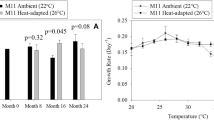
Abstract
Rising temperatures are expected to favour the growth of bloom-forming cyanobacteria in temperate lakes, but may also change the composition of cyanobacterial communities. To predict future community and bloom dynamics, it is therefore important to understand how bloom-forming species respond to temperature. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya & Subba Raju is an invasive, toxin-producing, nitrogen-fixer that may benefit from warming. To understand how changing temperatures will influence its ability to compete against native North American bloom-formers, we characterized the thermal reaction norms and temperature traits of three C. raciborskii strains, four strains of Microcystis aeruginosa (Kützing) Kützing and one strain of Anabaena flos-aquae (Lyng.) Brèb. C. raciborskii strains had higher optimum temperatures and survived higher temperatures than toxic M. aeruginosa strains, but had no apparent advantage over the non-toxic M. aeruginosa strain or A. flos-aquae. M. aeruginosa strains and A. flos-aquae tolerated lower temperatures than C. raciborskii, suggesting that fitness differences at low temperature may be important in limiting the latter’s spread. Furthermore, we found that nutrient availability strongly influenced thermal reaction norm shape: nitrogen deprivation lowered growth rates and decreased both low- and high-temperature tolerance, but did not affect the optimum temperature in C. raciborskii.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker, H. A., 1935. The culture and physiology of the marine dinoflagellates. Archiv für Mikrobiologie 6: 157–181.
Bonilla, S., L. Aubriot, M. C. S. Soares, M. González-Piana, A. Fabre, V. L. M. Huszar, M. Lürling, D. Antoniades, J. Padisák & C. Kruk, 2012. What drives the distribution of the bloom-forming cyanobacteria Planktothrix agardhii and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii? FEMS Microbiology Ecology 79: 594–607.
Boyd, P. W., T. A. Rynearson, E. A. Armstrong, F. Fu, K. Hayashi, Z. Hu, D. A. Hutchins, R. M. Kudela, E. Litchman, M. R. Mulholland, U. Passow, R. F. Strzepek, K. A. Whittaker, E. Yu & M. K. Thomas, 2013. Marine phytoplankton temperature versus growth responses from polar to tropical waters - Outcome of a scientific community-wide study. PLoS ONE 8: e63091.
Briand, J.-F., J.-F. Humbert, C. Leboulanger, C. Bernard & P. Dufour, 2004. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) invasion at mid-latitudes: selection, wide physiological tolerance, or global warming? Journal of Phycology 40: 231–238.
Chapman, A. D. & C. L. Schelske, 1997. Recent appearance of Cylindrospermopsis in five hypereutrophic Florida lakes. Journal of Phycology 33: 191–195.
Chonudomkul, D., W. Yongmanitchai, G. Theeragool, M. Kawachi, F. Kasai, K. Kaya & M. M. Watanabe, 2004. Morphology, genetic diversity, temperature tolerance and toxicity of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) strains from Thailand and Japan. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 48: 345–355.
Chorus, I. & J. Bartram, 1999. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring, and Management. E & FN Spon, London.
Chu, Z., X. Jin, N. Iwami & Y. Inamori, 2007. The effect of temperature on growth characteristics and competitions of Microcystis aeruginosa and Oscillatoria mougeotii in a shallow, eutrophic lake simulator system. Hydrobiologia 581: 217–223.
Conroy, J. D., E. L. Quinlan, D. D. Kane & D. A. Culver, 2007. Cylindrospermopsis in Lake Erie: testing its association with other cyanobacterial genera and major limnological parameters. Journal of Great Lakes Research 33: 519–535.
Dauta, A., J. Devaux, F. Piquemal & L. Boumnich, 1990. Growth rate of four freshwater algae in relation to light and temperature. Hydrobiologia 207: 221–226.
de Stasio, B. T., D. K. Hill, J. M. Kleinhans & N. P. Nibbelink, 1996. Potential effects of global climate change on small north-temperate lakes: physics, fish, and plankton. Limnology and Oceanography 41: 1136–1149.
Droop, M. R., 1973. Some thoughts on nutrient limitation in algae. Journal of Phycology 9: 264–272.
Edwards, K. F., M. K. Thomas, C. A. Klausmeier & E. Litchman, 2015. Light and growth in marine phytoplankton: allometric, taxonomic, and environmental variation. Limnology and Oceanography 60: 540–552.
