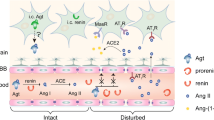
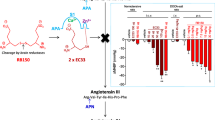
Abstract
From the outset, the concept of a brain renin-angiotensin system (RAS) has been controversial and this controversy continues to this day. In addition to the unresolved questions as to the means by which, and location(s) where brain Ang II is synthesized, and the uncertainties regarding the functionality of the different subtypes of Ang II receptors in the brain, a new controversy has arisen with respect to the identity of the angiotensin peptide(s) that activate brain AT1 receptors. While it has been known for some time that Ang III can activate Ang II receptors with equivalent or near-equivalent efficacy to Ang II, it has been proposed that in the brain, only Ang III is active. This proposal, which we have named “The Angiotensin III Hypothesis” states that Ang II must be converted to Ang III in order to activate brain AT1 receptors. This review examines several aspects of the controversies regarding the brain RAS with a special focus on brain aminopeptidases, studies that either support or refute The Angiotensin III Hypothesis, and the implications of The Angiotensin III Hypothesis for the activity of the brain RAS. It also addresses the need for further research that can test The Angiotensin III Hypothesis and definitively identify the angiotensin peptide(s) that activate brain AT1 receptor-mediated effects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harding JW, Yoshida MS, Dilts RP, Woods TM, Wright JW (1986) Cerebroventricular and intravascular metabolism of [125I]angiotensins in rat. J Neurochem 46:1292–1297
Ahmad S, Ward PE (1990) Role of aminopeptidase activity in the regulation of the pressor activity of circulating angiotensins. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 252:643–650
Karamyan V, Speth R (2007) Enzymatic pathways of the brain renin-angiotensin system: unsolved problems and continuing challenges. Regul Pept 143:15–27
von Bohlen O, Halbach U (2005) The renin-angiotensin system in the mammalian central nervous system. Curr Protein Pept Sci 6:355–371
Wright JW, Harding JW, (1995) Brain angiotensin receptor subtypes AT(1), AT(2), and AT(4) and their functions. Regul Pept 59:269–295
Albiston AL, McDowall SG, Matsacos D, Sim P, Clune E, Mustafa T, Lee J, Mendelsohn FA, Simpson RJ, Connolly LM, Chai SY (2001) Evidence that the angiotensin IV (AT4) receptor is the enzyme insulin regulated aminopeptidase. J Biol Chem 276:48623–48626
Miller-Wing AV, Hanesworth JM, Sardinia MF, Hall KL, Wright JW, Speth RC, Grove KL, Harding JW (1993) Central angiotensin IV binding sites: distribution and specificity in guinea pig brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266:1718–1726
Tsujimoto M, Hattori A (2005) The oxytocinase subfamily of M1 aminopeptidases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1751:9–18
Gibson RE, Thorpe HH, Cartwright ME, Frank JD, Schorn TW, Bunting PB, Siegl PK (1991) Angiotensin II receptor subtypes in renal cortex of rats and rhesus monkeys. Am J Physiol 261:F512–F518
Gibson AM, Biggins JA, Lauffart B, Mantle D, McDermott JR (1991) Human brain leucyl aminopeptidase: isolation, characterization and specificity against some neuropeptides. Neuropeptides 19:163–168
Kugler P (1982) Aminopeptidase A is angiotensinase A. II. Biochemical studies on the rat kidney homogenate. Histochemistry 74:247–261
Hayashi M, Oshima K (1980) Isolation and characterization of aminotripeptidase from monkey brain. J Biochem (Tokyo) 87:1403–1411
Gallegos ME, Zannatha MM, Osornio EG, Sanchez AS, Posadas del rio FA (1999) The activities of six exo-and endopeptidases in the substantia nigra, neostriatum, and cortex of the rat brain. Neurochem Res 24:1557–1561
Turzynski A, Mentlein R (1990) Prolyl aminopeptidase from rat brain and kidney. Action on peptides and identification as leucyl aminopeptidase. Eur J Biochem 190:509–515
