Abstract
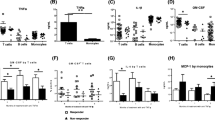
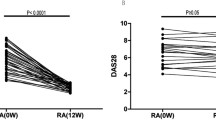
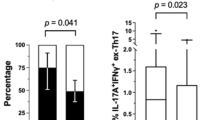
The aims of this study are to compare plasma levels of IL17A, A/F, and F biomarkers in RA patients versus controls, and to determine responsiveness to methotrexate (MTX), anti-TNFs, and abatacept. We selected plasma samples from RA cohorts consisting of a cross-sectional RA cohort (N = 78) not receiving DMARDs at the time of sampling, as well as from longitudinal drug start cohorts (N = 71 patients) with pre/post samples including anti-TNF, abatacept, and MTX-treated patients. We assayed IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL17-A/F using a highly sensitive immunoassay system. Plasma levels of IL-17A, IL-17A/F, and IL-17F were all significantly increased in RA versus controls. The difference was largest in IL-17F, with median IL-17F levels in RA patients being approximately 18-fold higher than controls (81 pg/mL in RA vs. 4.4 pg/mL in controls, p < 0.001). Among the forms of IL-17, only IL-17F was decreased after therapy in the MTX cohort (p = 0.006), abatacept cohort (p < 0.001), and anti-TNF cohorts (p = 0.02), whereas IL-17A and IL-17A/F were not significantly decreased for any of the three drug cohorts. Synovial fluid analysis demonstrated higher IL-17F levels in RA (p = 0.016) than healthy controls. These results suggest a specific role for IL-17F in human RA pathogenesis and as a therapeutic target.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- hsCRP:
-
High sensitivity C-reactive protein
- DMARD:
-
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- ESR:
-
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- IL-1 IL-1B:
-
Interleukin-1
- IL-1B:
-
Interleukin-1 beta
- IL-17:
-
Interleukin-17
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IL-6R alpha:
-
Interleukin 6 receptor alpha
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- MTX:
-
Methotrexate
- OA:
-
Osteoarthritis
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- RANKL:
-
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand
- sTNFRII:
-
Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 2
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
References
Miossec, P., T. Korn, and V.K. Kuchroo. 2009. Interleukin-17 and type 17 helper T cells. The New England Journal of Medicine 361: 888–98.
Pappu, R., V. Ramirez-Carrozzi, and A. Sambandam. 2011. The interleukin-17 cytokine family: critical players in host defence and inflammatory diseases. Immunology 134: 8–16.
Gaffen, S.L. 2009. The role of interleukin-17 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Current Rheumatology Reports 11: 365–70.
Hot, A., S. Zrioual, M.L. Toh, et al. 2011. IL-17A- versus IL-17F-induced intracellular signal transduction pathways and modulation by IL-17RA and IL-17RC RNA interference in rheumatoid synoviocytes. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 70: 341–8.
Zrioual, S., R. Ecochard, A. Tournadre, et al. 2009. Genome-wide comparison between IL-17A- and IL-17 F-induced effects in human rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. Journal of Immunology 182: 3112–20.
Metawi, S.A., D. Abbas, M.M. Kamal, et al. 2011. Serum and synovial fluid levels of interleukin-17 in correlation with disease activity in patients with RA. Clinical Rheumatology 30: 1201–7.
Chen, D.Y., Y.M. Chen, H.H. Chen, et al. 2011. Increasing levels of circulating Th17 cells and interleukin-17 in rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to anti-TNF-alpha therapy. Arthritis Research & Therapy 13: R126.
Yue, C., X. You, L. Zhao, et al. 2010. The effects of adalimumab and methotrexate treatment on peripheral Th17 cells and IL-17/IL-6 secretion in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatology International 30: 1553–7.
Zhang, L., J.M. Li, X.G. Liu, et al. 2011. Elevated Th22 cells correlated with Th17 cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Clinical Immunology 31: 606–14.
Todd, J., B. Freese, A. Lu, et al. 2007. Ultrasensitive flow-based immunoassays using single-molecule counting. Clinical Chemistry 53: 1990–5.
Wang, T.J., K.C. Wollert, M.G. Larson, et al. 2012. Prognostic utility of novel biomarkers of cardiovascular stress: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 126: 1596–604.
Tarawneh, R., J.M. Lee, J.H. Ladenson, et al. 2012. CSF VILIP-1 predicts rates of cognitive decline in early Alzheimer disease. Neurology 78: 709–19.
St Ledger, K., S.J. Agee, M.T. Kasaian, et al. 2009. Analytical validation of a highly sensitive microparticle-based immunoassay for the quantitation of IL-13 in human serum using the Erenna immunoassay system. Journal of Immunological Methods 350: 161–70.
van Gestel, A.M., M.L. Prevoo, M.A. van’t Hof, et al. 1996. Development and validation of the European League Against Rheumatism response criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Comparison with the preliminary American College of Rheumatology and the World Health Organization/International League Against Rheumatism Criteria. Arthritis and Rheumatism 39: 34–40.
Buch, M.H., and P. Emery. 2011. New therapies in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 23: 245–51.
Attur, M.G., R.N. Patel, S.B. Abramson, et al. 1997. Interleukin-17 up-regulation of nitric oxide production in human osteoarthritis cartilage. Arthritis and Rheumatism 40: 1050–3.
LeGrand, A., B. Fermor, C. Fink, et al. 2001. Interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interleukin-17 synergistically up-regulate nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 production in explants of human osteoarthritic knee menisci. Arthritis and Rheumatism 44: 2078–83.
Cua, D.J., and C.M. Tato. 2010. Innate IL-17-producing cells: the sentinels of the immune system. Nature Reviews. Immunology 10: 479–89.
Suurmond, J., A.L. Dorjee, M.R. Boon, et al. 2011. Mast cells are the main interleukin 17-positive cells in anticitrullinated protein antibody-positive and -negative rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis synovium. Arthritis Research & Therapy 13: R150.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by US National Institutes of Health grant R01-AR054817 (S.B.A.). Dr Greenberg received salary support from the NIH (K23AR054412).
Contributions
MJ carried out data analysis, interpretation, and supervised manuscript drafting/revision.
MA supervised data acquisition, interpretation, and manuscript revision.
VF carried out data acquisition.
JT supervised data acquisition, interpretation, and manuscript drafting/revision.
ML carried out data analysis and manuscript drafting/revision.
QL carried out data analysis.
RR generated biomarker results and carried out data analysis.
SA supervised data analysis, interpretation, and manuscript revision.
JG supervised data acquisition, analysis, interpretation, and manuscript revision.
Conflict of Interest
JT, RR, and QL are employees of Singulex, the manufacturer of the assays used in the study. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, M., Attur, M., Furer, V. et al. Increased Plasma IL-17F Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Are Responsive to Methotrexate, Anti-TNF, and T Cell Costimulatory Modulation. Inflammation 38, 180–186 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-0020-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-0020-1