Figueredo, C. C., A. Giani & D. F. Bird, 2007. Does allelopathy contribute to Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) bloom occurrence and geographic expansion? Journal of Phycology 43: 256–265.
Fujimoto, N., R. Sudo, N. Sugiura & I. Yuhei, 1997. Nutrient-limited growth of Microcystis aeruginosa and Phormidium tenue and competition under various N:P supply ratios and temperatures. Limnology and Oceanography 42: 250–256.
Guillard, R. R. L., 1975. Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In Smith, W. L. & M. H. Chantey (eds), Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals. Plenum Press, New York: 29–60.
Hong, Y., A. Steinman, B. Biddanda, R. Rediske & G. Fahnenstiel, 2006. Occurrence of the toxin-producing cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Mona and Muskegon Lakes, Michigan. Journal of Great Lakes Research 32: 645–652.
Huisman, J., J. Sharples, J. M. Stroom, P. M. Visser, W. E. A. Kardinaal, J. M. H. Verspagen & B. Sommeijer, 2004. Changes in turbulent mixing shift competition for light between phytoplankton species. Ecology 85: 2960–2970.
Imai, H., K.-H. Chang & S. Nakano, 2009. Growth responses of harmful algal species Microcystis (Cyanophyceae) under various environmental conditions. In Obayashi, Y., T. Isobe, A. Subramanian, S. Suzuki & S. Tanabe (eds), Interdisciplinary Studies on Environmental Chemistry – Environmental Research in Asia. Terrapub, Tokyo: 269–275.
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report, 2007. Climate Change 2007: the physical science basis. In Solomon, S., D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K. B. Averyt, M. Tignor & H. L. Miller (eds), Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Isvánovics, V., H. M. Shafik, M. Présing & S. Juhos, 2000. Growth and phosphate uptake kinetics of the cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanophyceae) in throughflow cultures. Freshwater Biology 43: 257–275.
Jöhnk, K. D., P. M. Visser, J. Huisman, J. M. Stroom, J. Sharples & B. Sommeijer, 2008. Summer heatwaves promote blooms of harmful cyanobacteria. Global Change Biology 14: 495–512.
Kahru, M., J. M. Leppanen & O. Rud, 1993. Cyanobacterial blooms cause heating of the sea surface. Marine Ecology Progress Series 101: 1–7.
Karentz, D. & T. J. Smayda, 1984. Temperature and seasonal occurrence patterns of 30 dominant phytoplankton species in Narragansett Bay over a 22-year period (1959–1980). Marine Ecology Progress Series 18: 277–293.
Kehoe, M., K. R. O. Brien, A. Grinham & M. A. Burford, 2015. Primary production of lake phytoplankton, dominated by the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, in response to irradiance and temperature. Inland Waters 5: 93–10.
Kingsolver, J. G., 2009. The well-temperatured biologist. The American Naturalist 174: 755–768.
Kling, H. J., 2009. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria): a brief historic overview and recent discovery in the Assiniboine River (Canada). Fottea 9: 45–47.
Kormas, K. A., S. Gkelis, E. Vardaka & M. Moustaka-Gouni, 2011. Morphological and molecular analysis of bloom-forming Cyanobacteria in two eutrophic, shallow Mediterranean lakes. Limnologica 41: 167–173.
Kosten, S., V. L. M. Huszar, E. Bécares, L. S. Costa, E. van Donk, L.-A. Hansson, E. Jeppesen, C. Kruk, G. Lacerot, N. Mazzeo, L. de Meester, B. Moss, M. Lürling, T. Nõges, S. Romo & M. Scheffer, 2012. Warmer climates boost cyanobacterial dominance in shallow lakes. Global Change Biology 18: 118–126.
Litchman, E., 2000. Growth rates of phytoplankton under fluctuating light. Freshwater Biology 44: 223–235.
Litchman, E., 2010. Invisible invaders: non-pathogenic invasive microbes in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecology Letters 13: 1560–1572.
Litchman, E., P. de Tezanos Pinto, C. A. Klausmeier, M. K. Thomas & K. Yoshiyama, 2010. Linking traits to species diversity and community structure in phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 653: 15–28.
Litchman, E., K. F. Edwards & C. A. Klausmeier, 2015. Microbial resource utilization traits and trade-offs: implications for community structure, functioning, and biogeochemical impacts at present and in the future. Frontiers in Microbiology 6: 254.