Gainer H, Russell JT, Loh YP (1984) An aminopeptidase activity in bovine pituitary secretory vesicles that cleaves the N-terminal arginine from beta-lipotropin60–65. FEBS Lett 175:135–139
Nagatsu I, Gillespie L, Folk JE, Glenner GG (1965) Serum aminopeptidases, “angiotensinase,” and hypertension. I. Degradation of angiotensin II by human serum. Biochem Pharmacol 14:721–728
Gilmartin L, O’Cuinn G (1999) Dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV and aminopeptidase P, two proline specific enzymes from the cytoplasm of guinea-pig brain: their role in metabolism of peptides containing consecutive prolines. Neurosci Res 34:1–11
Harbeck HT, Mentlein R (1991) Aminopeptidase P from rat brain. Purification and action on bioactive peptides. Eur J Biochem 198:451–458
Gil J, Larrinaga G, Meana JJ, Rodriguez-Puertas R, Irazusta J, Casis L (2001) Regional and subcellular distribution of soluble aminopeptidase in the human and the rat brain: a comparative study. Neuropeptides 35:276–284
Mantle D, Lauffart B, Perry EK, Perry RH (1989) Comparison of major cortical aminopeptidase activity in normal brain and brain from patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 89:227–234
Sharma KK Ortwerth BJ (1987) Purification and characterization of an aminopeptidase from bovine cornea. Exp Eye Res 45:117–126
Gee NS, Kenny AJ (1985) Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. The 130 kDa protein in pig kidney, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK5C1, is an ectoenzyme with aminopeptidase activity. Biochem J 230:753–764
Yoshida A, Lin M (1972) NH 2 -terminal formylmethionine- and NH 2 -terminal methionine-cleaving enzymes in rabbits. J Biol Chem 247:952–957
Sim MK, Choo MHH, Qiu XS (1994) Degradation of angiotensin I to [des-Asp(1)]angiotensin I by a novel aminopeptidase in the rat hypothalamus. Biochem Pharmacol 48:1043–1046
Sim MK, Lim BC (1997) Determination of aminopeptidase X activity in tissues of normo- and hypertensive rats by capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 697:259–262
Wilk S, Wilk E, Magnusson RP (1998) Purification, characterization, and cloning of a cytosolic aspartyl aminopeptidase. J Biol Chem 273:15961–15970
Lee CM, Snyder SH (1982) Dipeptidyl-aminopeptidase III of rat brain. Selective affinity for enkephalin and angiotensin. J Biol Chem 257:12043–12050
Erdos EG, Skidgel RA (1990) Renal metabolism of angiotensin I and II. Kidney Int Suppl 30:S24–S27
Alba F, Arenas JC, Lopez MA (1995) Properties of rat brain dipeptidyl aminopeptidases in the presence of detergents. Peptides 16:325–329
Mentlein R, Struckhoff G (1989) Purification of two dipeptidylaminopeptidases from rat brain and their action on proline-containing neuropeptides. J Neurochem 52:1284–1293
Smyth M, Ocuinn G (1994) Dipeptidyl aminopeptidase III of guinea-pig brain: specificity for short oligopeptide sequences. J Neurochem 63:1439–1445
Koike M, Shibata M, Ohsawa Y, Kametaka S, Waguri S, Kominami E, Uchiyama Y (2002) The expression of tripeptidyl peptidase I in various tissues of rats and mice. Arch Histol Cytol 65:219–232
Du PG, Kato S, Li YH, Maeda T, Yamane T, Yamamoto S, Fujiwara M, Yamamoto Y, Nishi K, Ohkubo I (2001) Rat tripeptidyl peptidase I: molecular cloning, functional expression, tissue localization and enzymatic characterization. Biol Chem 382:1715–1725
Warburton MJ, Bernardini F (2001) The specificity of lysosomal tripeptidyl peptidase-I determined by its action on angiotensin-II analogues. FEBS Lett 500:145–148
Warburton MJ, Bernardini F (2002) Tripeptidyl peptidase-I is essential for the degradation of sulphated cholecystokinin-8 (CCK-8S) by mouse brain lysosomes. Neurosci Lett 331:99–102
Tomkinson B, Nyberg F (1995) Distribution of tripeptidyl-peptidase II in the central nervous system of rat. Neurochem Res 20:1443–1447
Wilson C, Gibson AM, McDermott JR (1993) Purification and characterization of tripeptidylpeptidase-II from post-mortem human brain. Neurochem Res 18:743–749
