Science, 11, 338–342.
Cattell, R. B., & Scheier, I. H. (1963). Handbook for the IPAT Anxiety Scale (2nd ed.). Champaign, IL: Institute for Personality and Ability Testing.
Cohen, D. J., Dibble, E., Grawe, J. M., & Pollin, W. (1973). Separating identical from fraternal twins. Archives of General Psychiatry, 29, 465–469.
Edelbrock, C., Costello, A. J., Dulcan, M. K., Conover, N. C., & Kala, R. (1986). Parent-child agreement on child psychiatric symptoms assessed via structured interview. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 27, 181–190.
Eley, T. C., & Gregory, A. M. (2004). Behavioral Genetics. In T. L. Morris & J. S. March (Eds.), Anxiety Disorders in Children and Adolescents (2nd ed., pp. 71–97). New York: Guildford Press.
Eley, T. C., & Stevenson, J. (1999). Exploring the covariation between anxiety and depression symptoms: A genetic analysis of the effects of age and sex. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 40, 1273–1284.
Eley, T. C., Sugden, K., Gregory, A. M., Sterne, A., Plomin, R., & Craig, I. W. (2004). Gene-environment interaction analysis of serotonin system markers with adolescent depression. Molecular Psychiatry, 9, 908–915.
Endler, N. S., & Kocovski, N. L. (2001). State and trait anxiety revisited. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 15, 231–245.
Finlay-Jones, R., & Brown, G. W. (1981). Types of stressful life events and the onset of anxiety and depressive disorders. Psychological Medicine, 11, 803–815.
Freud, S. (1924). Collected papers , Vol. 1. London: Hogarth Press.
Goodyer, I. M. (1990). Family relationships, life events and childhood psychopathology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 31, 161–192.
Goodyer, I. M., Wright, C., & Altham, P. M. E. (1990). The friendships and recent life events of anxious and depressed school-age children. British Journal of Psychiatry, 156, 689–698.
Gray, J. A. (1988). The neuropsychological basis of anxiety. In C. G. Last & M. Hersen (Eds.), Handbook of anxiety disorders (pp. 10–37). New York: Pergamon Press.
Hariri, A. R., Mattay, V. S., Tessitore, A., Kolachana, B., Fera, F., Goldman, D., Egan, M. F., & Weinberger, D. R. (2002). Serotonin transporter genetic variation and the response of the human amygdala. Science, 297, 400–403.
Jardine, R., Martin, N. G., & Henderson, A. S. (1984). Genetic covariation between neuroticism and the symptoms of anxiety and depression. Genetic Epidemiology, 1, 89–107.
Legrand, L. N., McGue, M., & Iacono, W. G. (1999). A twin study of state and trait anxiety in childhood and adolescence. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 40, 953–958.
Lesch, K. P., Bengel, D., Heils, A., Zhang Sabol, S., Greenburg, B. D., Petri, S., Benjamin, J., Muller, C. R., Hamer, D. H., & Murphy, D. L. (1996). Association of anxiety-related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region. Science, 274, 1527–1531.
Lewinsohn, P. M., Gotlib, I. H., Lewinsohn, M., Seeley, J. R., & Allen, N. B. (1998). Gender differences in anxiety disorders and anxiety symptoms in adolescents. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 107, 109–117.
McGue, M., & Bouchard, T. J., Jr. (1984). Adjustment of twin data for the effects of age and sex. Behavior Genetics, 14, 325–343.
Merrell, K. W., McClun, L. A., Kempf, K. K. G., & Lund, J. (2002). Using self-report assessment to identify children with internalizing problems: Validity of the internalizing symptoms scale for children. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 20, 223–239.
Mesman, J., & Koot, H. M. (2001). Early preschool predictors of preadolescent internalizing and externalizing DSM-IV diagnoses. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 40, 1029–1036.
Miech, R. A., Caspi, A., Moffit, T. E., Wright, B. R. E., & Silva, P. A. (1999). Low Socioeconomic status and mental disorders: A longitudinal study of selection and causation during young adulthood. American Journal of Sociology, 104, 1096–1131.
Muris, P., Rapee, R., Meesters, C., Schouten, E., & Geers, M. (2003). Threat perception abnormalities in children: The role of anxiety disorder symptoms, chronic anxiety, and state anxiety. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 17, 271–287.
Neale, M. C. (1997). Mx: Statistical Modeling. (4th ed.) Box 126 MCV, Richmond, VA 23298: Department of Psychiatry.
Neale, M. C., & Cardon, L. R. (1992). Methodology for genetic studies of twins and families. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publications.
Office for National Statistics (2002). Living in Britain: Results from the 2000/01 General Household Survey. London: Stationery Office.
Purcell, S. (2002). Variance components models for gene-environment interaction in twin analysis. Twin Research, 5, 554–571.
Purdue, O., & Spielberger, C. D. (1966). Anxiety and the perception of punishment. Mental Hygiene, 50, 390.
Reynolds, C. R. (1980). Concurrent validity of I think and feel: The revised children's and manifest scale. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 48, 774–775.
Scourfield, J., Rice, F., Thapar, A., Harold, G. T., Martin, N., & McGuffin, P. (2003). Depressive symptoms in children and adolescents: Changing aetiological influences with development. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 44, 968–976.
Silberg, J., Rutter, M., Neale, M., & Eaves, L. (2001). Genetic moderation of environmental risk for depression and anxiety in adolescent girls. British Journal of Psychiatry, 179, 116–121.
Smoller, J. W., & Tsuang, M. T. (1998). Panic and phobic anxiety: Defining phenotypes for genetic studies. American Journal of Psychiatry, 155, 1152–1162.
Spielberger, C. (1973). Preliminary test manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory for Children. Palo Alto: Consulting Psychologists Press, Inc.
Spielberger, C. D. (1966). Anxiety and Behaviour. New York: Academic Press.
Thapar, A., & McGuffin, P. (1994). A twin study of depressive symptoms in childhood. British Journal of Psychiatry, 165, 259–265.
Topolski, T. D., Hewitt, J. K., Eaves, L., Meyer, J. M., Silberg, J. L., Simonoff, E., & Rutter, M. (1999). Genetic and environmental influences on ratings of manifest anxiety by parents and children. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 13, 371–397.
Warren, S. L., Schmitz, S., & Emde, R. N. (1999). Behavioral genetic analyses of self-reported anxiety at 7 years of age. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 38, 1403–1408.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lau, J.Y.F., Eley, T.C. & Stevenson, J. Examining the State-Trait Anxiety Relationship: A Behavioural Genetic Approach. J Abnorm Child Psychol 34, 18–26 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-005-9006-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-005-9006-7