Lürling, M., F. Eshetu, E. J. Faassen, S. Kosten & V. L. M. Huszar, 2013. Comparison of cyanobacterial and green algal growth rates at different temperatures. Freshwater Biology 58: 552–559.
Magnuson, J. J., K. E. Webster, R. A. Assel, C. J. Bowser, P. J. Dillon, J. G. Eaton, H. E. Evans, E. J. Fee, R. I. Hall, L. R. Mortsch, D. W. Schindler & F. H. Quinn, 1997. Potential effects of climate changes on aquatic systems: Laurentian great lakes and Precambrian Shield region. Hydrological Processes 11: 825–871.
Marinho, M. M. & V. L. M. Huszar, 2002. Nutrient availability and physical conditions as controlling factors of phytoplankton composition and biomass in a tropical reservoir (Southeastern Brazil). Archiv für Hydrobiologie 153: 443–468.
Martin, T. L. & R. B. Huey, 2008. Why “suboptimal” is optimal: Jensen’s inequality and ectotherm thermal preferences. The American Naturalist 171: E102–E118.
Mehnert, G., F. Leunert, S. Cires, K. D. Jöhnk, J. Rucker, B. Nixdorf & C. Wiedner, 2010. Competitiveness of invasive and native cyanobacteria from temperate freshwaters under various light and temperature conditions. Journal of Plankton Research 32: 1009–1021.
Moisander, P. H., L. A. Cheshire, J. Braddy, E. S. Calandrino, M. Hoffman, M. F. Piehler & H. W. Paerl, 2012. Facultative diazotrophy increases Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii competitiveness under fluctuating nitrogen availability. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 79: 800–811.
Molica, R. J. R., E. J. A. Oliveira, P. V. V. C. Carvalho, A. N. S. F. Costa, M. C. C. Cunha, G. L. Melo & S. M. F. O. Azevedo, 2005. Occurrence of saxitoxins and an anatoxin-a(s)-like anticholinesterase in a Brazilian drinking water supply. Harmful Algae 4: 743–753.
Moreira, C., A. Fathalli, V. Vasconcelos & A. Antunes, 2015. Phylogeny and biogeography of the invasive cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Archiv für Mikrobiologie 197: 47–52.
Nalewajko, C. & T. P. Murphy, 2001. Effects of temperature, and availability of nitrogen and phosphorus on the abundance of Anabaena and Microcystis in Lake Biwa, Japan: an experimental approach. Limnology 2: 45–48.
Novak, J. T. & D. E. Brune, 1985. Inorganic carbon limited growth kinetics of some freshwater algae. Water Research 19: 215–225.
Padisák, J., 1997. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya et Subba Raju, an expanding, highly adaptive cyanobacterium: worldwide distribution and review of its ecology. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Supplementband Monographische Beiträge 107: 563–593.
Paerl, H. W. & J. Huisman, 2009. Climate change: a catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environmental Microbiology Reports 1: 27–37.
Piccini, C., L. Aubriot, A. Fabre, V. Amaral, M. Gonza, A. Giani, C. C. Figueredo, L. Vidal, C. Kruk & S. Bonilla, 2011. Genetic and eco-physiological differences of South American Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii isolates support the hypothesis of multiple ecotypes. Harmful Algae 10: 644–653.
Pierangelini, M., S. Stojkovic, P. T. Orr & J. Beardall, 2014. Photosynthetic characteristics of two Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains differing in their toxicity. Journal of Phycology 50: 292–302.
Posselt, A. J., M. A. Burford & G. Shaw, 2009. Pulses of phosphate promote dominance of the toxic cyanophyte Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in a subtropical water reservoir. Journal of Phycology 45: 540–546.
R Core Team, 2012. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna.
Reynolds, C. S., 2006. The Ecology of Phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Reynolds, C. S., R. L. Oliver & A. E. Walsby, 1987. Cyanobacterial dominance: the role of buoyancy regulation in dynamic lake environments. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 21: 379–390.
Robarts, R. D. & T. Zohary, 1987. Temperature effects on photosynthetic capacity, respiration, and growth rates of bloom-forming cyanobacteria. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 21: 391–399.
Rzymski, P., B. Poniedziałek, M. Kokociński, T. Jurczak, D. Lipski & W. Wiktorowicz, 2014. Interspecific allelopathy in cyanobacteria: Cylindrospermopsin and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii effect on the growth and metabolism of Microcystis aeruginosa. Harmful Algae 35: 1–8.