Orning L, Gierse JK, Fitzpatrick FA (1994) The bifunctional enzyme leukotriene-A4 hydrolase is an arginine aminopeptidase of high efficiency and specificity. J Biol Chem 269:11269–11273
Diaz-Perales A, Quesada V, Sanchez LM, Ugalde AP, Suarez MF, Fueyo A, Lopez-Otin C (2005) Identification of human aminopeptidase O, a novel metalloprotease with structural similarity to aminopeptidase B and leukotriene A4 hydrolase. J Biol Chem 280:14310–14317
Axton R, Wallis JA, Taylor H, Hanks M, Forrester LM (2007) Aminopeptidase O contains a functional nucleolar localization signal and is implicated in vascular biology. J Cell Biochem Sep 5 [Epub ahead of print]
Maruyama M, Hattori A, Goto Y, Ueda M, Maeda M, Fujiwara H, Tsujimoto M (2007) Laeverin/aminopeptidase Q, a novel bestatin-sensitive leucine aminopeptidase belonging to the M1 family of aminopeptidases. J Biol Chem 282:20088–20096
Schomburg L, Kollmus H, Friedrichsen S, Bauer K (2000) Molecular characterization of a puromycin-insensitive leucyl-specific aminopeptidase, PILS-AP. Eur J Biochem 267:3198–3207
Taylor WL Dixon JE (1978) Characterization of a pyroglutamate aminopeptidase from rat serum that degrades thyrotropin-releasing hormone. J Biol Chem 253:6934–6940
Stornetta RL, Hawelu-Johnson CL, Guyenet PG, Lynch KR (1988) Astrocytes synthesize angiotensinogen in brain. Science 242:1444–1446
Thomas WG, Greenland KJ, Shinkel TA, Sernia C (1992) Angiotensinogen is secreted by pure rat neuronal cell cultures. Brain Res 588:191–200
Imboden H, Harding JW, Hilgenfeldt U, Celio MR, Felix D (1987) Localization of angiotensinogen in multiple cell types of rat brain. Brain Res 410:74–77
Yang G, Gray TS, Sigmund CD, Cassell MD, (1999) The angiotensinogen gene is expressed in both astrocytes and neurons in murine central nervous system. Brain Res 817:123–131
Deschepper CF, Bouhnik J, Ganong WF (1986) Colocalization of angiotensinogen and glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes in rat brain. Brain Res 374:195–198
Murakami E, Eggena P, Barrett JD, Sambhi MP (1984) Heterogeneity of renin substrate released from hepatocytes and in brain extracts. Life Sci 34:385–392
Reid IA (1976) The use of saralasin to evaluate the function of the brain renin-angiotensin system. Prog Biochem Pharmacol 12:117–134
Kawasaki H, Takasaki K, Furukawa T (1987) Exaggerated pressor response to centrally administered renin in freely moving, spontaneously hypertensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol 138:351–357
Corvol P, Michaud A, Soubrier F, Williams TA (1995) Recent advances in knowledge of the structure and function of the angiotensin I converting enzyme. J Hypertens 13:S3–S10
Strittmatter SM, Lo MMS, Javitch JA, Snyder SH (1984) Autoradiographic visualization of angiotensin-converting enzyme in rat brain with [3H]captopril: localization to a striatonigral pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 81:1599–1603
Koshiya K, Kato T, Tanaka R, Kato T (1984) Brain peptidases: their possible neuronal and glial localization. Brain Res 324:261–270
Larrinaga G, Callado LF, Agirregoitia N, Varona A, Gil J (2005) Subcellular distribution of membrane-bound aminopeptidases in the human and rat brain. Neurosci Lett 383:136–140
Murphy TJ, Alexander RW, Griendling KK, Runge MS, Bernstein KE (1991) Isolation of a cDNA encoding the vascular type-1 angiotensin II receptor. Nature 351:233–236
Mukoyama M, Nakajima M, Horiuchi M, Sasamura H, Pratt RE, Dzau VJ (1993) Expression cloning of type 2 angiotensin II receptor reveals a unique class of seven-transmembrane receptors. J Biol Chem 268:24539–24542
Kambayashi Y, Bardhan S, Takahashi K, Tsuzuki S, Inui H, Hamakubo T, Inagami T (1993) Molecular cloning of a novel angiotensin II receptor isoform involved in phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibition. J Biol Chem 268:24543–24546
Kakar SS, Riel KK, Neill JD (1992) Differential expression of angiotensin II receptor subtype mRNAs (AT-1A and AT-1B) in the brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 185:688–692
Eggena P, Zhu JH, Clegg K, Barrett JD (1993) Nuclear angiotensin receptors induce transcription of renin and angiotensinogen mRNA. Hypertension 22:496–501
Pendergrass KD, Averill DB, Ferrario CM, Diz DI, Chappell MC (2006) Differential expression of nuclear AT1 receptors and angiotensin II within the kidney of the male congenic mRen2.Lewis rat. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F1497–F1506
Chen R, Mukhin YV, Garnovskaya MN, Thielen TE, Iijima Y, Huang C, Raymond JR, Ullian ME, Paul RV (2000) A functional angiotensin II receptor-GFP fusion protein: evidence for agonist-dependent nuclear translocation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279:F440–F448
Lee DK, Lanca AJ, Cheng R, Nguyen T, Ji XD, Gobeil F Jr, Chemtob S, George SR, O’Dowd BF (2004) Agonist-independent nuclear localization of the Apelin, angiotensin AT1, and bradykinin B2 receptors. J Biol Chem 279:7901–7908
Lu D, Yang H, Shaw G, Raizada MK (1998) Angiotensin II-induced nuclear targeting of the angiotensin type 1 (AT(1)) receptor in brain neurons. Endocrinology 139:365–375
Huang J, Hara Y, Anrather J, Speth RC, Iadecola C, Pickel VM (2003) Angiotensin II subtype 1A (AT1A) receptors in the rat sensory vagal complex: subcellular localization and association with endogenous angiotensin. Neuroscience 122:21–36
Lippoldt A, Bunnemann B, Iwai N, Metzger R, Inagami T, Fuxe K, Ganten D (1993) Cellular localization of angiotensin type 1 receptor and angiotensinogen mRNAs in the subfornical organ of the rat brain. Neurosci Lett 150:153–158
Raizada MK, Phillips MI, Crews FT, Sumners C (1987) Distinct angiotensin II receptor in primary cultures of glial cells from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:4655–4659
Sumners C, Tang W, Zelezna B, Raizada MK (1991) Angiotensin II receptor subtypes are coupled with distinct signal-transduction mechanisms in neurons and astrocytes from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:7567–7571
Gebke E, Muller AR, Jurzak M, Gerstberger R (1998) Angiotensin II-induced calcium signalling in neurons and astrocytes of rat circumventricular organs. Neuroscience 85:509–520
Muscella A, Aloisi F, Marsigliante S, Levi G (2000) Angiotensin II modulates the activity of Na+,K+-ATPase in cultured rat astrocytes via the AT1 receptor and protein kinase C-delta activation. J Neurochem 74:1325–1331
Yoshida H, Imaizumi T, Tanji K, Sakaki H, Metoki N, Sato Y, Wakabayashi K, Kimura H, Satoh K (2006) Interleukin-1beta enhances the angiotensin-induced expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 through angiotensin receptor upregulation in human astrocytes. Brain Res 1073–1074:38–47
Matute C, Pulakat L, Rio C, Valcarcel C, Miledi R (1994) Properties of angiotensin II receptors in glial cells from the adult corpus callosum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:3774–3778
Fogarty DJ, Matute C (2001) Angiotensin receptor-like immunoreactivity in adult brain white matter astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Glia 35:131–146
Paton JF, Deuchars J, Ahmad Z, Wong LF, Murphy D, Kasparov S (2001) Adenoviral vector demonstrates that angiotensin II-induced depression of the cardiac baroreflex is mediated by endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the nucleus tractus solitarii of the rat. J Physiol 531:445–458
Thomas MA, Fleissner G, Stohr M, Hauptfleisch S, Lemmer B (2004) Localization of components of the renin-angiotensin system in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of normotensive Sprague-Dawley rats: part B. angiotensin II (AT1)-receptors, a light and electron microscopic study. Brain Res 1008:224–235
Thomas MA, Fleissner G, Hauptfleisch S, Lemmer B (2003) Subcellular identification of angiotensin I/II- and angiotensin II (AT1)-receptor-immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of rats. Brain Res 962:92–104