Saker, M. L. & D. J. Griffiths, 2000. The effect of temperature on growth and cylindrospermospsin content of seven isolates of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanophyceae) from water bodies in Northern Australia. Phycologia 39: 349–354.
Saker, M. L. & D. J. Griffiths, 2001. Occurrence of blooms of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszyńska) Seenayya and Subba Raju in a north Queensland domestic water supply. Marine & Freshwater Research 52: 907–915.
Shafik, H. M., S. Herodek, M. Présing & L. Vörös, 2001. Factors effecting growth and cell composition of cyanoprokaryote Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Wołoszyńska) Seenayya et Subba Raju. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Supplementband Algological Studies 140: 75–93.
Shatwell, T., A. Nicklisch & J. Köhler, 2012. Temperature and photoperiod effects on phytoplankton growing under simulated mixed layer light fluctuations. Limnology and Oceanography 57: 541–553.
Sinha, R., L. A. Pearson, T. W. Davis, M. A. Burford, P. T. Orr & B. A. Neilan, 2012. Increased incidence of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in temperate zones - Is climate change responsible? Water Research 46: 1408–1419.
Smith, V. H., 1983. Low nitrogen to phosphorus ratios favour dominance by blue-green algae in lake phytoplankton. Science 221: 669–671.
Soares, M. C. S., M.I. de A. Rocha, M. M. Marinho, S. M. F. O. Azevedo, C. W. C. Branco & V. L. M. Huszar, 2009. Changes in species composition during annual cyanobacterial dominance in a tropical reservoir: physical factors, nutrients and grazing effects. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 57: 137–149.
Swan, B. K., B. Tupper, A. Sczyrba, F. M. Lauro, M. Martinez-Garcia, J. M. Gonzalez, H. Luof, J. J. Wright, Z. C. Landry, N. W. Hanson, B. P. Thompson, N. J. Poulton, P. Schwientek, S. G. Acinas, S. J. Giovannoni, M. A. Moran, S. J. Hallam, R. Cavicchioli, T. Woyke & R. Stepanauskas, 2013. Prevalent genome streamlining and latitudinal divergence of planktonic bacteria in the surface ocean. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 110: 11463–11468.
Thomas, M. K., C. T. Kremer, C. A. Klausmeier & E. Litchman, 2012. A global pattern of thermal adaptation in marine phytoplankton. Science 338: 1085–1088.
Tilman, D., 1982. Resource Competition and Community Structure. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ.
Tilman, D. & R. L. Kiesling, 1984. Freshwater algal ecology: taxonomic trade-offs in the temperature dependence of nutrient competitive abilities. In Klug, M. J. & C. A. Reddy (eds), Current Perspectives in Microbial Ecology: Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Microbial Ecology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.: 314–319.
Uehlinger, V. U., 1981. Experimental studies of the autecology of Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Supplementband Algological Studies 60: 260–288.
Vitousek, P. M., S. Hättenschwiler, L. Olander & S. Allison, 2002. Nitrogen and nature. Ambio 31: 97–101.
Walther, G.-R., A. Roques, P. E. Hulme, M. T. Sykes, P. Pyšek, I. Kühn & M. Zobel, 2009. Alien species in a warmer world: risks and opportunities. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 24: 686–693.
Wiedner, C., J. Rücker, R. Brüggemann & B. Nixdorf, 2007. Climate change affects timing and size of populations of an invasive cyanobacterium in temperate regions. Oecologia 152: 473–484.
Wilson, A. E., W. A. Wilson & M. E. Hay, 2006. Intraspecific variation in growth and morphology of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 72: 7386–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank Carole Lembi and Julianne Dyble-Bressie for providing us with C. raciborskii cultures, Alan Wilson for M. aeruginosa cultures, and G. G. Mittelbach, J. A. Lau, and C. A. Klausmeier for useful comments on the manuscript. This research was in part supported by the NSF grants (DEB 06-10531 and DEB 08-45932) to E.L., a grant by the J.S. McDonnell Foundation to C. Klausmeier and E. L. and an MSU College of Natural Science fellowship to M.K.T. This is Kellogg Biological Station Contribution No. 1711.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Judit Padisák
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, M.K., Litchman, E. Effects of temperature and nitrogen availability on the growth of invasive and native cyanobacteria. Hydrobiologia 763, 357–369 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2390-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2390-2