Allen AM, Dosanjh JK, Erac M, Dassanayake S, Hannan RD, Thomas WG (2006) Expression of constitutively active angiotensin receptors in the rostral ventrolateral medulla increases blood pressure. Hypertension 47:1054–1061
Blair-West JR, Coghlan JP, Denton DA, Funder JW, Scoggins BA, Wright RD (1971) The effect of the heptapeptide (2–8) and hexapeptide (3–8) fragments of angiotensin II on aldosterone secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 32:575–578
Devynck MA, Pernollet MG, Matthews PG, Khosla MC, Bumpus FM, Meyer P (1977) Specific receptors for des-Asp1-angiotensin II (“angiotensin III”) in rat adrenals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74:4029–4032
Harding JW, Felix D (1987) The effects of the aminopeptidase inhibitors amastatin and bestatin on angiotensin-evoked neuronal activity in rat brain. Brain Res 424:299–304
Wright JW, Mizutani S, Murray CE, Amir HZ, Harding JW (1990) Aminopeptidase-induced elevations and reductions in blood pressure in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Hypertens 8:969–974
Wright JW, Roberts KA, Cook VI, Murray CE, Sardinia MF, Harding JW (1990) Intracerebroventricularly infused [D-Arg1]angiotensin III, is superior to [D-Asp1]angiotensin II, as a pressor agent in rats. Brain Res 514:5–10
Zini S, Fournie-Zaluski MC, Chauvel E, Roques BP, Corvol P, Llorens-Cortes C (1996) Identification of metabolic pathways of brain angiotensin II and III using specific aminopeptidase inhibitors: predominant role of angiotensin III in the control of vasopressin release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:11968–11973
Song LJ, Wilk S, Healy DP (1997) Aminopeptidase A antiserum inhibits intracerebroventricular angiotensin II-induced dipsogenic and pressor responses. Brain Res 744:1–6
Reaux A, Fournie-Zaluski MC, David C, Zini S, Roques BP, Corvol P, Llorens-Cortes C, (1999) Aminopeptidase A inhibitors as potential central antihypertensive agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:13415–13420
Reaux A, Fournie-Zaluski MC, Llorens-Cortes C (2001) Angiotensin III: a central regulator of vasopressin release and blood pressure. Trends Endocrinol Metab 12:157–162
Wright JW, Tamura-Myers E, Wilson WL, Roques BP, Llorens-Cortes C, Speth RC Harding JW (2003) Conversion of brain angiotensin II to angiotensin III is critical for pressor response in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 284:R725–R733
Wilson WL, Roques BP, Llorens-Cortes C, Speth RC, Harding JW, Wright JW (2005) Roles of brain angiotensins II and III in thirst and sodium appetite. Brain Res 1060:108–117
Sullivan MJ, Harding JW, Wright JW (1988) Differential effects of aminopeptidase inhibitors on angiotensin-induced pressor responses. Brain Res 456:249–253
Burson JM, Aguilera G, Gross KW, Sigmund CD (1994) Differential expression of angiotensin receptor 1A and 1B in mouse. Am J Physiol 267:E260–E267
Kakar SS, Sellers JC, Devor DC, Musgrove LC, Neill JD (1992) Angiotensin II type-1 receptor subtype cDNAs: differential tissue expression and hormonal regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 183:1090–1096
Sandberg K, Ji H, Clark AJ, Shapira H, Catt KJ (1992) Cloning and expression of a novel angiotensin II receptor subtype. J Biol Chem 267:9455–9458
Yamano Y, Ohyama K, Chaki S, Guo D-F, Inagami T (1992) Identification of amino acid residues of rat angiotensin II receptor for ligand binding by site directed mutagenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 187:1426–1431
George SR, Fan T, Xie Z, Tse R, Tam V, Varghese G, O’Dowd BF (2000) Oligomerization of mu- and delta-opioid receptors. Generation of novel functional properties. J Biol Chem 275:26128–26135
Hays JL Watowich SJ (2004) Oligomerization-dependent changes in the thermodynamic properties of the TPR-MET receptor tyrosine kinase. Biochem 43:10570–10578
Abhold RH, Sullivan MJ, Wright JW, Harding JW (1987) Binding, degradation and pressor activity of angiotensins II and III after aminopeptidase inhibition with amastatin and bestatin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 242:957–962
Karamyan V, Gadepalli R, Rimoldi J, Speth R (2007) Preservation of 125-I-Angiotensin II in brain AT-1 receptor binding assays. 2007 Experimental Biology Meeting abstracts, Abstract # 571.3;http://www.eb2007-online.com/bin/faseb.html
Kokje R, Wilson W, Brown T, Karamyan V, Wright J, Speth R (2007) Pressor actions of aminopeptidase-resistant analogs of angiotensin II in the rat brain: challenging the angiotensin III hypothesis. Hypertension 49:1328–1335
Regoli D, Rioux F, Park WK, Choi C (1974) Role of the N-terminal amino acid for the biological activities of angiotensin and inhibitory analogues. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 52:39–49
Faber F, Gembardt F, Sun X, Mizutani S, Siems WE, Walther T (2006) Lack of angiotensin II conversion to angiotensin III increases water but not alcohol consumption in aminopeptidase A-deficient mice. Regul Pept 136:130–137
Rangel R, Sun Y, Guzman-Rojas L, Ozawa MG, Sun J, Giordano RJ, Van Pelt CS, Tinkey PT, Behringer RR, Sidman RL, Arap W, Pasqualini R (2007) Impaired angiogenesis in aminopeptidase N-null mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:4588–4593
Goto Y, Hattori A, Ishii Y, Mizutani S, Tsujimoto M (2006) Enzymatic properties of human aminopeptidase A. Regulation of its enzymatic activity by calcium and angiotensin IV. J Biol Chem 281:23503–23513
Mobley SC, Mandel DA, Schreihofer AM (2006) Systemic cholecystokinin differentially affects baro-activated GABAergic neurons in rat caudal ventrolateral medulla. J Neurophysiol 96:2760–2768
Matsas R, Stephenson SL, Hryszko J, Kenny AJ, Turner AJ (1985) The metabolism of neuropeptides. Phase separation of synaptic membrane preparations with Triton X-114 reveals the presence of aminopeptidase N. Biochem J 231:445–449
Danziger RS (2007) Aminopeptidase N in arterial hypertension. Heart Fail Rev Nov 16 [Epub ahead of print]
Keay KA, Crowfoot LJ, Floyd NS, Henderson LA, Christie MJ, Bandler R (1997) Cardiovascular effects of microinjections of opioid agonists into the ‘Depressor Region’ of the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray region. Brain Res 762:61–71
Li P, Tjen AL, Longhurst JC (2001) Rostral ventrolateral medullary opioid receptor subtypes in the inhibitory effect of electroacupuncture on reflex autonomic response in cats. Auton Neurosci 89:38–47
Nagashima A, Takano Y, Tateishi K, Matsuoka Y, Hamaoka T, Kamiya H (1989) Cardiovascular roles of tachykinin peptides in the nucleus tractus solitarii of rats. Brain Res 487:392–396
von Bohlen Und HO (2005) The renin-angiotensin system in the mammalian central nervous system. Curr Protein Pept Sci 6:355–371
Chauvel EN, Llorens-Cortes C, Coric P, Wilk S, Roques BP, Fournie-Zaluski MC (1994) Differential inhibition of aminopeptidase A and aminopeptidase N by new beta-amino thiols. J Med Chem 37:2950–2957
Rawlings ND, Morton FR, Barrett AJ (2006) MEROPS: the peptidase database. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D270–D272
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Erick Bourassa for the preparation of figure 2. In preparing this manuscript the authors frequently visited the web site of the Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (NC-IUBMB) http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iubmb/enzyme/ and the web site of MEROPS peptidase database http://www.merops.sanger.ac.uk/ for background information [111]. Vardan T. Karamyan is supported by the Peptide Radioiodination Service Center of the School of Pharmacy of the University of Mississippi and by NIH Division of Research Resources grant (RR-0212929).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Speth, R.C., Karamyan, V.T. The significance of brain aminopeptidases in the regulation of the actions of angiotensin peptides in the brain. Heart Fail Rev 13, 299–309 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-007-9078-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-007-9078-2